Switch connection control (scc) policy – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 304
the local device may authenticate. Every device may share a secret key pair with any other device or
host in a fabric.
Shared secret keys have the following characteristics:
• The shared secrets must be configured locally on every device.
• If shared secrets are not set up for a link, authentication fails. The "Authentication Failed" error is
reported for the port.
• The minimum length of a shared secret is 8 bytes and the maximum 40 bytes.
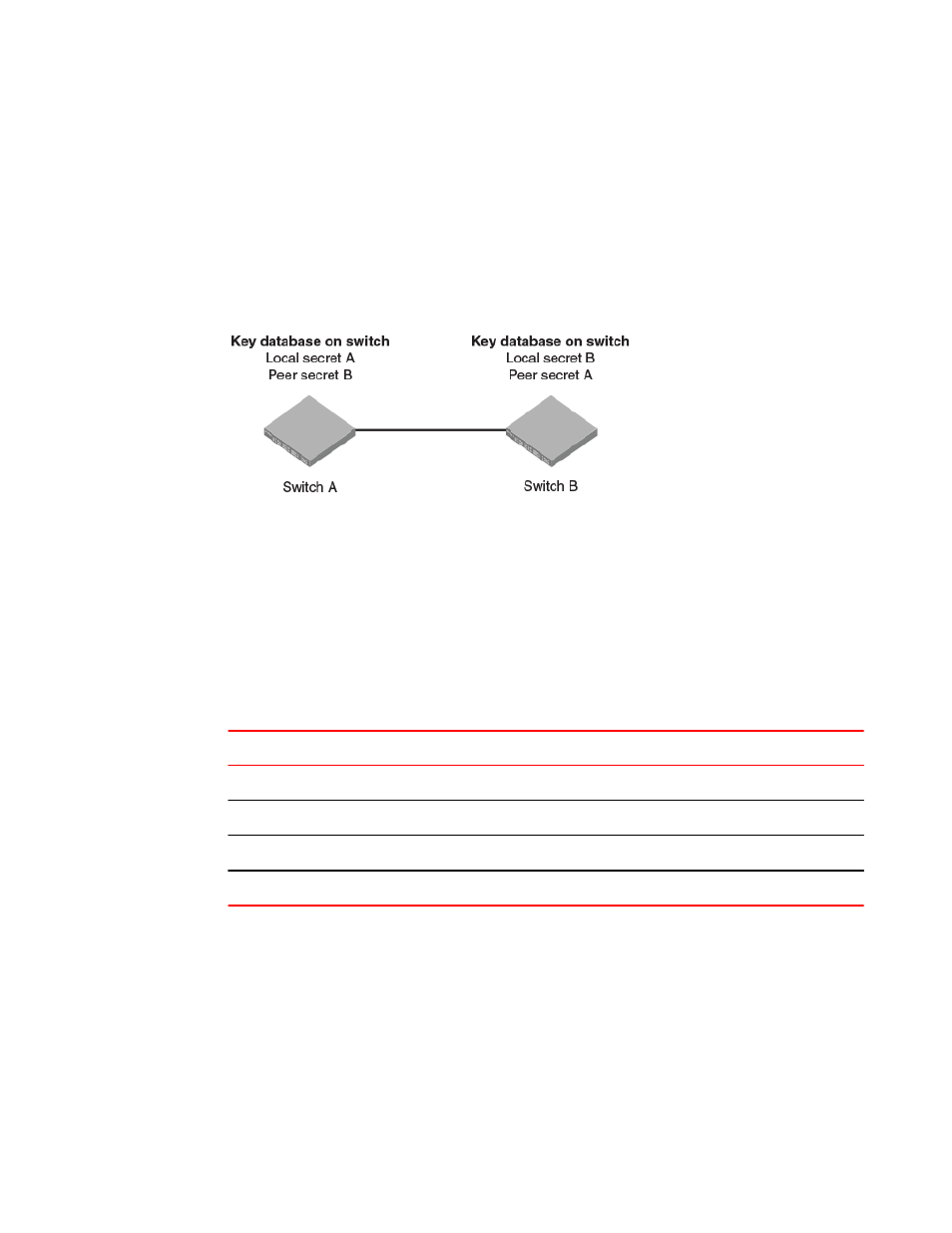
FIGURE 36 DH-CHAP authentication
The preceding figure illustrates how the secrets are configured. Assume two devices, A and B. Each
device has a local secret (local secret A and local secret B), and a matching peer secret (peer secret A
and peer secret B). If device B wants to shake hands with A, it will use A’s local secret (B's peer secret
A) to send the information. In doing so, A authenticates B by confirming its identity through the
exchange of matching secret pairs. Conversely, B authenticates A when A sends information to B
using B's local secret (A's peer secret B).
On the FC router, the authentication configuration for EX_Ports is set to fixed default values and
cannot be changed. The Fabric OS authutil command is applicable only to the E_Ports on the FC
router, not to EX_Ports. The following table shows the default authentication configuration for
EX_Ports:
Default EX_Port configuration
TABLE 52
Operand
Value
Auth-type
DHCHAP
Auth-Policy
PASSIVE
Auth-Group
* (0, 1, 2, 3, 4)
Auth-Hash
msd5, sha1
Switch connection control (SCC) policy
The Switch Connection Control (SCC) policy controls access between neighboring devices. The policy
defines and restricts which devices can join the fabric. Each time an E_Port-to-EX_Port connection is
attempted, the devices are checked against the policy and the connection is either accepted or
rejected depending on whether the connecting device is listed in the policy. The policy is named
SCC_POLICY and accepts members listed as world wide names (WWNs).
A device configured with an active SCC policy reviews its database whenever a neighboring device
tries to establish a connection. If the WWN of the connecting device is found in the SCC active policy
Switch connection control (SCC) policy
304
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
53-1003225-04
