Ii. basic message exchange procedure in radius – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 302
Operation Manual – AAA – RADIUS – HWTACACS
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration
1-3
z
Server: RADIUS Server runs on a computer or workstation at the center. It stores
and maintains user authentication information and network service access
information.
z
Client: RADIUS Client runs on dial-in access server devices throughout the
network.
RADIUS is based on client/server model. A switch acting as a RADIUS client passes
user information to a specified RADIUS server, and takes appropriate action (such as
establishing/terminating user connection) depending on the responses returned from
the server. The RADIUS server receives user connection requests, authenticates users,
and returns all required information to the switch.
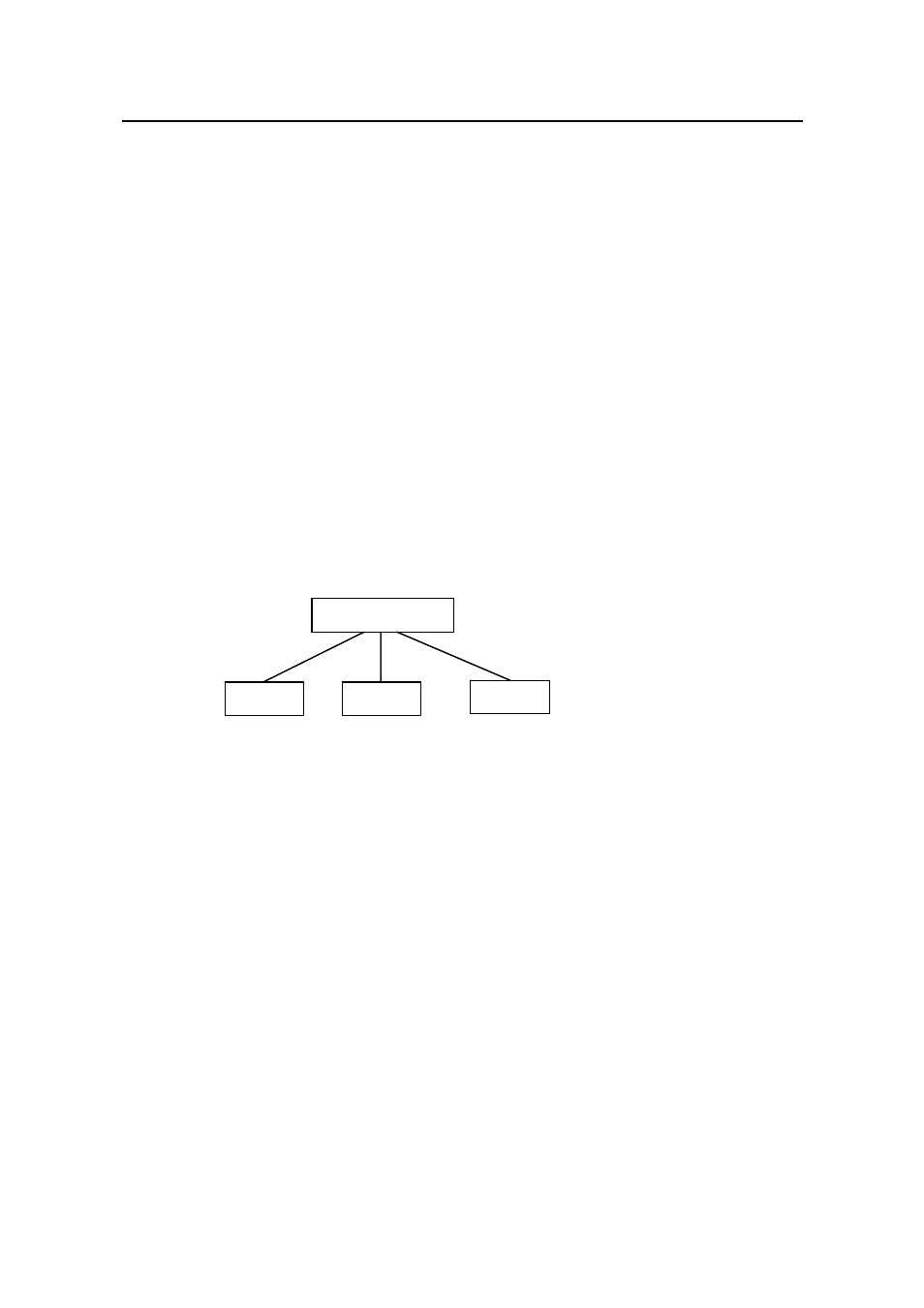
Generally, a RADIUS server maintains the following three databases (see Figure 1-1):
z
Users: This database stores information about users (such as user name,
password, protocol adopted and IP address).
z
Clients: This database stores information about RADIUS clients (such as shared
key).
z
Dictionary: The information stored in this database is used to interpret the
attributes and attribute values in the RADIUS protocol.
RADIUS server
Users
Clients
Dictionary
RADIUS server
Users
Clients
Dictionary
Figure 1-1
Databases in a RADIUS server
In addition, a RADIUS server can act as a client of some other AAA server to provide
authentication or accounting proxy service.
II. Basic message exchange procedure in RADIUS
The messages exchanged between a RADIUS client (a switch, for example) and a
RADIUS server are verified through a shared key. This enhances the security. The
RADIUS protocol combines the authentication and authorization processes together by
sending authorization information along with the authentication response message.
Figure 1-2 depicts the message exchange procedure between user, switch and
RADIUS server.
