Rainbow Electronics AT91CAP9S250A User Manual
Page 54
54
6264A–CAP–21-May-07
AT91CAP9S500A/AT91CAP9S250A
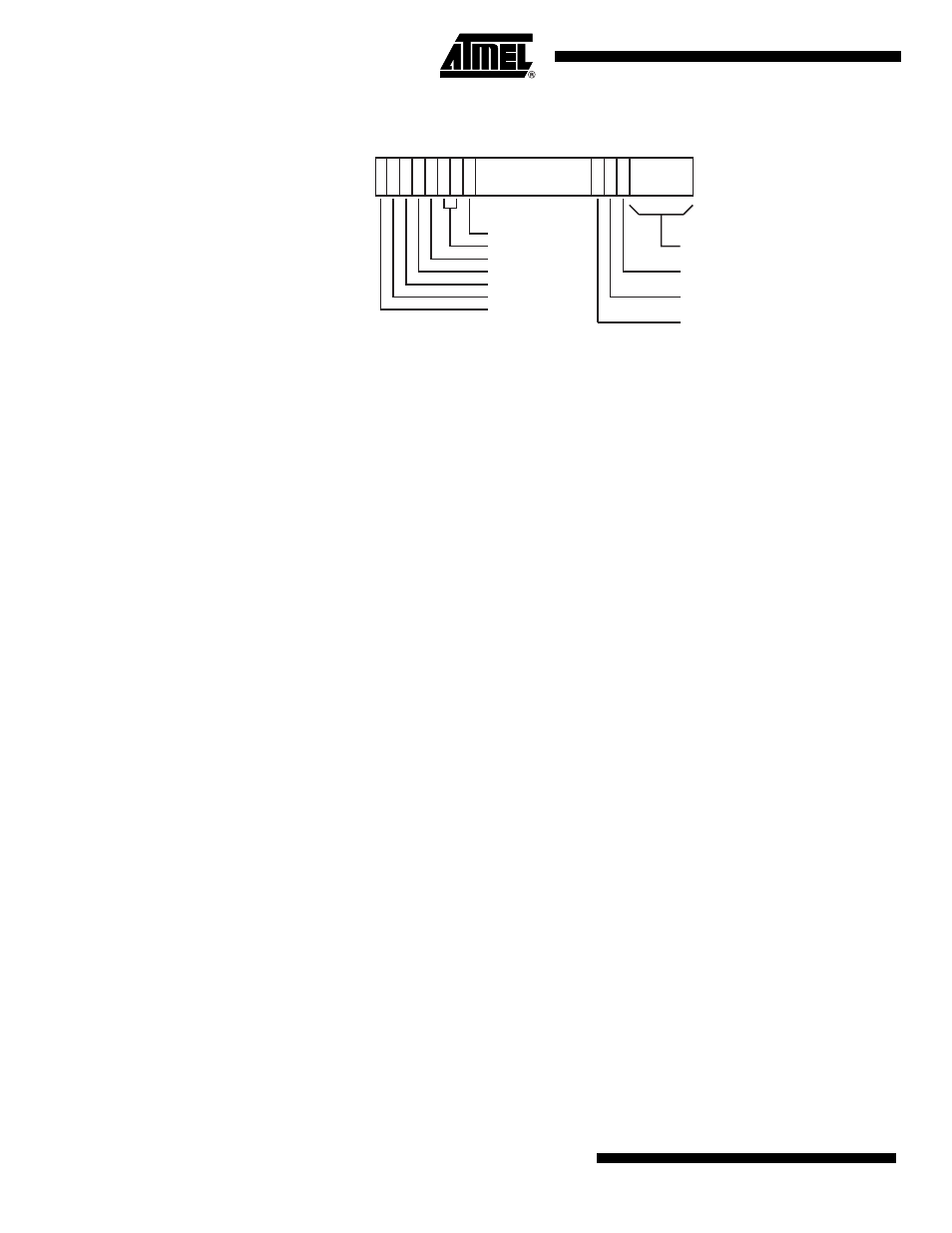
Figure 12-2. Status Register Format
shows the status register format, where:
• N: Negative, Z: Zero, C: Carry, and V: Overflow are the four ALU flags
• The Sticky Overflow (Q) flag can be set by certain multiply and fractional arithmetic
instructions like QADD, QDADD, QSUB, QDSUB, SMLAxy, and SMLAWy needed to achieve
DSP operations.
The Q flag is sticky in that, when set by an instruction, it remains set until explicitly cleared by
an MSR instruction writing to the CPSR. Instructions cannot execute conditionally on the
status of the Q flag.
• The J bit in the CPSR indicates when the ARM9EJ-S core is in Jazelle state, where:
– J = 0: The processor is in ARM or Thumb state, depending on the T bit
– J = 1: The processor is in Jazelle state.
• Mode: five bits to encode the current processor mode
12.3.7.2
Exceptions
Exception Types and Priorities
The
ARM9EJ-S supports five types of exceptions. Each type drives the ARM9EJ-S in a privi-
leged mode. The types of exceptions are:
• Fast interrupt (FIQ)
• Normal interrupt (IRQ)
• Data and Prefetched aborts (Abort)
• Undefined instruction (Undefined)
• Software interrupt and Reset (Supervisor)
When an exception occurs, the banked version of R14 and the SPSR for the exception mode
are used to save the state.
More than one exception can happen at a time, therefore the ARM9EJ-S takes the arisen excep-
tions according to the following priority order:
• Reset (highest priority)
• Data Abort
• FIQ
• IRQ
• Prefetch Abort
• BKPT, Undefined instruction, and Software Interrupt (SWI) (Lowest priority)
N Z C V Q
J
I
F T
Mode
Reserved
Mode bits
Thumb state bit
FIQ disable
IRQ disable
Jazelle state bit
Reserved
Sticky Overflow
Overflow
Carry/Borrow/Extend
Zero
Negative/Less than
31 30 29 28 27
24
7 6 5
0
