4 raid 1, 5 raid 5, 4 raid 1 2.5.5 raid 5 – Avago Technologies MegaRAID Fast Path Software User Manual
Page 34
Page 34
LSI Corporation Confidential
|
July 2011
MegaRAID SAS Software User Guide
Chapter 2: Introduction to RAID
|
RAID Levels
Figure 7:
RAID 0 Drive Group Example with Two Drives
2.5.4
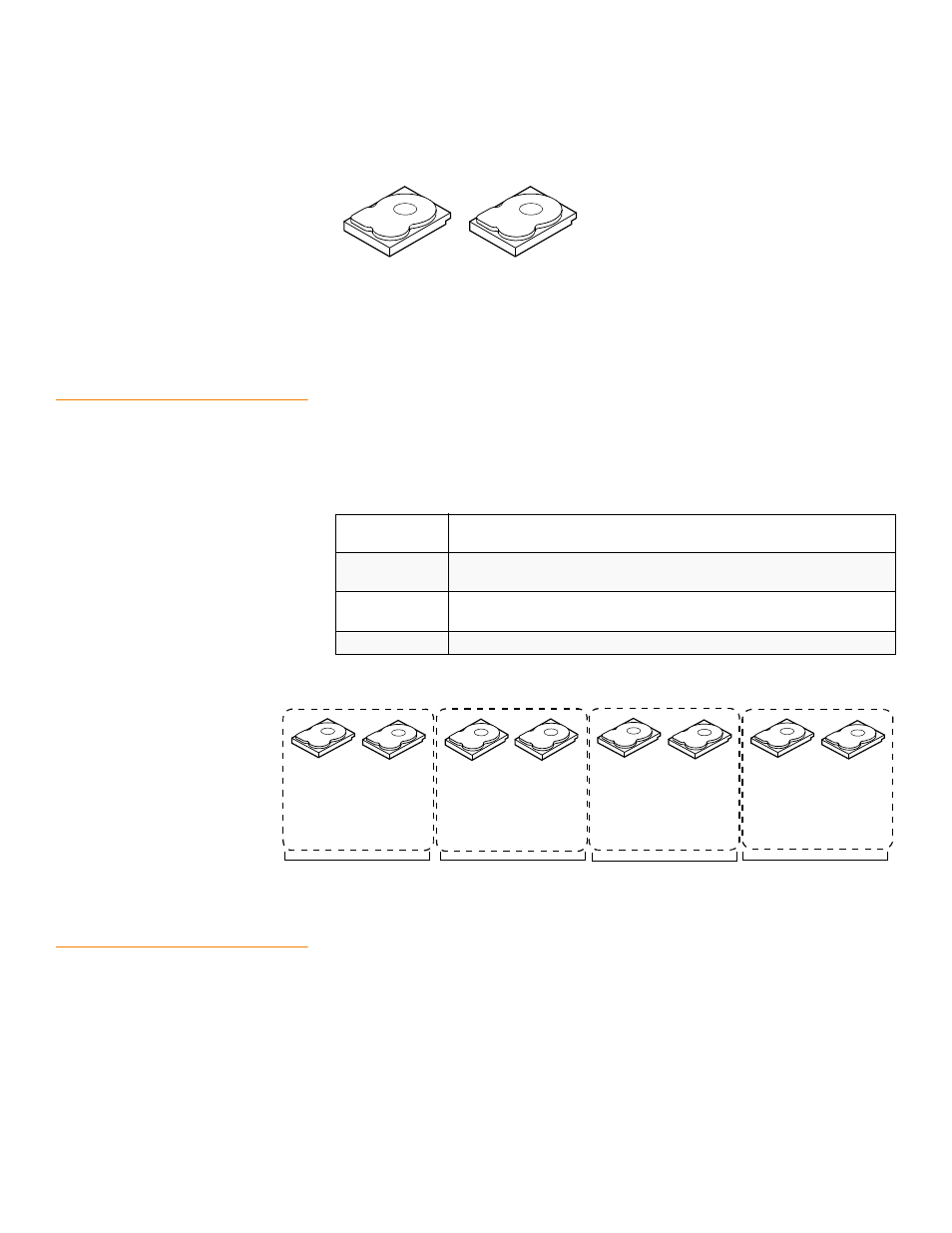
RAID
1
In RAID 1, the RAID controller duplicates all data from one drive to a second drive in the
drive group. RAID 1 supports an even number of drives from 2 through 32 in a single
span. RAID 1 provides complete data redundancy, but at the cost of doubling the
required data storage capacity.
provides an overview of RAID 1.
provides a graphic example of a RAID 1 drive group.
Figure 8:
RAID 1 Drive Group
2.5.5
RAID
5
RAID 5 includes disk striping at the block level and parity. Parity is the data’s property of
being odd or even, and parity checking is used to detect errors in the data. In RAID 5,
the parity information is written to all drives. RAID 5 is best suited for networks that
perform a lot of small input/output (I/O) transactions simultaneously.
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for random I/O operations. Because each drive
contains both data and parity, numerous writes can take place concurrently.
Segment 1
Segment 3
Segment 5
Segment 2
Segment 4
Segment 6
Segment 7
Segment 8
Table 8:
RAID 1 Overview
Uses
Use RAID 1 for small databases or any other environment that requires fault
tolerance but small capacity.
Strong points
Provides complete data redundancy. RAID 1 is ideal for any application that
requires fault tolerance and minimal capacity.
Weak points
Requires twice as many drives. Performance is impaired during drive
rebuilds.
Drives
2 through 32 (must be an even number of drives)
Segment 1
Segment 1
Duplicate
Segment 2
Segment 3
Duplicate
Segment 4
Duplicate
Segment 3
Segment 4
Segment 5
Segment 6
Segment 7
Segment 8
Segment 5
Duplicate
Segment 6
Duplicate
Segment 7
Duplicate
Segment 8
Duplicate
Segment 2
Duplicate
...
...
...
...
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
RAID1
- MegaRAID SAS 9240-4i MegaRAID SAS 9240-8i MegaRAID SAS 9260-16i MegaRAID SAS 9260-4i MegaRAID SAS 9260-8i MegaRAID SAS 9261-8i MegaRAID SAS 9280-16i4e MegaRAID SAS 9280-4i4e MegaRAID SAS 9280-8e MegaRAID SafeStore Software MegaRAID SAS 9361-4i MegaRAID SAS 9361-8i MegaRAID SAS 9266-4i MegaRAID SAS 9266-8i MegaRAID SAS 9270-8i MegaRAID SAS 9271-4i MegaRAID SAS 9271-8i MegaRAID SAS 9271-8iCC MegaRAID SAS 9286-8e MegaRAID SAS 9286CV-8e MegaRAID SAS 9286CV-8eCC MegaRAID CacheCade Pro 2.0 Software MegaRAID SAS 9341-4i MegaRAID SAS 9341-8i MegaRAID SAS 9380-8e MegaRAID SAS 9380-4i4e
