Rockwell Automation 8520 9/Series CNC Lathe User Manual
Page 759
Chapter 30
Using a 9/Series Dual--Processing System
30-19
The Interference Checking feature is designed to help prevent collisions by
the axes of a dual-processing machine.
Interference checking provides an area (usually around the cutting tool or
tool turret for each process) that defines a boundary that moves with the
tool. The other process cannot enter into this boundary. This helps prevent
collisions.
For interference checking to function properly, you must define and
activate this boundary for both processes. When one process’s boundary
attempts to enter another process’s boundary, one process enters cycle
suspend, preventing it from entering the protected area. In the case of an
unavoidable direct collision, both processes stop. An error message is
displayed for both processes. The two boundaries cannot intersect.
CAUTION: These interference boundaries only help prevent
collision with another interference boundary configured for
another process. They do not protect against collisions with
other machine fixtures that may or may not be protected by a
programmable zone or software overtravel. They do not
account for any tool offsets that are active at the time. They are
absolute positions.
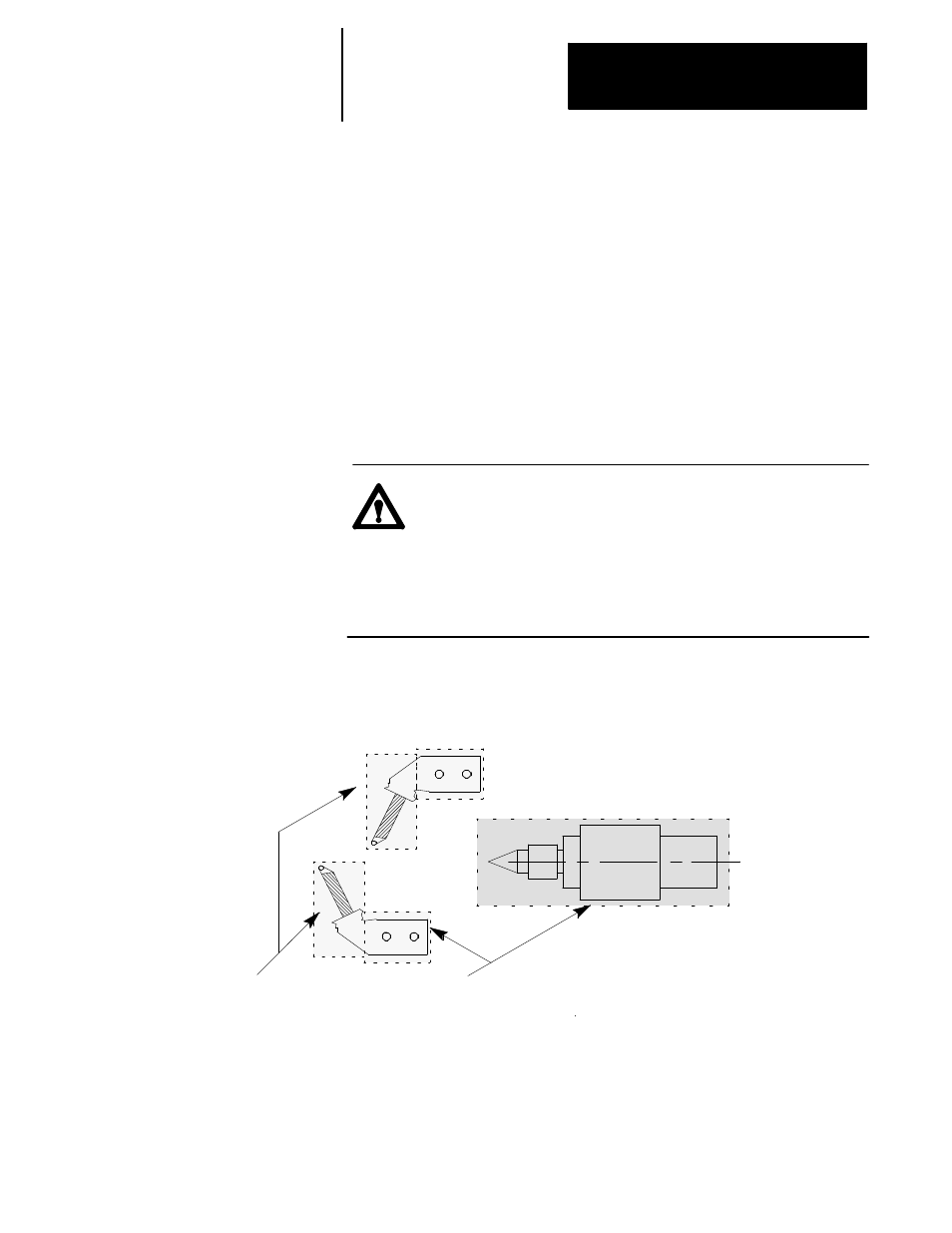
Figure 30.8
Interference Check Helps Prevent Tool Fixtures from Colliding
Programmable
Zone 1
Area protected against
collision by interference
checking. No collision
between these areas.
Interference checking does not protect programmable zones.
Only tool tip location is monitored for a programmable zone. Possible
collision between these areas.
Tailstock
12603-I
30.5
Using Interference Checking
with a Dual-Process Lathe
