Lsan zones, Lsan zones overview – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 169
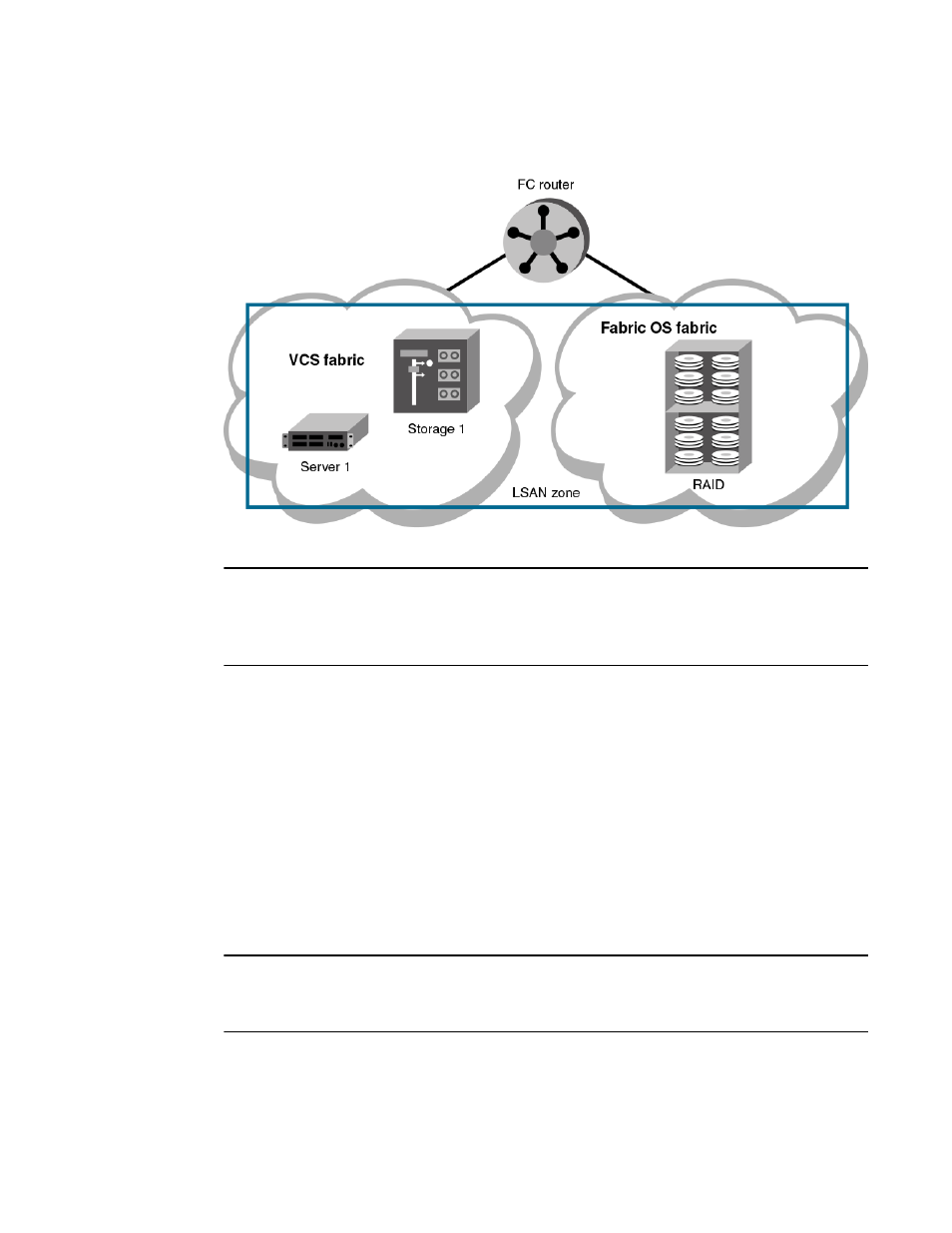
FIGURE 25 LSAN zoning
NOTE
Zoning in Network OS 4.0.0 and later has the following restrictions:
• Zone objects based on physical port number or port ID (D,I ports) are not supported.
• You cannot access a target on a Network OS fabric from a server on the Fabric OS fabric.
LSAN zones
LSAN zones are distinct from conventional zones. This section details how to define and manage LSAN
zones and provides recommendations about LSAN zone naming.
LSAN zones overview
A Logical SAN (LSAN) consists of zones in two or more edge or backbone fabrics that contain the same
devices. LSANs essentially provide selective device connectivity between fabrics without forcing you to
merge those fabrics. FC routers provide multiple mechanisms to manage inter-fabric device connectivity
through extensions to existing switch management interfaces. For details of this FC-FC routing service,
refer to the Fabric OS Administrator's Guide.
NOTE
A backbone fabric consists of one or more FC switches with configured EX_Ports. These EX_Ports in
the backbone connect to edge fabric switches through E_Ports. This type of EX_Port-to-E_Port
connectivity is called an "Inter-Fabric Link (IFL)".
The Brocade VCS Fabric connection to the FC router is an ISL that connects an FC port on a Brocade
VDX 6730 to an EX_Port on the FC router. Similarly, an FC port on the Fabric OS fabric connects to an
EX_Port on the FC router.
LSAN zones
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
169
53-1003225-04
