Ii. ethernet multicast mac address – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 235
Operation Manual – Multicast
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 1 Multicast Overview
1-8
Description
Class D address range
224.0.0.15 All
core-based tree (CBT) routers
224.0.0.16
The specified subnetwork bandwidth
management (SBM)
224.0.0.17 All
SBMS
224.0.0.18
Virtual router redundancy protocol
(VRRP)
224.0.0.19 to 224.0.0.255
Other protocols
Note:
Like having reserved the private network segment 10.0.0.0/8 for unicast, IANA has also
reserved the network segments ranging from 239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 for
multicast. These are administratively scoped addresses. With the administratively
scoped addresses, you can define the range of multicast domains flexibly to isolate IP
addresses between different multicast domains, so that the same multicast address
can be used in different multicast domains without causing collisions.
II. Ethernet multicast MAC address
When a unicast IP packet is transported in an Ethernet network, the destination MAC
address is the MAC address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transported in
an Ethernet network, a multicast MAC address is used as the destination address
because the destination is a group with an uncertain number of members.
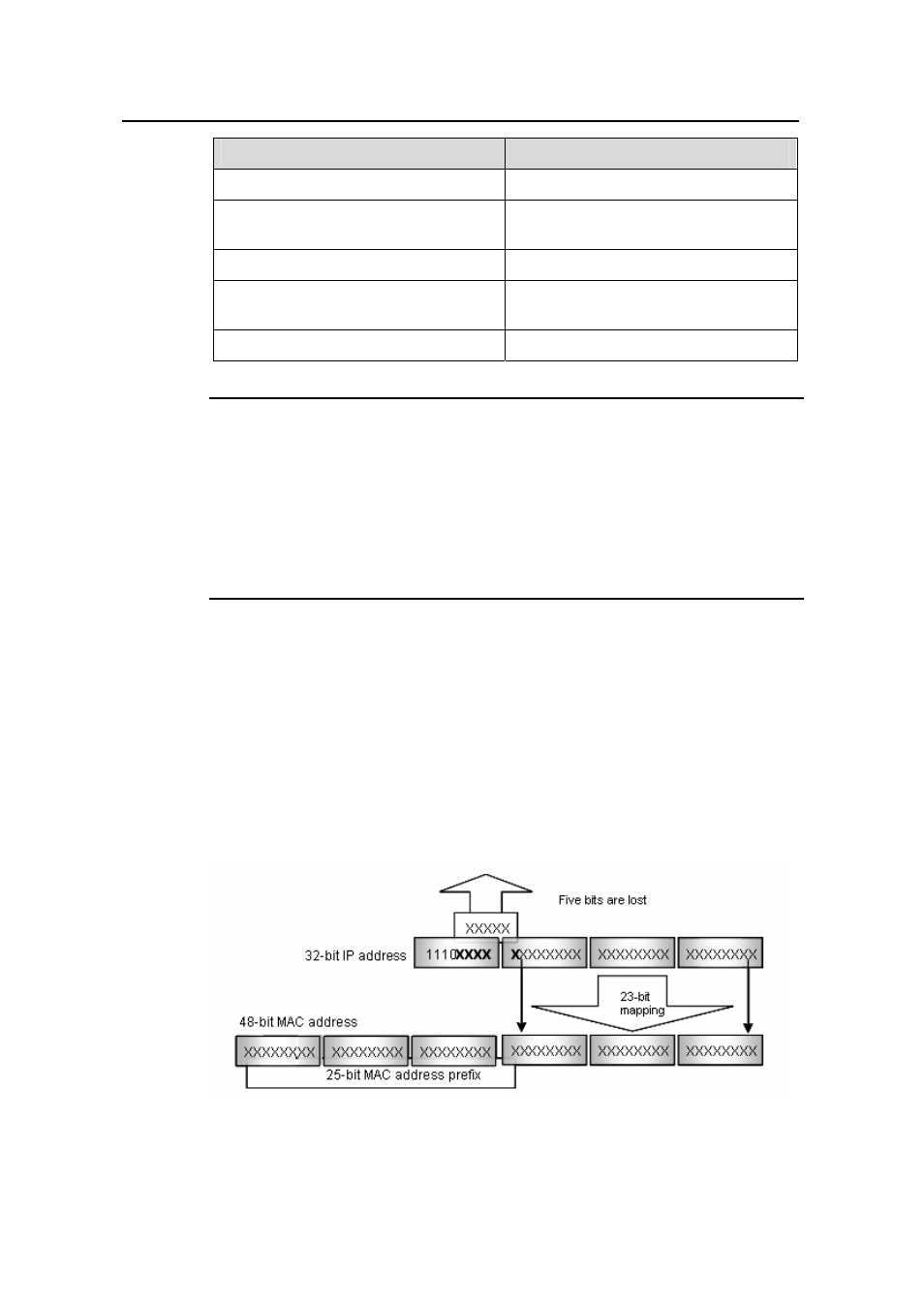
As stipulated by IANA, the high-order 24 bits of a multicast MAC address are 0x01005e,
while the low-order 23 bits of a MAC address are the low-order 23 bits of the multicast
IP address. Figure 1-5 describes the mapping relationship:
Figure 1-5
Mapping relationship between multicast IP address and multicast MAC
address
