Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 383
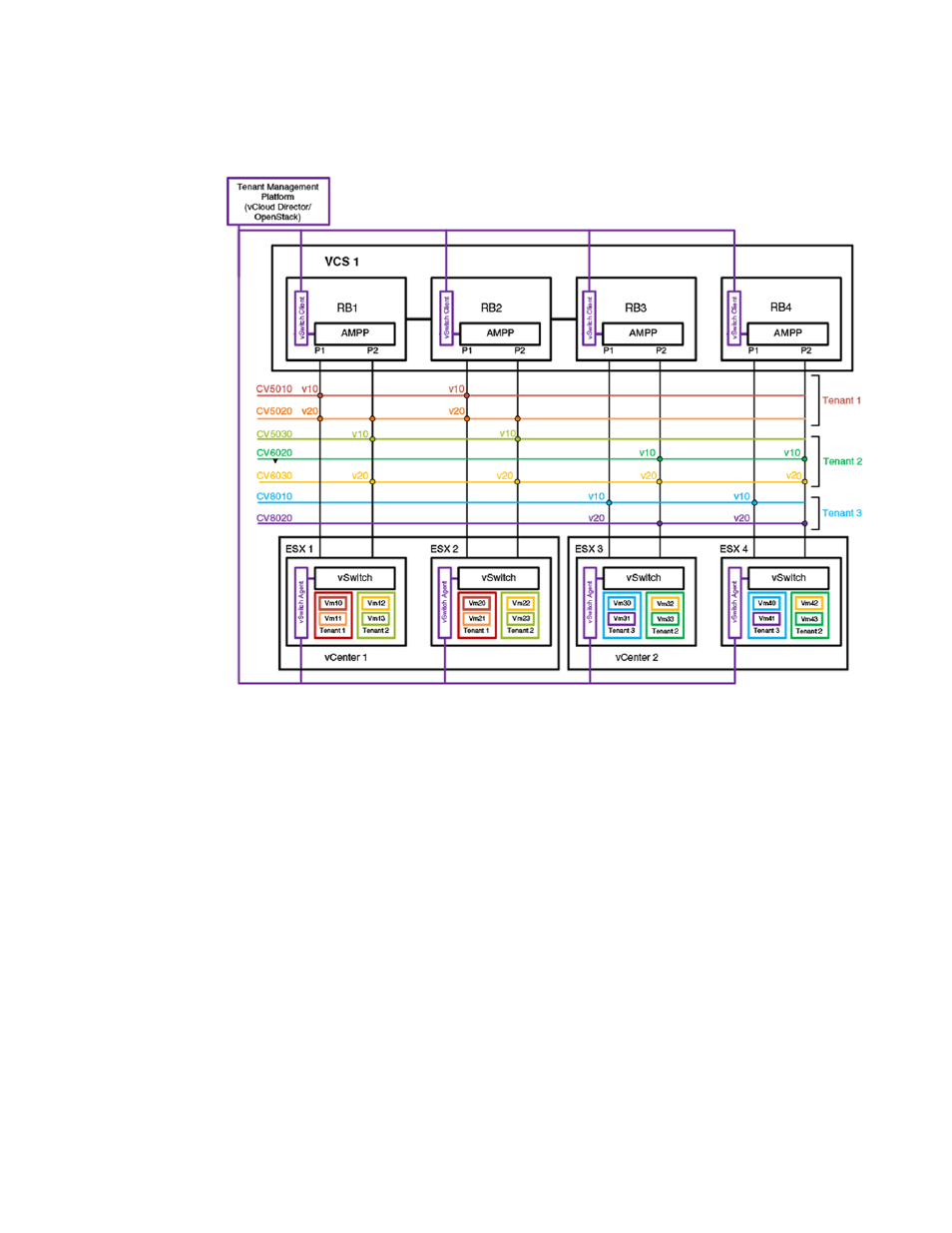
FIGURE 46 VDC infrastructure
In a VMware-based cloud provider network, a VCS Fabric is connected to multiple vCenters, where
each data center manages its own set of tenant networks. VMware vCloud/OpenStack is responsible for
orchestrating tenant VLAN configuration through the vCenter agent integrated into a VCS RBridge and
its ESXi servers. Each data center connects to the VCS Fabric by means of dedicated edge ports. The
ability of the VCS Fabric to support 802.1Q VLAN virtualization allows each data center to support more
than 4000 tenant VLANs. ESXi servers may use the same 802.1Q VLAN to represent different tenant
VLANs at the edge port, or have them belong to a single VLAN domain. A vCenter agent running at an
RBridge achieves VLAN virtualization by collating information obtained from the ESXi servers and the
vCenter database. AMPP port profiles with service VF classifications are configured on the respective
server ports.
The topology above shows two vCenters. vCenter1 is connected to VCS RBridges1 and2. Because the
VCS Fabric supports VLAN virtualization, the vCenter can assign two tenant networks, CV5010 and
CV5030, that use the same 802.1Q VLAN (VLAN 10) on the ESXi server. Similarly, in vCenter2, three
tenant VLANs —CV5030, CV6020, and CV8010— are configured, each representing a unique VLAN
domain, but all using the same customer classification, C-TAG 10. If a VM application needs to run
across applications, then the same service VF can be configured on both vCenters; this is illustrated by
CV6030, which is configured at all RBridges and uses the same C-TAG (C-TAG 20).
The service VF configuration at each edge port can be done as part of an AMPP configuration or
automatically through vCenter orchestration. (Refer to VMware documentation for details of the vCenter
Orchestrator.)
Configuring Virtual Fabrics
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
383
53-1003225-04
