Vlag and lag primary port with igmp snooping – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 642
• By sending an unsolicited IGMP join request.
• By sending an IGMP join request as a response to a general query from a multicast router.
In response to the request, the switch creates an entry in its Layer 2 forwarding table for that VLAN.
When other hosts send join requests for the same multicast, the switch adds them to the existing table
entry. Only one entry is created per VLAN in the Layer 2 forwarding table for each multicast group.
vLAG and LAG primary port with IGMP snooping
The current data center Ethernet (DCE) implementation of vLAGs and LAGs uses the concept of a so-
called primary port. One of the member ports of the vLAG and LAG is selected to be the primary port,
and all multicast traffic egressing from the LAG or vLAG is sent on the primary port. Thus, normal
hash-based forwarding is not performed for multicast traffic, whether it is control traffic or data. Now,
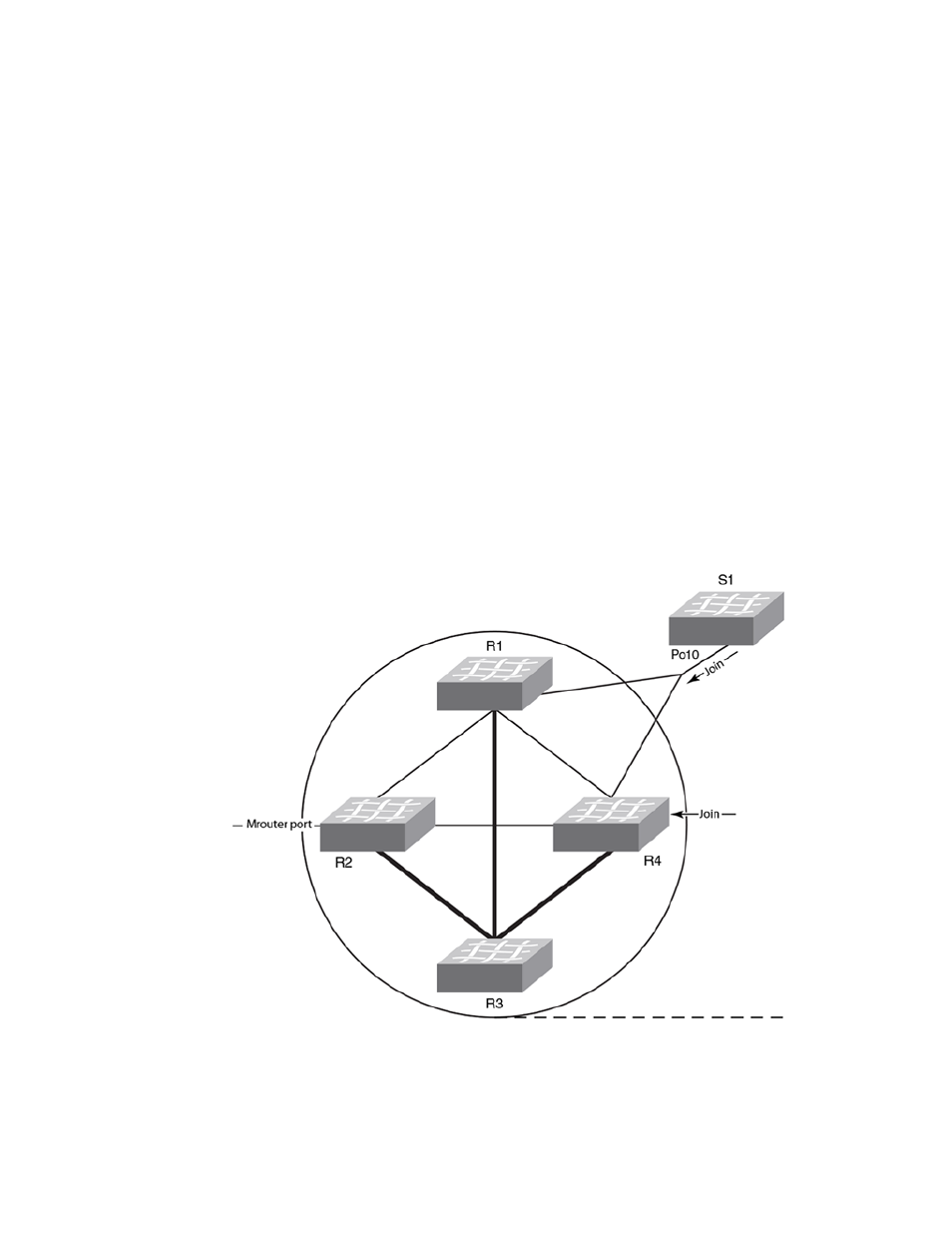
consider the case where RBridge R1 receives an IGMP join request for group G1 on Po10, shown in
the figure below. This causes Po10 to be added to the list of IGMP receivers for group G1. Now,
assume that the primary port of the vLAG is the link connecting R4 and S1. Therefore, any multicast
traffic received by the cluster for group G1 egresses on vLAG Po10 from R4 and not from R1, even
though the original join was received on R1.
If the primary port for the vLAG changes, such as if the link between R4 and S1 in the figure below
went down, then multicast traffic would egress out of the new primary port on the vLAG. In the above
case, the new primary port would be the link connecting R1 and S1.
FIGURE 76 IGMP snooping in Brocade VCS Fabric mode
vLAG and LAG primary port with IGMP snooping
642
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
53-1003225-04
