Texas Instruments MSP430x1xx User Manual
Page 40
Interrupt Processing
3-10
8) The content of the appropriate interrupt vector is loaded into the program
counter: the program continues with the interrupt handling routine at that
address.
The interrupt latency is six cycles, starting with the acceptance of an interrupt
request, and lasting until the start of execution of the appropriate
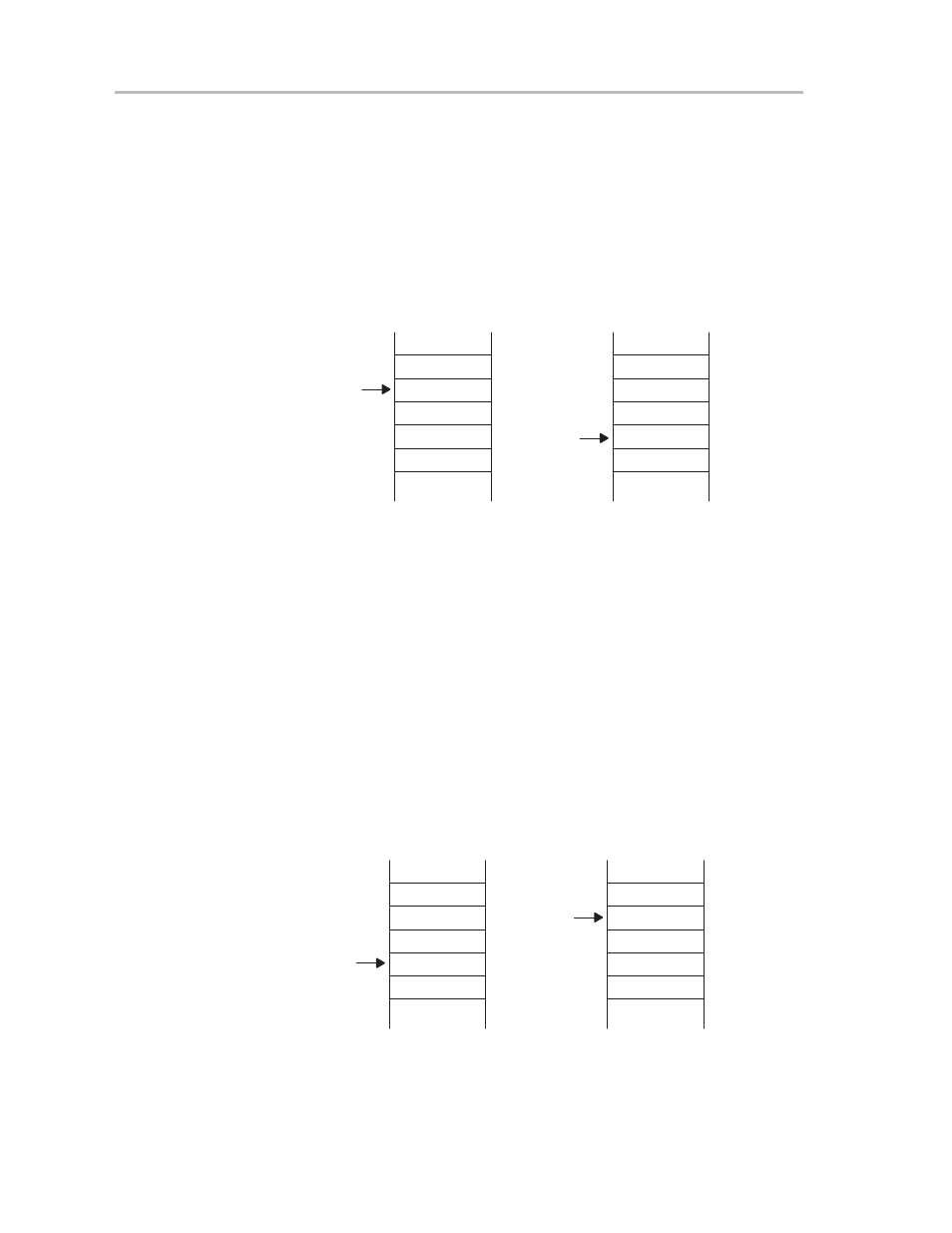
interrupt-service routine first instruction, as shown in Figure 3–7.
Figure 3–7. Interrupt Processing
Item1
Item2
SP
TOS
Item1
Item2
SP
TOS
PC
SR
Before
Interrupt
After
Interrupt
The interrupt handling routine terminates with the instruction:
RETI
(return from an interrupt service routine)
which performs the following actions:
1) The status register with all previous settings pops from the stack. All pre-
vious settings of GIE, CPUOFF, etc. are now in effect, regardless of the
settings utilized during the interrupt service routine.
2) The program counter pops from the stack and begins execution at the
point where it was interrupted.
The return from the interrupt is illustrated in Figure 3–8.
Figure 3–8. Return From Interrupt
Item1
Item2
SP
TOS
Item1
Item2
SP
TOS
PC
SR
Before
After
PC
SR
Return From Interrupt
A RETI instruction takes five cycles. Interrupt nesting is activated if the GIE bit
is set inside the interrupt handling routine. The GIE bit is located in status
register SR/R2, which is included in the CPU as shown in Figure 3–9.
