Chapter 2 dhcp snooping configuration, 1 introduction to dhcp snooping, Chapter 2 dhcp snooping configuration -1 – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 358: 1 introduction to dhcp snooping -1
Operation Manual – DLDP
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 2 DHCP Snooping Configuration
2-1
Chapter 2 DHCP Snooping Configuration
2.1 Introduction to DHCP Snooping
For the sake of security, the IP addresses used by online DHCP clients need to be
tracked for the administrator to verify the corresponding relationship between the IP
addresses the DHCP clients obtained from DHCP servers and the MAC addresses of
the DHCP clients.
z
Layer 3 switches can track DHCP client IP addresses through DHCP relay.
z
Layer 2 switches can track DHCP client IP addresses through the DHCP snooping
function, which listens DHCP broadcast packets.
When an unauthorized DHCP server exists in the network, a DHCP client may obtains
an illegal IP address. To ensure that the DHCP clients obtain IP addresses from valid
DHCP servers, you can specify a port to be a trusted port or an untrusted port by the
DHCP snooping function.
z
Trusted ports can be used to connect DHCP servers or ports of other switches.
Untrusted ports can be used to connect DHCP clients or networks.
z
Untrusted ports drop the DHCP-ACK and DHCP-OFFER packets received from
DHCP servers. Trusted ports forward any received DHCP packets to ensure that
DHCP clients can obtain IP addresses from valid DHCP servers.
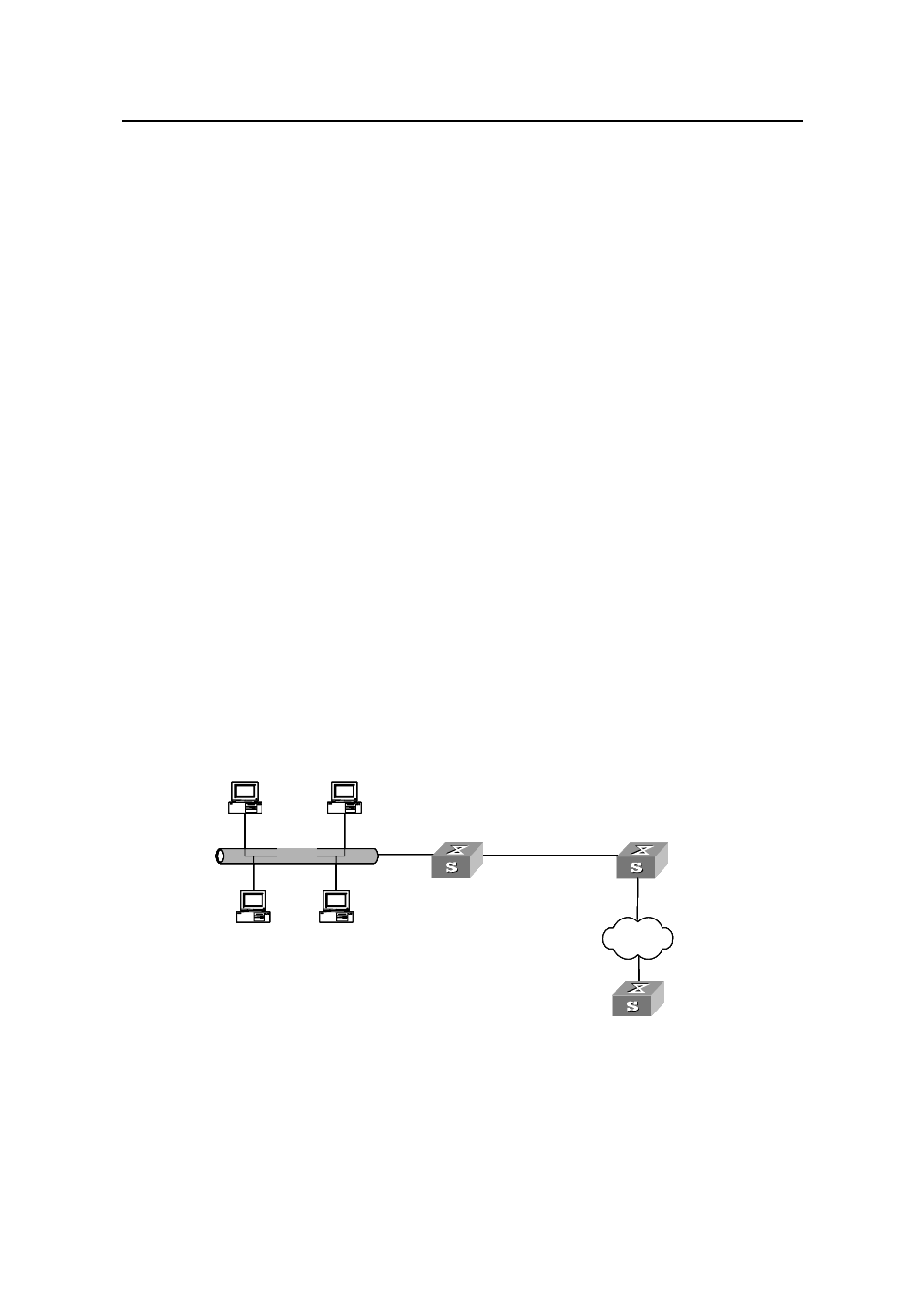
Figure 2-1 illustrates a typical network diagram for DHCP snooping application, where
Switch A is an S3100-52P series Ethernet switch.
Internet
DHCP client
DHCP client
DHCP client
Ethernet
DHCP client
DHCP server
Switch A (DHCP snooping)
Switch B (DHCP relay)
Internet
Ethernet
Ethernet
Internet
DHCP client
DHCP client
DHCP client
Ethernet
DHCP client
DHCP server
Switch A (DHCP snooping)
Switch B (DHCP relay)
Internet
Ethernet
Internet
DHCP client
DHCP client
DHCP client
Ethernet
DHCP client
DHCP server
Switch A (DHCP snooping)
Switch B (DHCP relay)
Internet
Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet
Figure 2-1
Typical network diagram for DHCP snooping application
Figure 2-2 illustrates the interaction between a DHCP client and a DHCP server.
