H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 411
Operation Manual – Mirroring
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 1 Mirroring Configuration
1-2
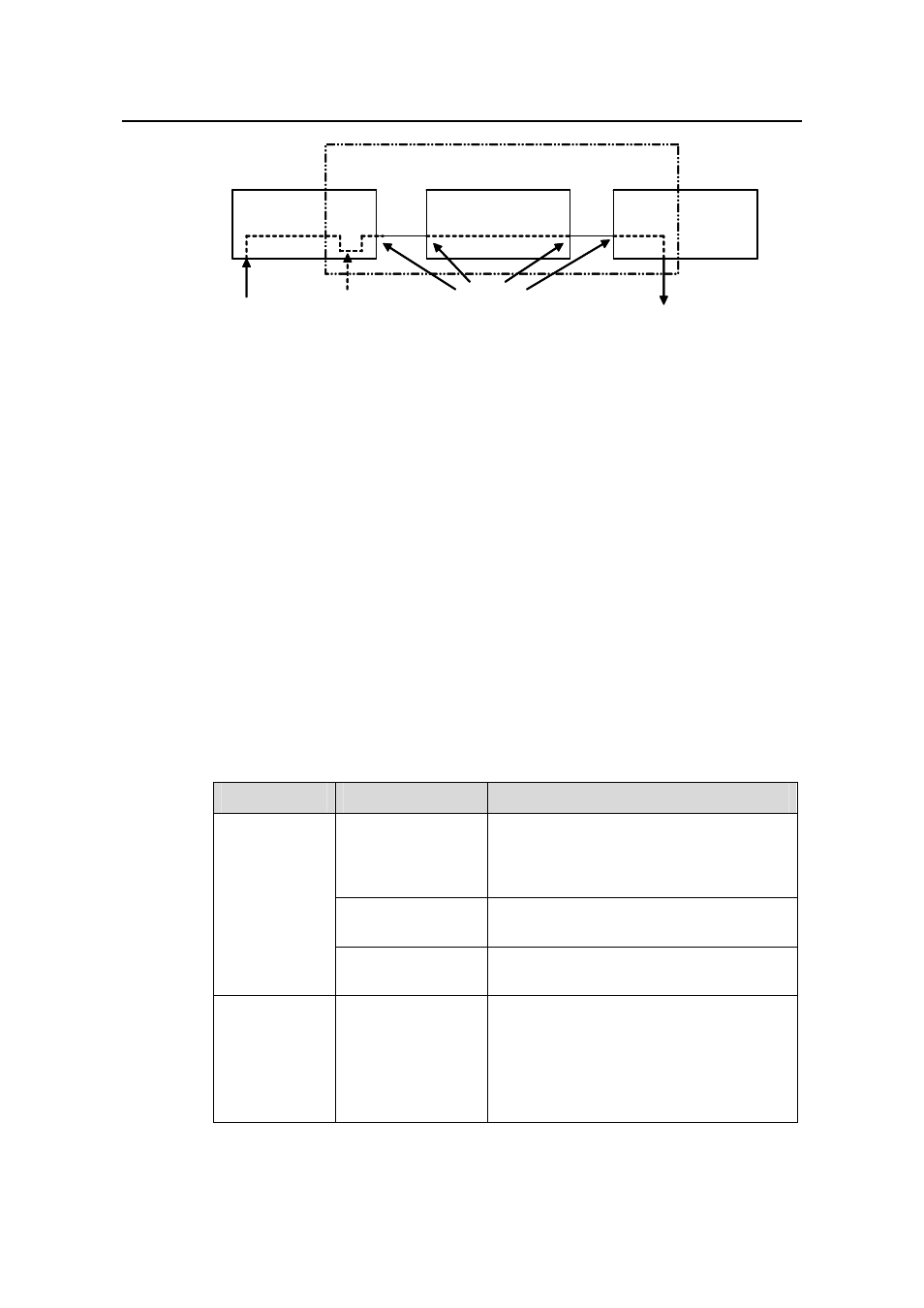
Source
Switch
Intermediate Switch
Reflector port
Source Port
Destination
Switch
Trunk port
Destination port
Remote-probe VLAN
Source
Switch
Intermediate Switch
Reflector port
Source Port
Destination
Switch
Trunk port
Destination port
Remote-probe VLAN
Figure 1-2
RSPAN application
There are three types of switches with the RSPAN enabled.
z
Source switch: The monitored port resident switch. Through Layer 2 forwarding, it
sends traffics to be mirrored to an intermediate switch or destination switch over
the remote-probe VLAN.
z
Intermediate switch: Switches between the source switch and destination switch
on the network. An intermediate switch forwards mirrored traffic flows to the next
intermediate switch or the destination switch. Circumstances can occur where no
intermediate switch is present, if a direct connection exists between the source
and destination switches.
z
Destination switch: The remote mirroring destination port resident switch. It
forwards mirrored traffic flows it received from the remote-probe VLAN to the
monitoring device through the destination port.
Table 1-1 describes how the ports on various switches are involved in the mirroring
operation.
Table 1-1
Ports involved in the mirroring operation
Switch
Ports involved
Function
Source port
Port monitored. It copies user data packets
to the specified reflector port through local
port mirroring. There can be more than one
source port.
Reflector port
Receives user data packets that are
mirrored on a local port.
Source switch
Trunk port
Sends mirrored packets to the intermediate
switch or the destination switch.
Intermediate
switch
Trunk port
Sends mirrored packets to the destination
switch.
Two Trunk ports are necessary for the
intermediate switch to connect the devices
at the source switch side and the
destination switch side.
