Managing the dsm/scm archive, Managing files (software inputs) in the archive, Figure 17-1 – HP Integrity NonStop H-Series User Manual
Page 314: Files in the archive
Managing DSM/SCM
DSM/SCM User’s Guide — 529846-014
17 - 21
Managing the DSM/SCM Archive
Managing the DSM/SCM Archive
The three areas of managing the DSM/SCM archive and its contents are:
Managing Files (Software Inputs) in the Archive
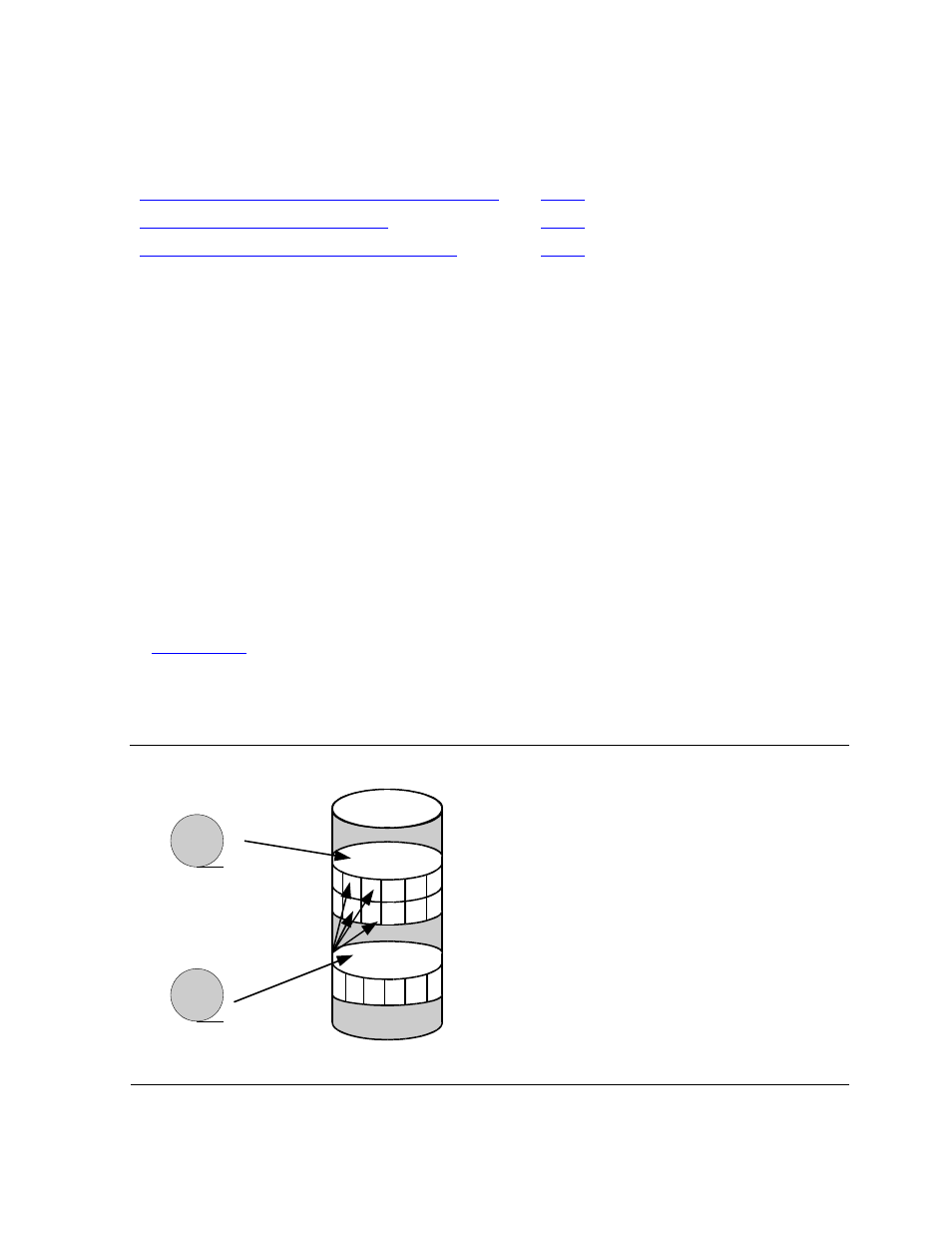
To efficiently manage archive space, first understand how DSM/SCM archives files. To
optimize archive space, DSM/SCM ensures files are not duplicated in the archive. If
two inputs contain identical files, as often occurs, the files are stored with the first
archived input and are referenced by pointers in the second archived input. This saves
considerable archive space. However, when an input is deleted or backed up, any files
common to other inputs or configuration revisions are not removed from the archive.
Therefore, deleting or backing up archive contents to manage disk space used by the
archive might not save as much space as you expect.
If any configuration revision references files are associated with a software input, you
cannot delete that input until you delete the revision. When you try to delete an input,
DSM/SCM determines whether a configuration references any files associated with it.
However, you can back up the input, which returns any space not shared with other
inputs.
In
, the archive contains inputs from two RVUs: X20.00 and X20.01.
Typically, most files do not change between RVUs. In this case, RVU X20.00 contains
450 files, and RVU X20.01 contains 460 files, with 20 new files and 10 files deleted.
440 files are identical in the two inputs.
Managing Files (Software Inputs) in the Archive
Exporting Files From the Archive
Moving the DSM/SCM Archive (ZPHIHMI)
Figure 17-1. Files in the Archive
SUT
X20.00
Archive
450 Files
20 Files
SUT
X20.01
460 files =
20 new files
10 files deleted
VST055.vsd
