1 multicast address, 1 multicast address -5 – H3C Technologies H3C S3100 Series Switches User Manual
Page 232
Operation Manual – Multicast
H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch
Chapter 1 Multicast Overview
1-5
z
Technologies of discovering a multicast source: Which multicast source should the
receivers receive information from?
z
Multicast addressing mechanism: Where should the multicast source transports
information?
z
Multicast routing: How is information transported?
IP multicast is a kind of peer-to-peer service. Based on the protocol layer sequence
from bottom to top, the multicast mechanism contains addressing mechanism, host
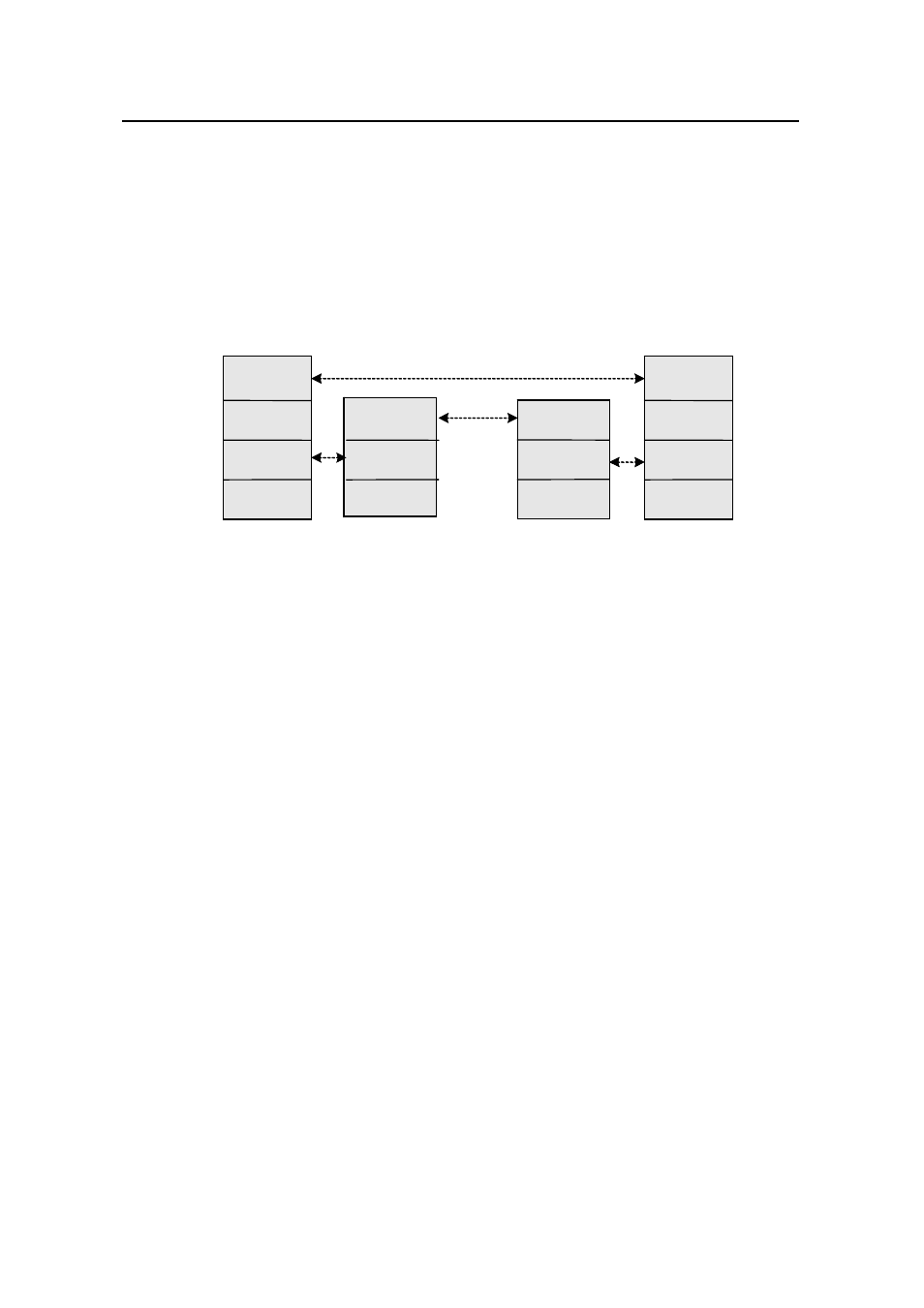
registration, multicast routing, and multicast application, as shown in Figure 1-4:
Multicast
route
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
Multicast
application
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
……
……
Multicast
source
(Host)
Multicast router
Receiver
(Host)
Multicast
route
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
Multicast router
Multicast
application
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
Multicast
route
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
Multicast
application
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
……
……
Multicast
source
(Host)
Multicast router
……
Receiver
(Host)
Multicast
route
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
Multicast router
Multicast
application
Host
registration
Addressing
mechanism
……
Figure 1-4
Architecture of the multicast mechanism
The multicast addressing mechanism involves the planning of multicast addresses.
Host registration and multicast routing are implemented based on the IP multicast
protocol. Multicast application software is not described in this chapter.
z
Addressing mechanism: Information is sent from a multicast source to a group of
receivers through multicast addresses.
z
Host registration: A receiving host joins and leaves a multicast group dynamically
to implement membership registration.
z
Multicast routing: A router or switch establishes a packet distribution tree and
transports packets from a multicast source to receivers.
z
Multicast application: A multicast source must support multicast applications, such
as video conferencing. The TCP/IP protocol suite must support the function of
sending and receiving multicast information.
1.2.1 Multicast Address
As receivers are multiple hosts in a multicast group, you should be concerned about the
following questions:
z
What destination should the information source send the information to in the
multicast mode?
z
How to select the destination address, that is, how does the information source
know who the user is?
