Allied Telesis AT-S60 User Manual
Page 190
AT-S60 Management Software User’s Guide
Section II: Local and Telnet Management
189
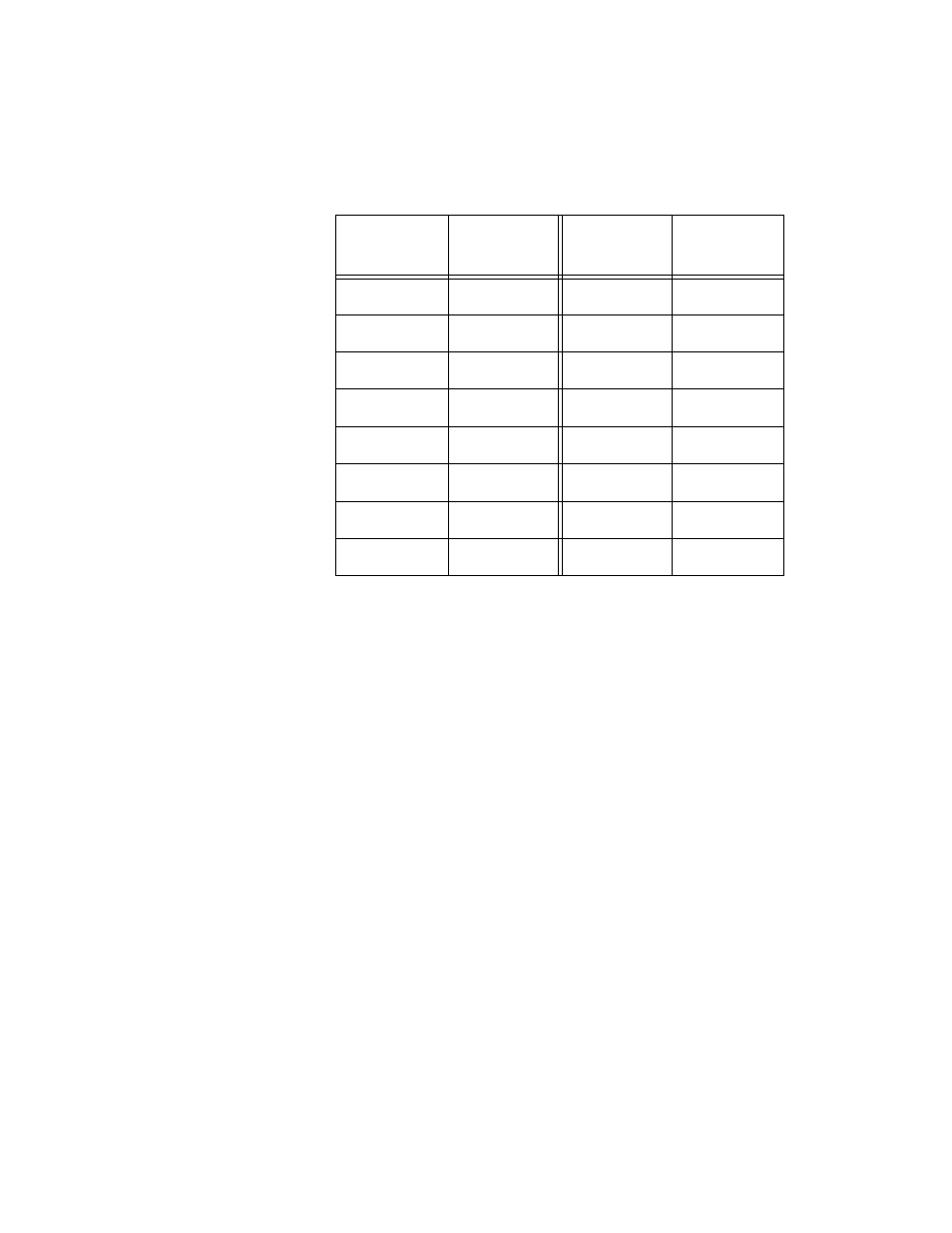
The range for port priority is 0 to 240 in increments of 16. Just as with the
bridge priority value, you specify the increment that corresponds to the
desired value. Table 7 lists the port priority increments. The default value
is 128, with an increment of 8.
Forwarding Delay and Topology Changes
If there is a change in the network topology due to a failure, removal, or
addition of any active components, the active topology may also
change. This may trigger a change in the state of some blocked ports.
However, a change in a port state is not activated immediately.
It might take time for the root bridge to notify all bridges that a topology
change has occurred, especially if it is a large network. If a topology
change is made before all bridges have been notified, a temporary data
loop could occur, and that could adversely impact network
performance.
To forestall the formation of temporarily data loops during topology
changes, a port designated to change from blocking to forwarding
passes through two additional states, listening and learning, before it
begins to forward frames. The amount of time a port spends in these
states is set by the forwarding delay value. This value controls the
amount of time that a port spends in the listening and learning states
prior to changing to the forwarding state.
Table 7 Port Priority Value Increments
Increment
Port
Priority
Increment
Port
Priority
0
0
8
128
1
16
9
144
2
32
10
160
3
48
11
176
4
64
12
192
5
80
13
208
6
96
14
224
7
112
15
240
