Rainbow Electronics AT91CAP9S250A User Manual
Page 691
691
6264A–CAP–21-May-07
AT91CAP9S500A/AT91CAP9S250A
CAN Bus Synchronization
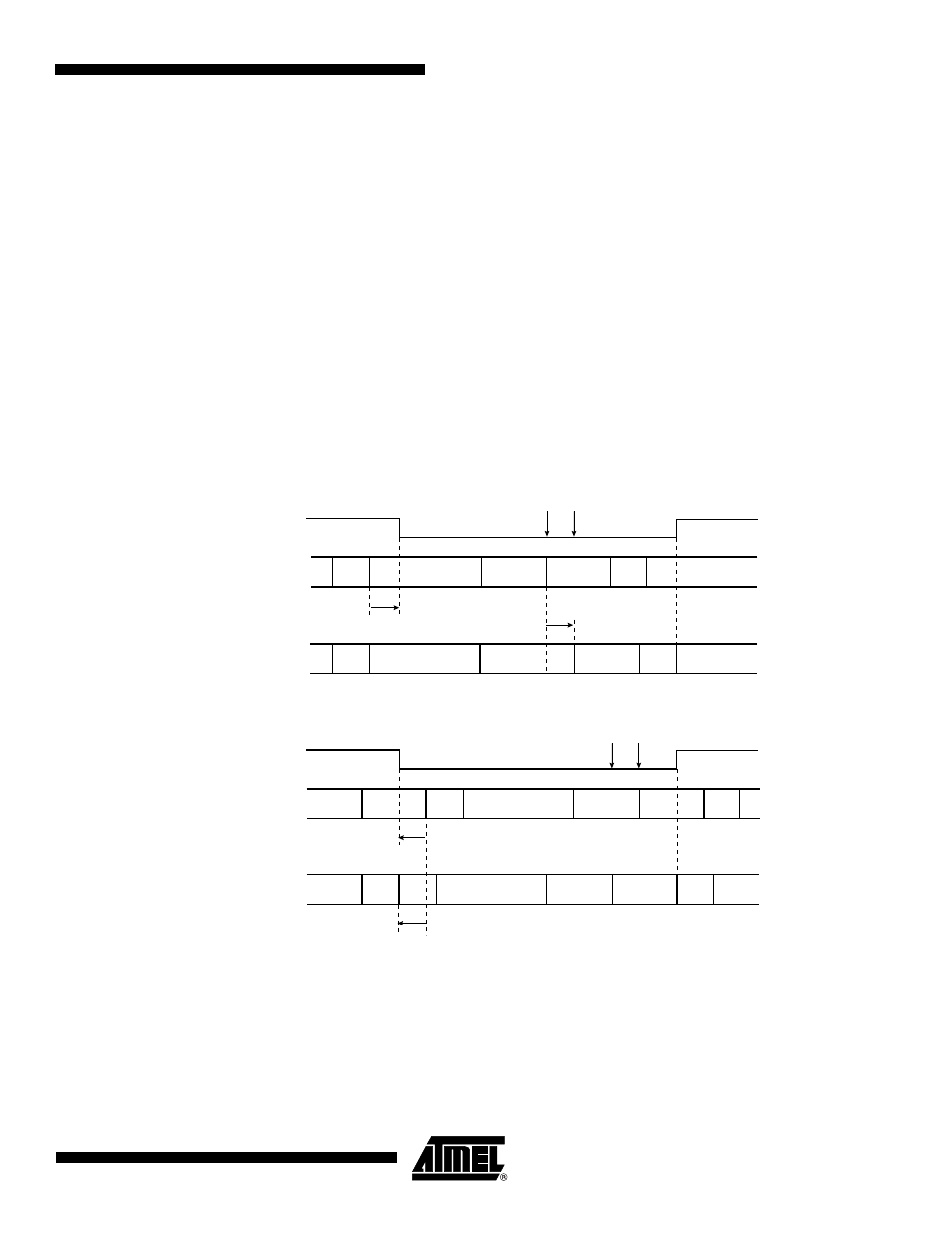
Two types of synchronization are distinguished: “hard synchronization” at the start of a frame
and “resynchronization” inside a frame. After a hard synchronization, the bit time is restarted
with the end of the SYNC_SEG segment, regardless of the phase error. Resynchronization
causes a reduction or increase in the bit time so that the position of the sample point is shifted
with respect to the detected edge.
The effect of resynchronization is the same as that of hard synchronization when the magni-
tude of the phase error of the edge causing the resynchronization is less than or equal to the
programmed value of the resynchronization jump width (t
SJW
).
When the magnitude of the phase error is larger than the resynchronization jump width and
• the phase error is positive, then PHASE_SEG1 is lengthened by an amount equal to the
resynchronization jump width.
• the phase error is negative, then PHASE_SEG2 is shortened by an amount equal to the
resynchronization jump width.
Figure 39-6. CAN Resynchronization
Autobaud Mode
The autobaud feature is enabled by setting the ABM field in the CAN_MR register. In this
mode, the CAN controller is only listening to the line without acknowledging the received mes-
sages. It can not send any message. The errors flags are updated. The bit timing can be
adjusted until no error occurs (good configuration found). In this mode, the error counters are
SYNC_
SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG1 PHASE_SEG2
SYNC_
SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG1
PHASE_SEG2
Phase error
Phase error (max Tsjw)
SYNC_
SEG
SYNC_
SEG
SYNC_
SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG1
PHASE_SEG2
SYNC_
SEG
PHASE_SEG2
SYNC_
SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG1
PHASE_
SEG2
SYNC_
SEG
PHASE_SEG2
Phase error
Nominal
Sample point
Sample point
after resynchronization
Nominal
Sample point
Sample point
after resynchronization
THE PHASE ERROR IS POSITIVE
(the transmitter is slower than the receiver)
Received
data bit
Received
data bit
Nominal bit time
(before resynchronization)
Bit time with
resynchronization
Bit time with
resynchronization
Phase error (max Tsjw)
Nominal bit time
(before resynchronization)
THE PHASE ERROR IS NEGATIVE
(the transmitter is faster than the receiver)
