How eld detects loops – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 321
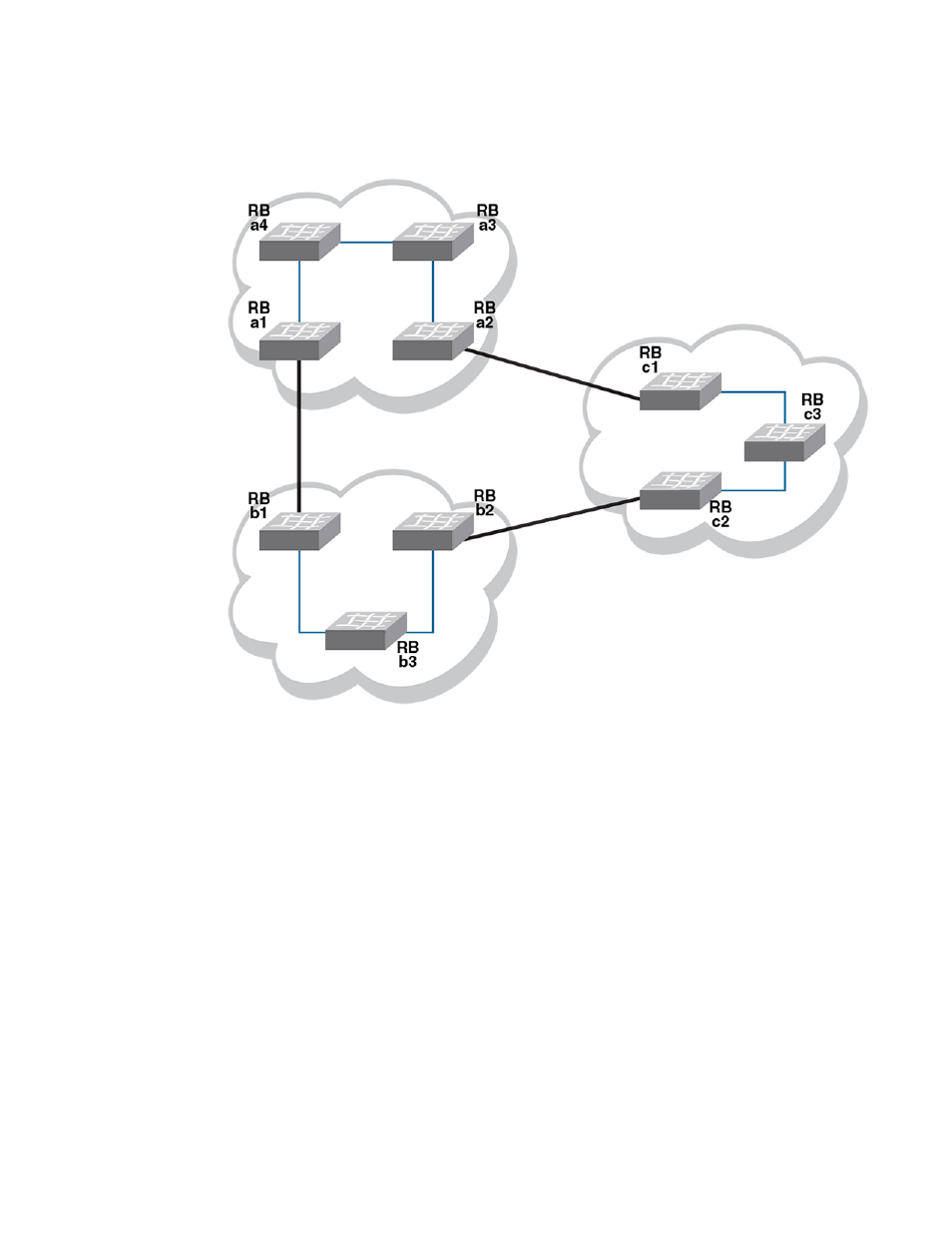
FIGURE 38 Interconnected Brocade VCS Fabric clusters cause loop
How ELD detects loops
ELD works by multicasting Protocol Data Unit (PDU) packets on edge ports. A device recognizes a loop
when it receives a PDU that it initiated. Once the device recognizes that a Layer 2 loop exists, it can
take action to disable a port and break the Layer 2 loop.
To minimize the number of disabled ports, ELD assigns a priority to each port and a unique receive limit
(pdu-rx-limit) to each Brocade VCS Fabric cluster. The port priority determines whether the sending or
receiving edge port of the cluster is disabled. The pdu-rx-limit determines on which Brocade VCS Fabric
the action takes place. Without these configured values, it is possible that a Layer 2 loop could be
detected in multiple clusters at the same time. As a result, multiple ports would be disabled, stopping
traffic among the Brocade VCS Fabric clusters.
The following figure shows the same interconnections as the previous figure under
on page 319, but with ELD enabled on each edge port, and with port priorities and receive
limits assigned.
How ELD detects loops
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
321
53-1003225-04
- ICX 6650 Hardware Installation Guide (98 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Administration Guide (362 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Feature and RFC Support Matrix (66 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Traffic Management Guide (100 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Stacking Configuration Guide (160 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Software Upgrade Guide (121 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Software Licensing Guide (58 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Security Configuration Guide (396 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Platform and Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide (454 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide (672 pages)
- FastIron Ethernet Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide (230 pages)
- FastIron SX, FCX, and ICX Diagnostic Reference (222 pages)
- ICX 7750 Hardware Installation Guide (80 pages)
- Network OS YANG Reference Manual v4.1.1 (238 pages)
- Network OS Software Licensing Guide v4.1.0 (34 pages)
- Network OS NETCONF Operations Guide v4.1.1 (622 pages)
- Network OS Message Reference v4.1.1 (478 pages)
- Network OS Feature and RFC Support Matrix (16 pages)
- Network OS Command Reference v4.1.0 (1418 pages)
- Mid-Mount Rack Kit (Switch) Installation Procedure (Supporting 300, 5100, 5300, 6505, 6510, 6520, 7800, 8000, VA-40FC, VDX 6710-54, and VDX 6740) (10 pages)
- Flush Mount Rack Kit Installation Procedure (Supporting VDX 6710-54, VDX 6720-24, VDX 6720-60, VDX 6730-32, VDX 6730-76, and VDX 6740) (10 pages)
- VDX 6710-54 QuickStart Guide (12 pages)
- VDX 6710-54 Hardware Reference Manual (72 pages)
- VDX 6730 Hardware Reference Manual (Supporting VDX 6730-32 and VDX 6730-76) (90 pages)
- VDX 6730 QuickStart Guide (Supporting VDX 6730-32 and VDX 6730-76) (12 pages)
- Fixed Rack Mount Kit Installation Procedure (Supporting 300, 5100, 5300, 6520, 7800, 8000) (12 pages)
- VDX 8770-8 Two-Post Flush and Mid-Mount Rack Kit Installation Procedure (8 pages)
- VDX 8770-8 QuickStart Guide (34 pages)
- VDX 8770-8 Hardware Reference Manual (136 pages)
- VDX 8770-8 Four-Post Flush and Recessed Mount Rack Kit Installation Procedure (10 pages)
- VDX 8770-4 Two-Post Flush and Mid-Mount Rack Kit Installation Procedure (10 pages)
- VDX 8770-4 QuickStart Guide (32 pages)
- VDX 8770-4 Hardware Reference Manual (132 pages)
- VDX 8770-4 Four-Post Flush Mount Rack Kit Installation Procedure (8 pages)
- VDX 8770-4 Four-Post Flush and Recessed Mount Intake Air Duct Rack Kit Installation Procedure (24 pages)
- VDX 6740 Hardware Reference Manual (Supporting VDX 6740, VDX 6740T, and VDX 6740T-1G) (78 pages)
- Universal Four Post Rack Kit Installation Procedure (Supporting VDX 6740T) (20 pages)
- Universal Two-Post Rack Kit Installation Procedure (Supporting VDX 6740T) (12 pages)
- FCX Series Hardware Installation Guide (112 pages)
- 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference (102 pages)
- 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Hardware Installation Guide (84 pages)
- 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Diagnostic Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) (88 pages)
- 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide (Supporting R2.2.0.0) (1240 pages)
- Unified IP MIB Reference (Supporting Multi-Service IronWare Release 05.6.00a) (771 pages)
