Pk/hnp), Figure 19 – Metrohm 900 Touch Control Manual User Manual
Page 425
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
29 Parameters
900 Touch Control
■■■■■■■■
409
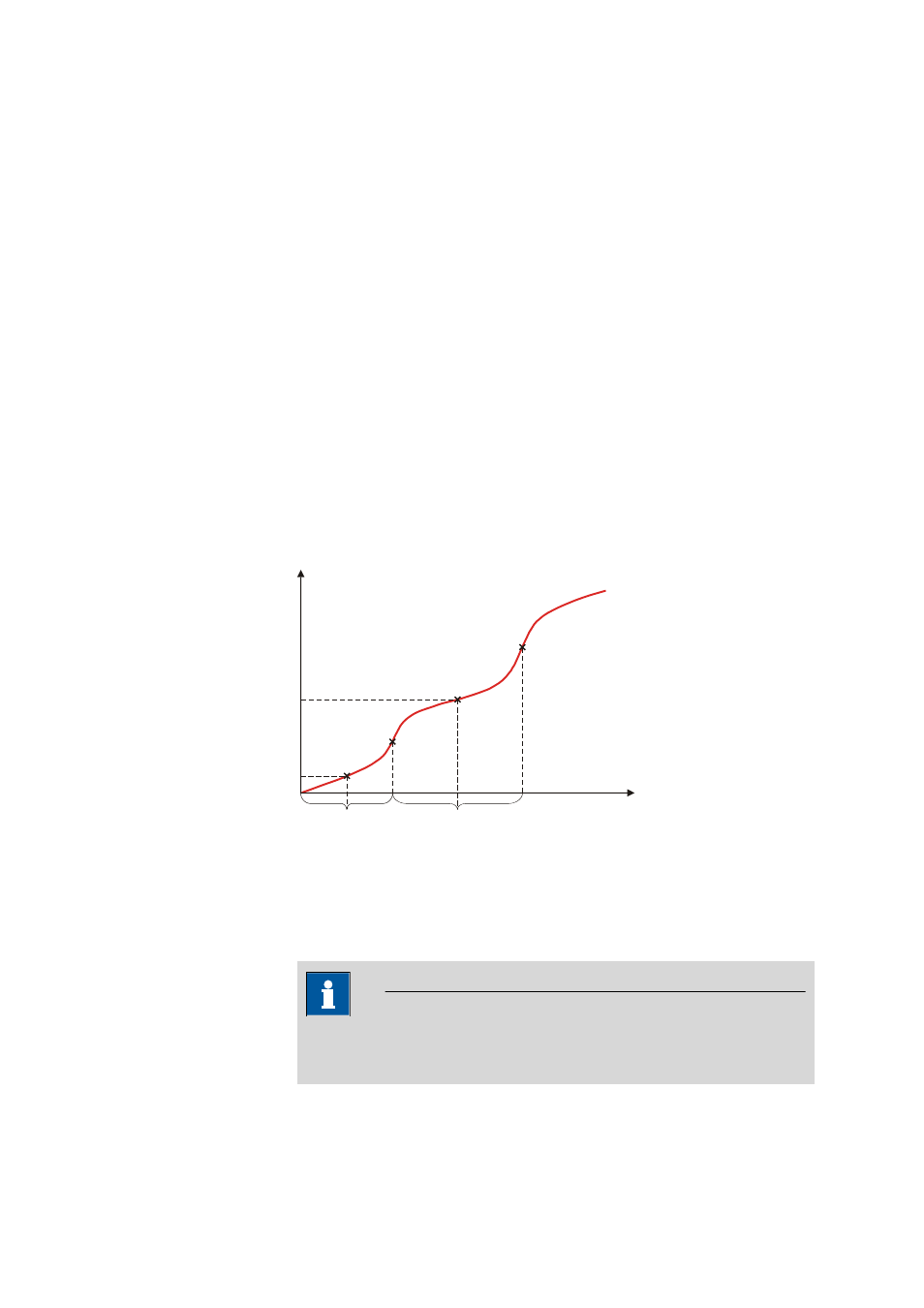
29.12.2 pK value and half neutralization potential evaluation (EVAL pK/
HNP)
The pK value (pH measuring mode) or the half neutralization potential (U
measuring mode) can be determined for DET and MET titrations.
The activities of conjugated acid-base pairs are linked by the so-called
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
pH = pK
a
+ log (a
B
/a
A
)
If the activities of the acid and the conjugated base are equal (a
A
= a
B
),
then pH=pK
a
. This is the value at the half neutralization point and can be
extrapolated from the titration curve. A careful pH calibration is necessary
for pK evaluations. Nonetheless, the determined pK value is only an
approximation, as the ionic strength is not taken into account. In order to
obtain more accurate values, titrations must be carried out with decreas-
ing ionic strength and the results extrapolated to the ionic strength zero.
pK evaluation in aqueous solution is limited to the range 3.5 < pK < 10.5
because of the leveling effect of strong acids and the lack of jumps with
very weak acids. pK values of mixtures of acids and polyvalent acids can
also be determined.
1/2
Volume
1/2
1/2
1/2
EP2
pK2
EP1
pK1
Measured value
Figure 19
Evaluation of pK value / half neutralization potential
In non-aqueous solutions the half neutralization potential (HNP) is fre-
quently used instead of the pK value. The HNP is evaluated in the same
way as the pK value.
No parameters can be edited for the command EVAL pK/HNP.
NOTE
If a start volume is to be added then it must be smaller than the half
endpoint volume.
