Overview of bgp4 – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 32
4
Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide
53-1003033-02
Overview of BGP4
Overview of BGP4
BGP4 is the standard Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) used on the Internet to route traffic between
Autonomous Systems (AS) and to maintain loop-free routing. An autonomous system is a collection
of networks that share the same routing and administration characteristics. For example, a
corporate Intranet consisting of several networks under common administrative control might be
considered an AS. The networks in an AS can but do not need to run the same routing protocol to
be in the same AS, nor do they need to be geographically close.
Devices within an AS can use different Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) such as RIP, IS-IS, and
OSPF to communicate with one another. However, for devices in different ASs to communicate, they
need to use an EGP. BGP4 is the standard EGP used by Internet devices and therefore is the EGP
implemented on the device.
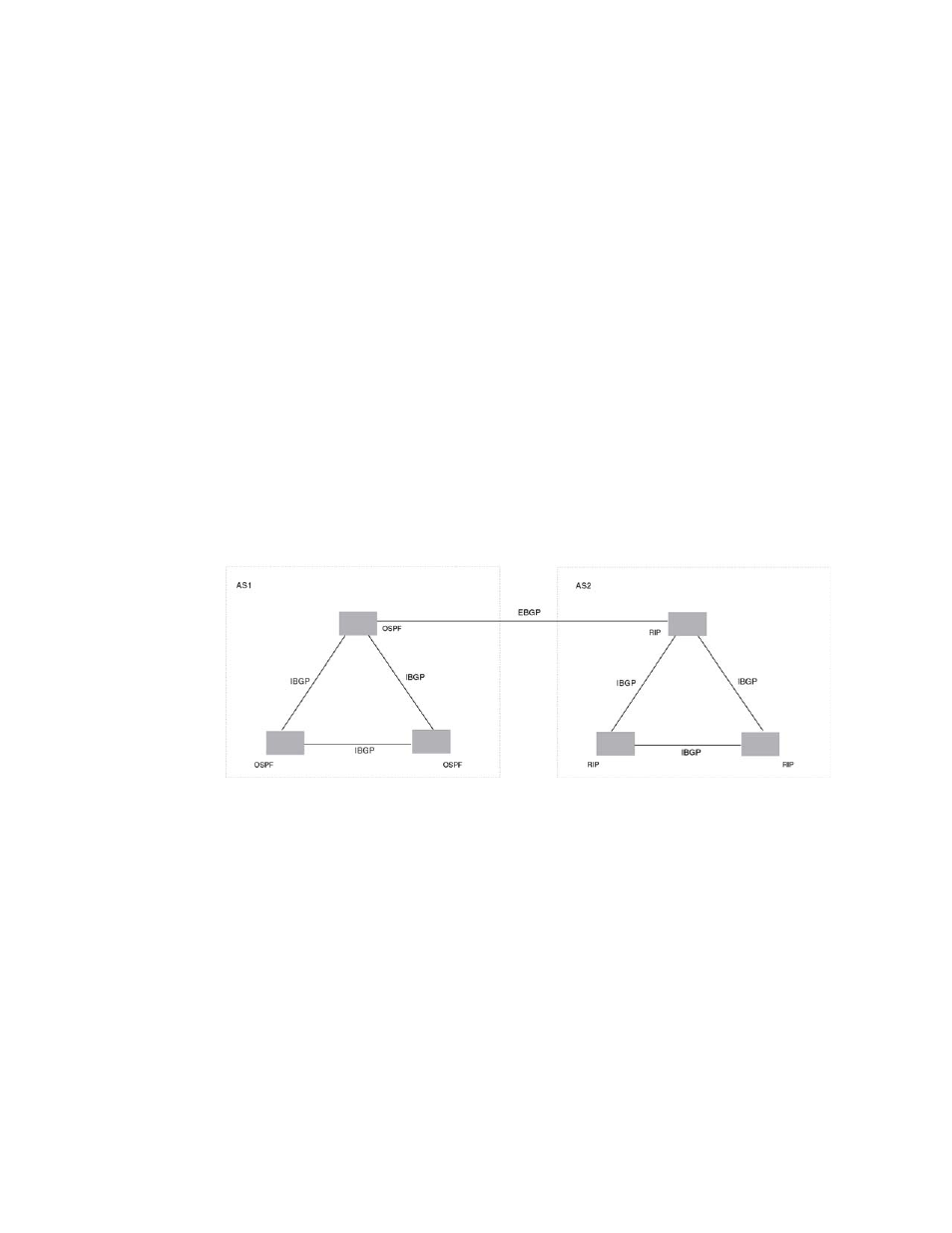
shows a simple example of two BGP4 ASs. Each AS contains three BGP4 devices. All of the
BGP4 devices within an AS communicate using IBGP. BGP4 devices communicate with other ASs
using EBGP. Notice that each of the devices also is running an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The
devices in AS1 are running OSPF and the devices in AS2 are running RIP. The device can be
configured to redistribute routes among BGP4, IS-IS, RIP, and OSPF. They also can redistribute
static routes.
FIGURE 1
Example BGP4 ASs
Relationship between the BGP4 route table and
the IP route table
The device BGP4 route table can have multiple routes or paths to the same destination, which are
learned from different BGP4 neighbors. A BGP4 neighbor is another device that also is running
BGP4. BGP4 neighbors communicate using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 179 for BGP4
communication. When you configure the device for BGP4, one of the configuration tasks you
perform is to identify the device’s BGP4 neighbors.
Although a device’s BGP4 route table can have multiple routes to the same destination, the BGP4
protocol evaluates the routes and chooses only one of the routes to send to the IP route table. The
route that BGP4 chooses and sends to the IP route table is the preferred route. This route is what
the device advertises to other BGP4 neighbors. If the preferred route goes down, BGP4 updates the
route information in the IP route table with a new BGP4 preferred route.
