Cache content sources – Adobe Dreamweaver CC 2014 v.13 User Manual
Page 620
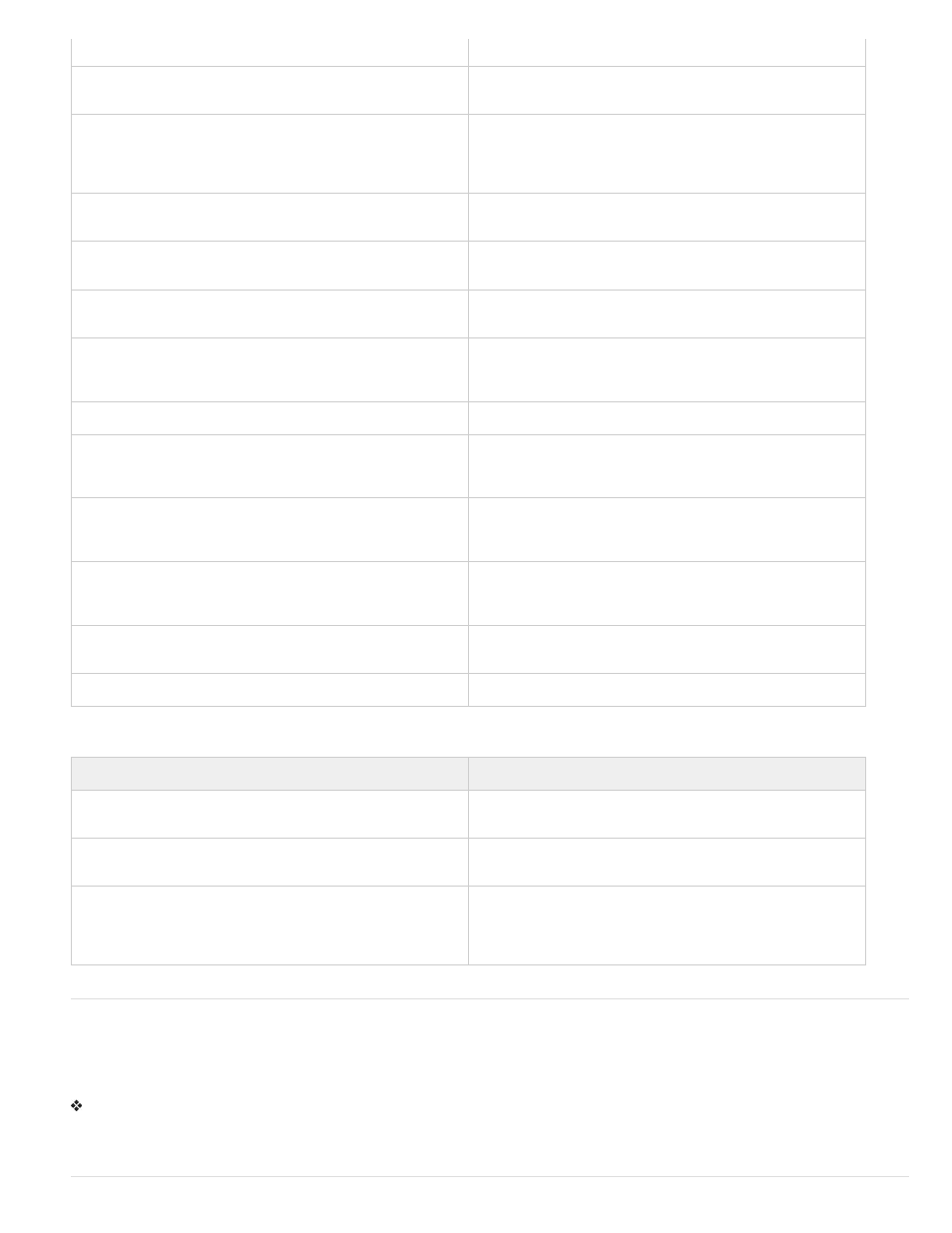
SERVER_PORT
The port number to which the request was sent.
REQUEST_METHOD
The method with which the request was made. For HTTP, this is
Get, Head, Post, and so on.
PATH_INFO
The extra path information, as given by the client. Scripts can be
accessed by their virtual pathname, followed by extra information
at the end of this path. The extra information is sent as
PATH_INFO.
PATH_TRANSLATED
The server provides a translated version of PATH_INFO, which
takes the path and does any virtual-to-physical mapping to it.
SCRIPT_NAME
A virtual path to the script being executed; used for self-
referencing URLs.
QUERY_STRING
The query information that follows the question mark (?) in the
URL that referenced this script.
REMOTE_HOST
The hostname making the request. If the server does not have
this information, it sets REMOTE_ADDR and does not set
REMOTE_HOST.
REMOTE_ADDR
The IP address of the remote host making the request.
AUTH_TYPE
If the server supports user authentication, and the script is
protected, this is the protocol-specific authentication method used
to validate the user.
REMOTE_USER AUTH_USER
If the server supports user authentication, and the script is
protected, this is the user name they have authenticated as. (Also
available as AUTH_USER.)
REMOTE_IDENT
If the HTTP server supports RFC 931 identification, this variable
is set to the remote user name retrieved from the server. Use this
variable for logging only.
CONTENT_TYPE
For queries that have attached information, such as HTTP POST
and PUT, this is the content type of the data.
CONTENT_LENGTH
The length of the content as given by the client.
The following table lists the most common CGI variables created by the browser and passed to the server:
Variable
Description
HTTP_REFERER
The referring document. This is the document that linked to or
submitted form data.
HTTP_USER_AGENT
The browser the client is currently using to send the request.
Format: software/version library/version.
HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE
The last time the page was modified. This variable is sent at the
discretion of the browser, usually in response to the server having
sent the LAST_MODIFIED HTTP header. It can be used to take
advantage of browser-side caching.
Cache content sources
You can cache—or store—sources of dynamic content in a Design Note. This lets you work on a site even if you don’t have access to the
database or application server storing the sources of dynamic content. Caching may also speed up development by eliminating repeated access
across a network to the database and application server.
Click the arrow button in the top right corner of the Bindings panel and toggle Cache in the pop-up menu.
If you make changes to one of the content sources, you can refresh the cache by clicking the Refresh button (the circle-arrow icon) in the upper-
right corner of the Bindings panel. (Expand the panel if you don’t see the button.)
613
