Texas Instruments MSP430x1xx User Manual
Page 283
Comparator_A in Applications
14-17
Comparator_A
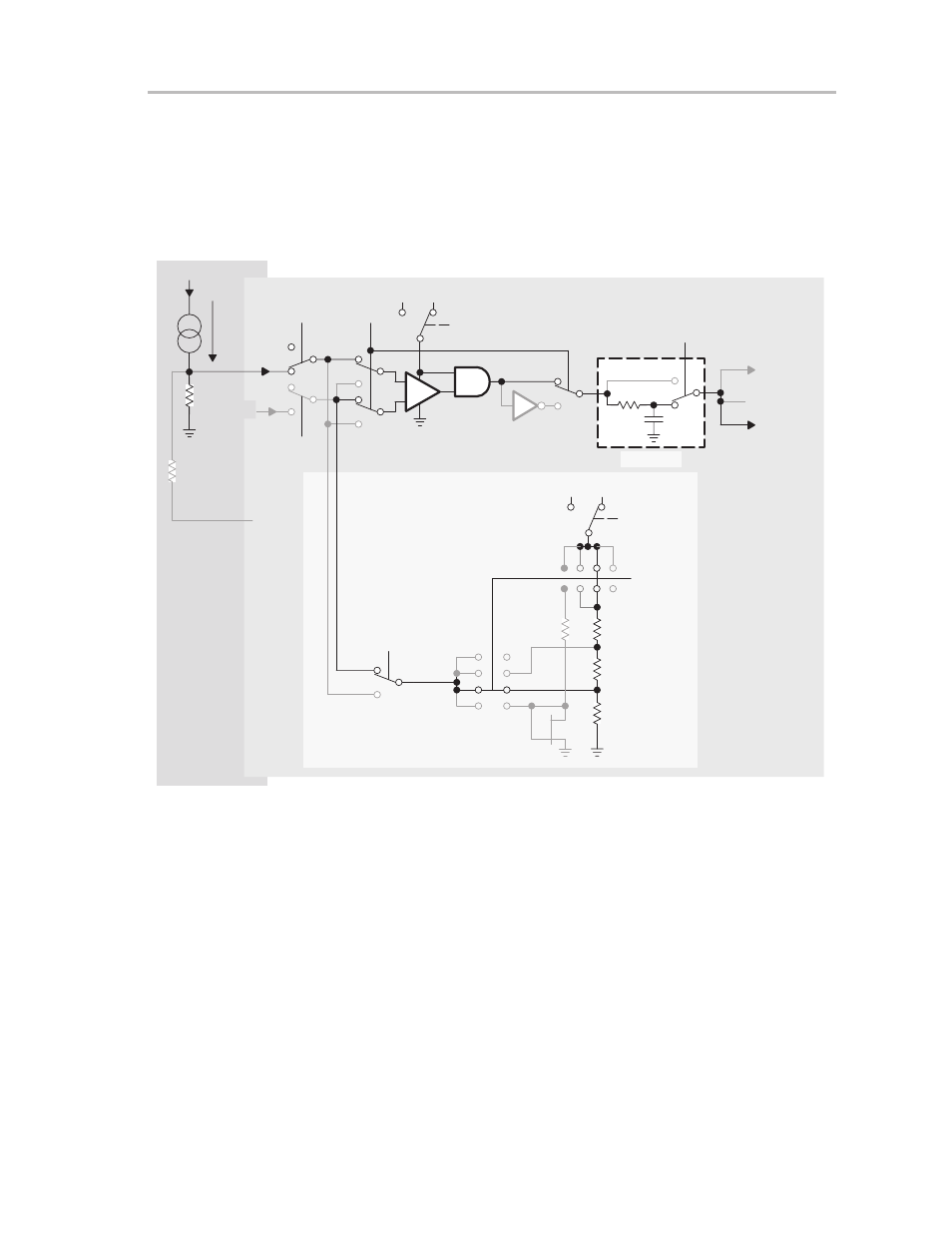
In Figure 14–13 current is transferred to an input voltage by I
×
R
(sense)
. The
current limit is set for example to 0.25
×
V
CC
. The current is below the limit as
long as CAOUT is reset.
Figure 14–13. Detect a Current Level Using an Internal Reference Level
_
+
0
1
CAF
Set
CAIFG
τ
∼
2
µ
s
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
CA0
CA1
0
1
P2CA0
P2CA1
VCAREF
CARSEL
0
1
2
3
3
2
1 0
CAREF
0.5
×
VCC
0.25
×
VCC
VCC
R(sense)
Optional
R(hyst)
Px.y
1
0
CAEX
CAON
VCC
0 V
1
0
CAON
VCC
0 V
1
0
e.g.
Capture
Input of
Timer_A
CAOUT to
External Pin
14.4.5 Comparator_A Used to Measure a Current or Voltage Level
In addition to detecting levels, the comparator can be used to measure
currents or voltages. To measure a voltage, a known, stable voltage source is
used to charge up an RC combination. The time required to charge the
combination to a threshold value set by the voltage to be measured is then
used to calculate the voltage level (see Figure 14–16). V
CAREF
can be used
as the known stable voltage source if V
CC
in the user’s system meets the
required stability and accuracy.
A similar approach is used to measure a current. A known, stable voltage
source is again used to charge an RC combination to a threshold value. In this
case, the threshold voltage is created by passing the current to be measured
through a known resistance (see Figure 14–14).
