Summary, Configuring multi-vrf – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 400
372
Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide
53-1003033-02
Configuring Multi-VRF
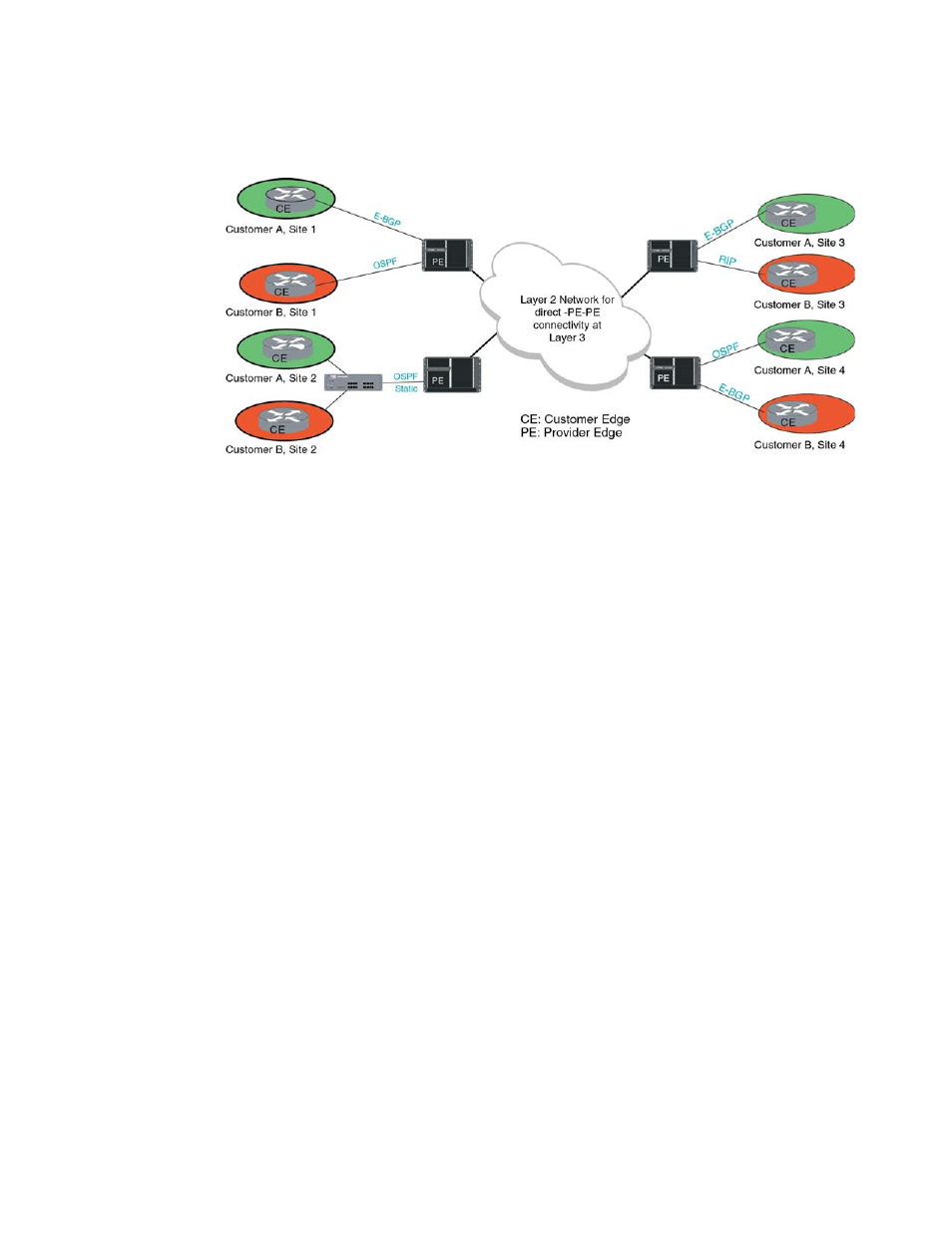
FIGURE 25
Multi-VRF in a service provider application
Summary
Multi-VRF provides a reliable mechanism for trusted virtual private networks to be built over a
shared infrastructure. The ability to maintain multiple virtual routing or forwarding tables allows
overlapping private IP addresses to be maintained across VPNs and accomplish goals very similar
to that those of more complex VPN technologies such as BGP or MPLS VPNs.
Configuring Multi-VRF
Configuration of the Multi-VRF feature uses the following commands that are defined in Configuring
BGP VPNs on a PE in the Multi-Service IronWare MPLS Configuration Guide.
•
Defining a VRF routing instance – This procedure describes how to define a VRF using the vrf
command.
•
Assigning a Route Distinguisher to a VRF – This procedure describes how to define a Route
Distinguisher (RD). The RD sets a unique identity to an instance of a VRF. As such, it allows the
same IP address to be used in different VPNs without creating any conflict.
•
Assigning a VRF routing instance to an interface – This procedure describes how to assign a
VRF to one or more virtual or physical interfaces.
•
Assigning a VRF routing instance to a LAG interface – This procedure describes how to assign a
VRF to a LAG interface.
The main difference between configurations described in Configuring BGP VPNs on a PE and
Multi-VRF is that there is no MPLS configuration required for Multi-VRF. This section provides a
common Multi-VRF configuration with two possible methods to achieve that configuration.
shows a typical network utilizing the multi-VRF feature to implement layer
3 VPNs across 2 directly connected (at layer3) PE routers.
