Multicast queue scheduling, Data center bridging qos – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 479
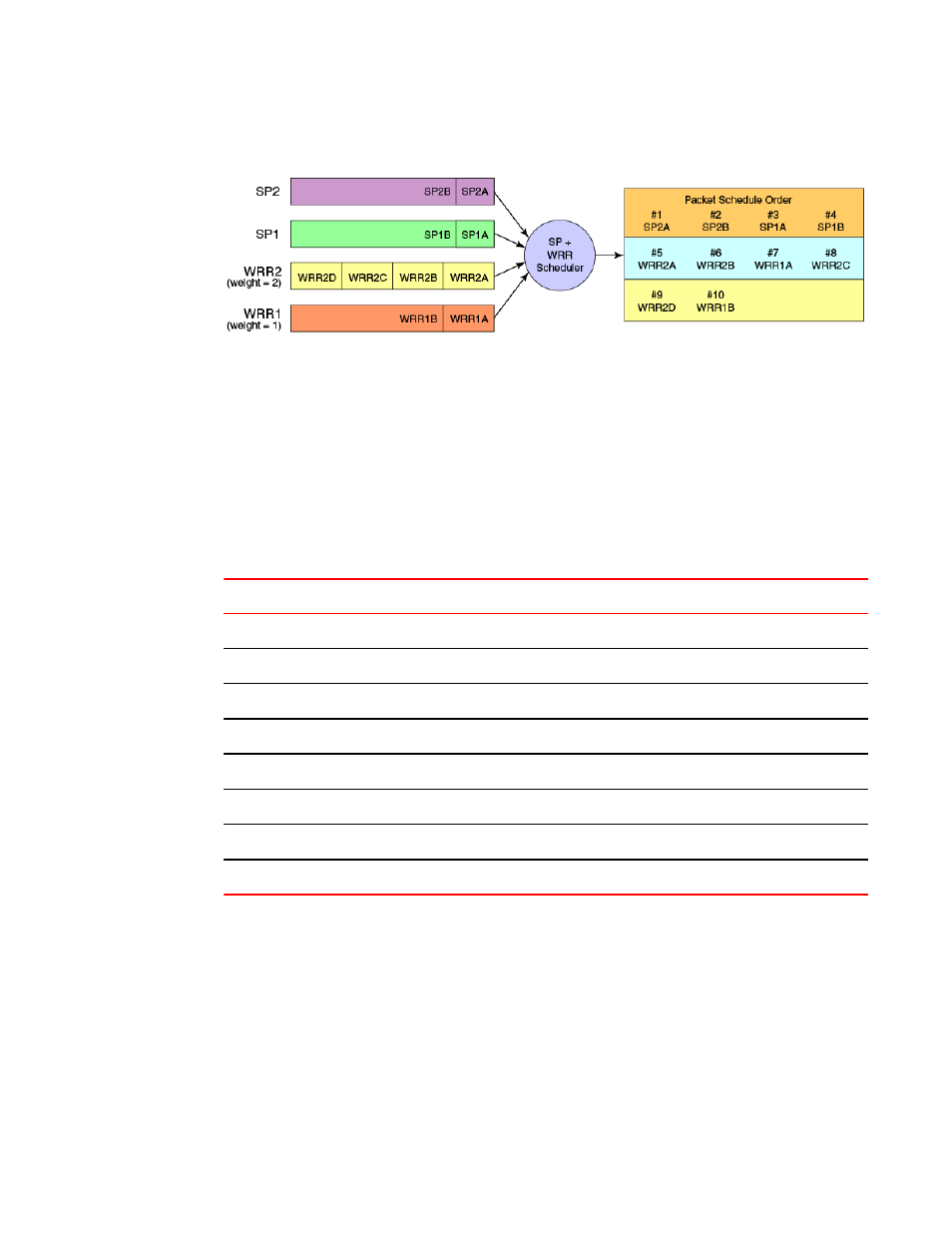
FIGURE 55 Strict priority and Weighted Round Robin scheduler
Multicast queue scheduling
The multicast traffic classes are numbered from 0 to 7; higher numbered traffic classes are considered
higher priority. A fixed mapping from multicast traffic class to equivalent unicast traffic class is applied to
select the queue scheduling behavior. The Multicast traffic class equivalence mapping table below
presents the multicast traffic class with the equivalence mapping applied.
Once the multicast traffic class equivalence mapping has been applied, then scheduling and any
scheduler configuration are inherited from the equivalent unicast traffic class. Refer to the table below
for details on exact mapping equivalencies.
Multicast traffic class equivalence mapping
TABLE 78
Multicast traffic class
Equivalent unicast traffic class
0
0
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
Unicast ingress and egress queueing utilizes a hybrid scheduler that simultaneously supports SP+WRR
service and multiple physical queues with the same service level. Multicast adds additional multicast
expansion queues. Because multicast traffic classes are equivalent to unicast service levels, they are
treated exactly as their equivalent unicast service policies.
Data Center Bridging QoS
Data Center Bridging (DCB) QoS covers frame classification, priority and traffic class (queue) mapping,
congestion control, and scheduling. Under the DCB provisioning model, all of these features are
configured on the basis of two configuration tables, Priority Group Table and Priority Table.
Multicast queue scheduling
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
479
53-1003225-04
