Rockwell Automation 1747-PT1, D1747NP002 Hand-Held Terminal User Manual
Page 385
Chapter 27
The Status File
27–17
Address
Description
5/02
5/01,
Fixed
S:6
Major Error Fault Code
Read/write. A hex code will be entered in this word by the processor
when a major error is declared (refer to S:1/13). The code defines
the type of fault, as indicated on the following pages. This word is not
cleared by the processor.
Error codes are presented, stored, and displayed in hexadecimal.
(appendix B explains hex numbering system.)
•
•
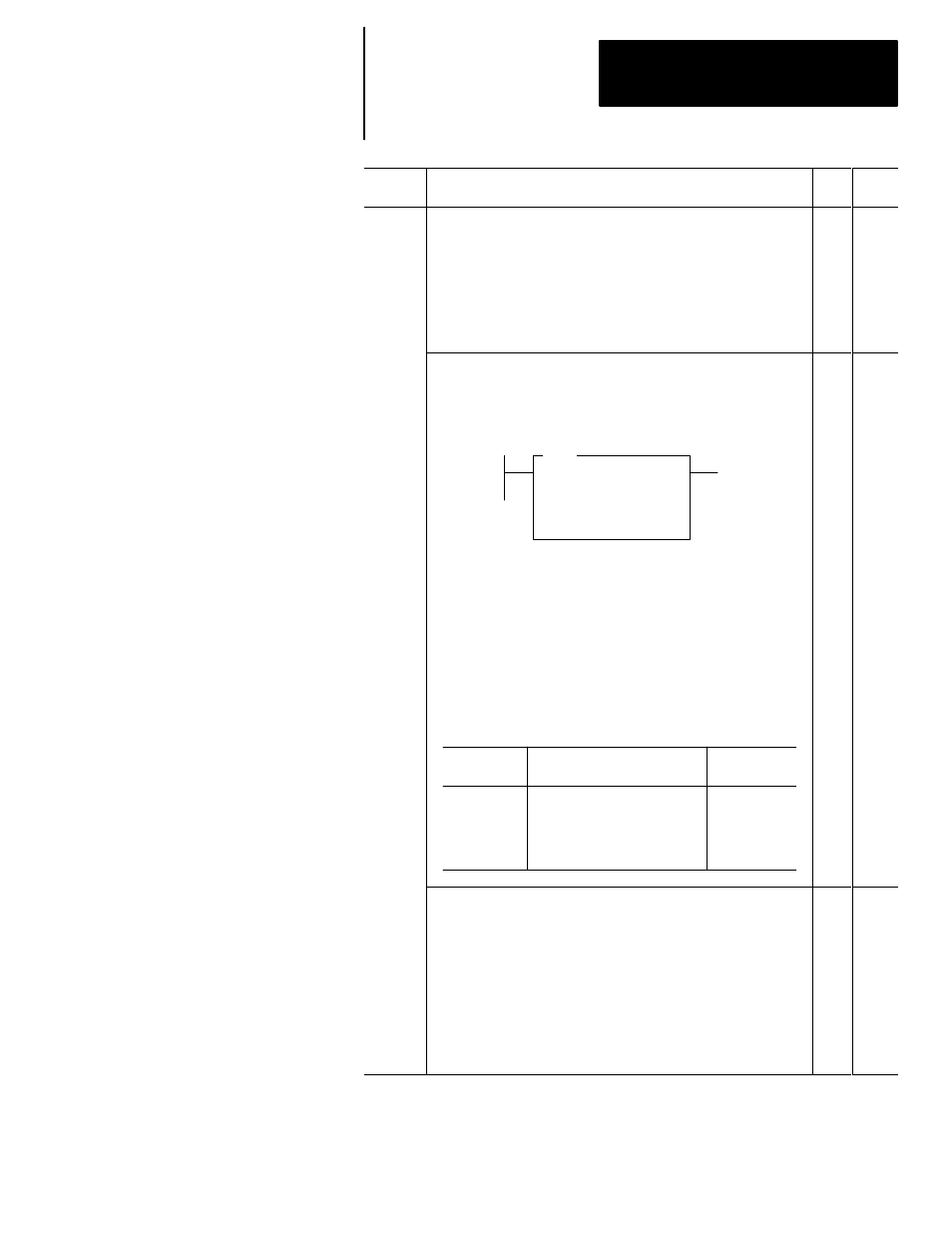
If you enter a fault code as a parameter in an instruction in your
ladder program, you must convert the code to decimal. For example,
if you program an EQU instruction to go true when the error 0016
occurs, enter S:6 as source A and 22, the decimal equivalent of
0016H, as source B:
Application note: You can declare your own application–specific
major fault by writing your own unique value to S:6 and then setting
bit S:1/13.
SLC 5/02 processor users: Interrogate the value of S:6 in your fault
routine to determine the type of fault that occurred. If your program
was saved with the test single step enabled, you can also interrogate
S:20 and S:21 to pinpoint the exact rung that was being executed
when the fault occurred.
Fault Classifications: Faults are classified as Non-User,
Non-Recoverable, and Recoverable, defined below.
Recoverable
User Fault
The fault routine
may clear the
fault by clearing
bit S:1/13.
Non-Recoverable
User Fault
The fault routine executes for 1
pass. (You may initiate a MSG
instruction to another node to
identify the fault condition of
the processor.)
Non-User
Fault
The fault
routine does
not execute.
EQU
EQUAL
Source A
S:6
Source B
22
•
Error code descriptions and classifications are listed on pages 27–18
through 27–22. Categories:
•
powerup errors
•
going to run errors
•
runtime errors
•
user program instruction errors
•
I/O errors
See chapter 28 for cause/recovery information on faults.
•
•
