Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 397
Multi-Service IronWare Routing Configuration Guide
369
53-1003033-02
Overview of Multi-VRF
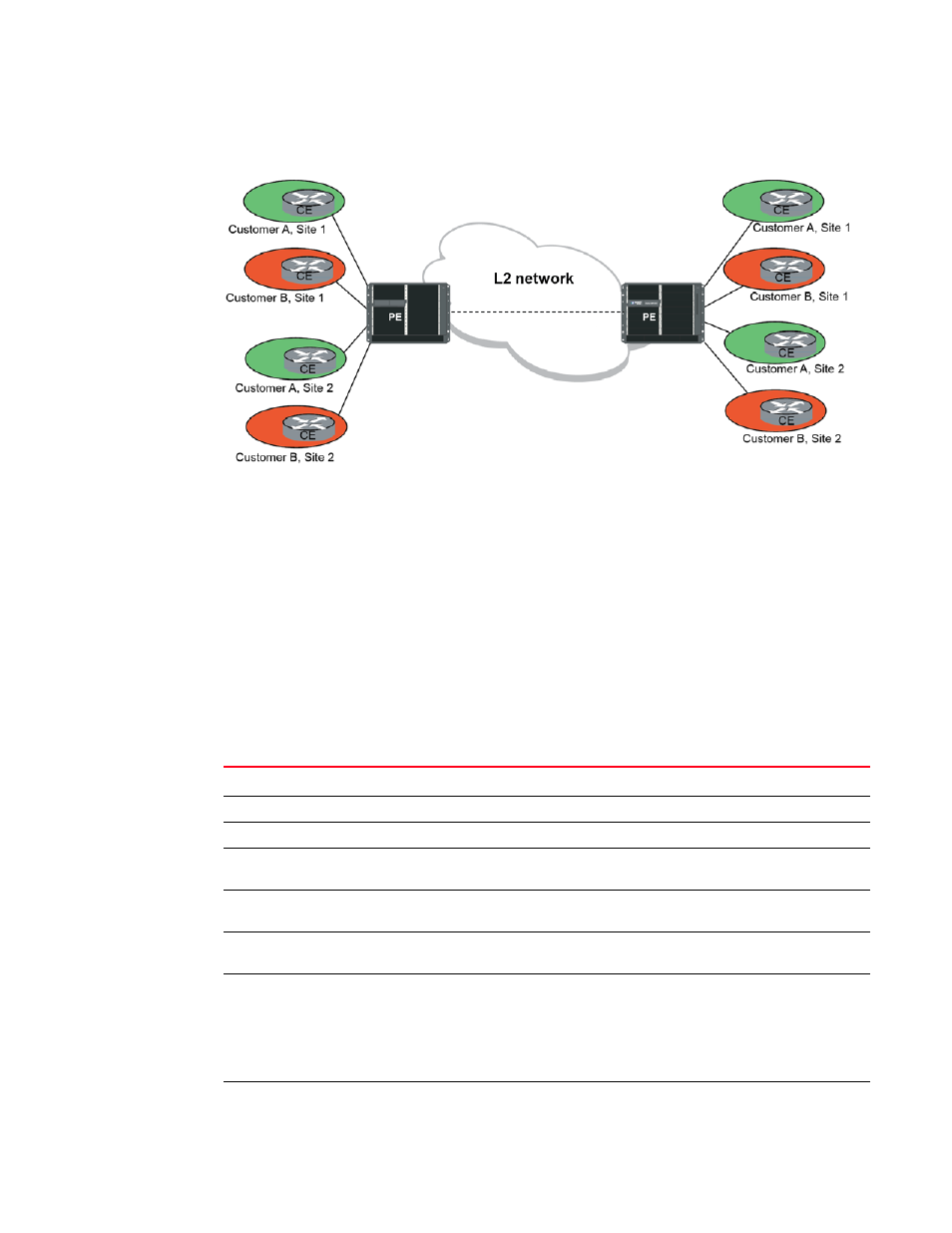
FIGURE 23
A Network deploying Multi-VRF
Multi-VRF and BGP or MPLS VPNs share some common aspects. For instance, in both cases the
edge router maintains a VRF for all directly connected sites that are part of the same VPN. Also in
both cases, the PE and CE routers share customer route information using a variety of PE-CE
routing protocols, such as OSPF, RIP, E-BGP or static routes. Overlapping address spaces among
different VPNs are allowed for both.
There are however, several differences between the two VPN technologies. The fundamental
difference between the two technologies is that Multi-VRF requires that peering PE routers be
directly connected at Layer 3. A Layer 2 network however, can be present between these
directly-connected PE routers. BGP or MPLS VPNs do not have this restriction. In BGP or MPLS
VPNs, the MPLS network determines the path to the peer router. In order to distinguish between
devices with overlapping IP addresses, route targets are used in BGP or MPLS VPNs. Multi-VRF
uses the input interface to uniquely identify the associated VPN, which is why the two PE routers
should be directly connected at Layer 3.
compares Multi-VRF and BGP or MPLS VPNs in
more detail
TABLE 61
Comparison between Multi-VRF and BGP or MPLS VPNs
Multi-VRF
BGP or MPLS VPN
PE-PE Routing Protocol
BGP, OSPF, RIP or Static routing
BGP
PE-CE Routing Protocol
BGP, OSPF, RIP or Static routing
BGP, OSPF, RIP or Static routing
PE-PE Routing Connectivity
PE Routers should be directly
connected at Layer 3
PE Routers are interconnected
through an IP or MPLS Network
Determination of VRF Instance
Based on input interface only
Based on route target (network
interface) or input interface (CE)
Number of Routing Protocol
Instances (PE to PE)
Unique routing protocol instance for
each VRF instance
Single routing protocol instance
Controlling Advertisement of
Routes
No need for route targets to be
used. Advertisement on one VRF is
independent of advertisement in
other VRFs.
Route targets used to identify the
customer VPN in advertised routes.
The destination PE filters the routes
advertised from a peer PE by
comparing the route target with the
VPNs maintained locally on that PE.
Number of VRF Instances
Unique VRF instance for each VPN
Unique VRF instance for each VPN
