Chapter 1 vlan-vpn configuration, 1 vlan-vpn overview, 1 introduction to vlan-vpn – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 605: 2 implementation of vlan-vpn, Chapter 1 vlan-vpn configuration -1, 1 vlan-vpn overview -1
Operation Manual – VLAN VPN
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 1 VLAN-VPN Configuration
1-1
Chapter 1 VLAN-VPN Configuration
1.1 VLAN-VPN Overview
1.1.1 Introduction to VLAN-VPN
The VLAN-VPN function enables packets to be transmitted across the operators’
backbone networks with VLAN tags of private networks encapsulated in those of public
networks. In public networks, packets of this type are transmitted by their outer VLAN
tags (that is, the VLAN tags of public networks). And those of private networks which
are encapsulated in the VLAN tags of public networks are shielded.
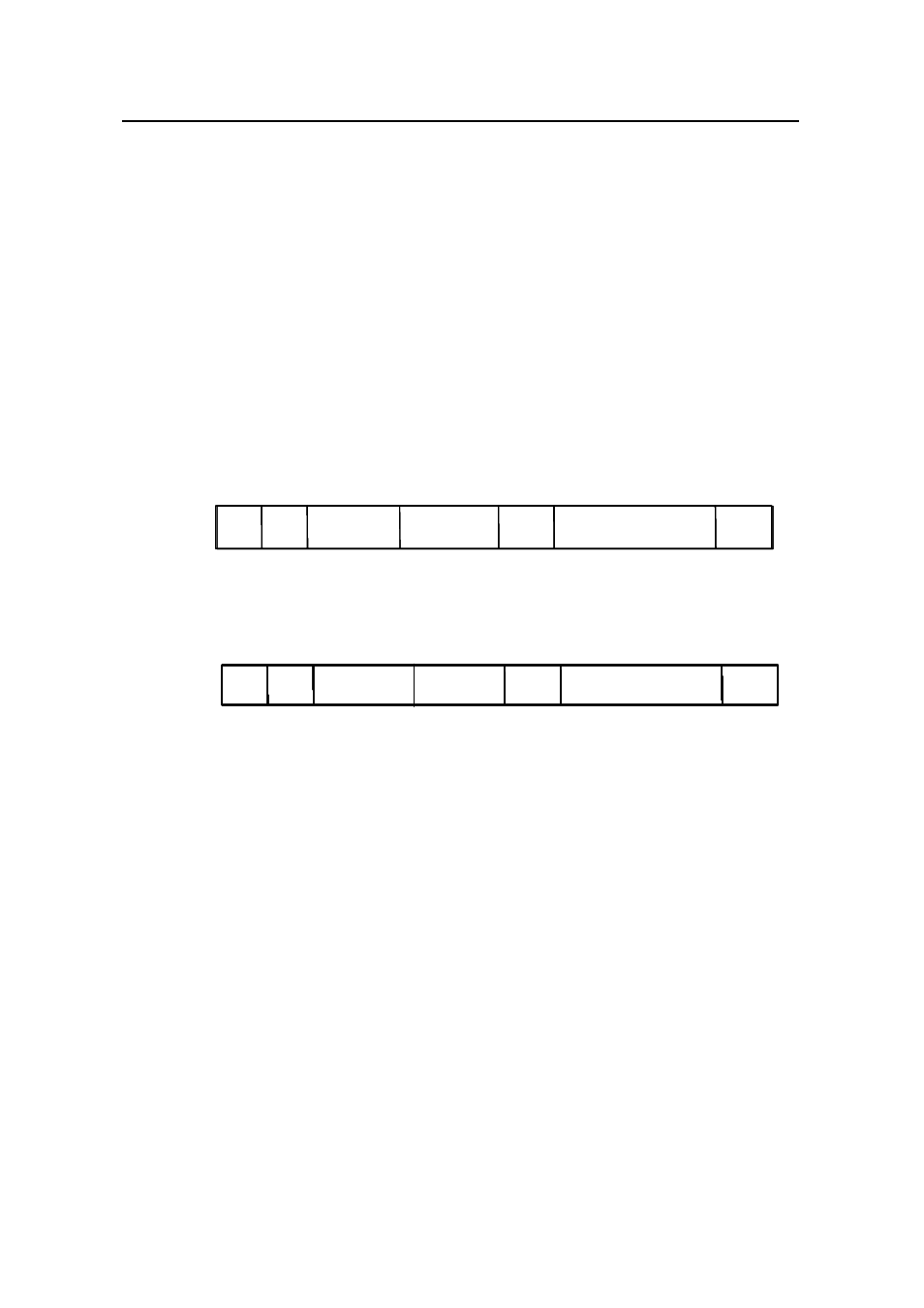
Figure 1-1 describes the structure of the packets with single-layer VLAN tags.
ETYPE(8100)
(2B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
User VLAN TAG
(2B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0 to 1,500B)
FCS
(4B)
ETYPE(8100)
(2B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
User VLAN TAG
(2B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0 to 1,500B)
FCS
(4B)
Figure 1-1
Structure of packets with single-layer VLAN tags
FCS
(4B)
Figure 1-2 describes the structure of the packets with nested VLAN tags.
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
User VLAN
Tag (2B)
Nested VLAN
Tag (2B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
(0~1500B)
FCS
(4B)
DA
(6B)
SA
(6B)
ETYPE
(2B)
DATA
FCS
(4B)
User VLAN
Tag (2B)
Nested VLAN
Tag (2B)
Figure 1-2
Structure of packets with double-layer VLAN tags
Compared with MPLS-based Layer 2 VPN, VLAN-VPN has the following features:
z
It provides Layer 2 VPN tunnels that are simpler.
z
VLAN-VPN can be implemented without the support of signaling protocols. You
can enable VLAN-VPN by static configuration.
The VLAN-VPN function provides you with the following benefits:
z
Saves public network VLAN ID resource.
z
You can have VLAN IDs of your own, which is independent of public network
VLAN IDs.
z
It allows for simple Layer 2 VPN solutions for small-sized MANs or intranets.
1.1.2 Implementation of VLAN-VPN
VLAN-VPN can be implemented by enabling the VLAN-VPN function on ports.
With the VLAN VPN function enabled, a received packet is tagged with the default
VLAN tag of the receiving port no matter whether or not the packet already carries a
