Ampp provisioning with service vfs – Brocade Network OS Administrator’s Guide v4.1.1 User Manual
Page 384
AMPP provisioning with service VFs
When the Automatic Migration of Port Profiles (AMPP) feature is used in Network OS 4.1.0 and later, a
VCS Fabric is partitioned into port-profile (PP) domains. A PP domain is a set of port-profiles whose
service VF ID cannot have conflicting C-TAG or MAC classifications. A port-profile domain supports a
maximum of 4096 service VFs. The scope of VM mobility is defined by the set of interfaces onto which
the port-profile domain is applied.
Port-profile domain topology
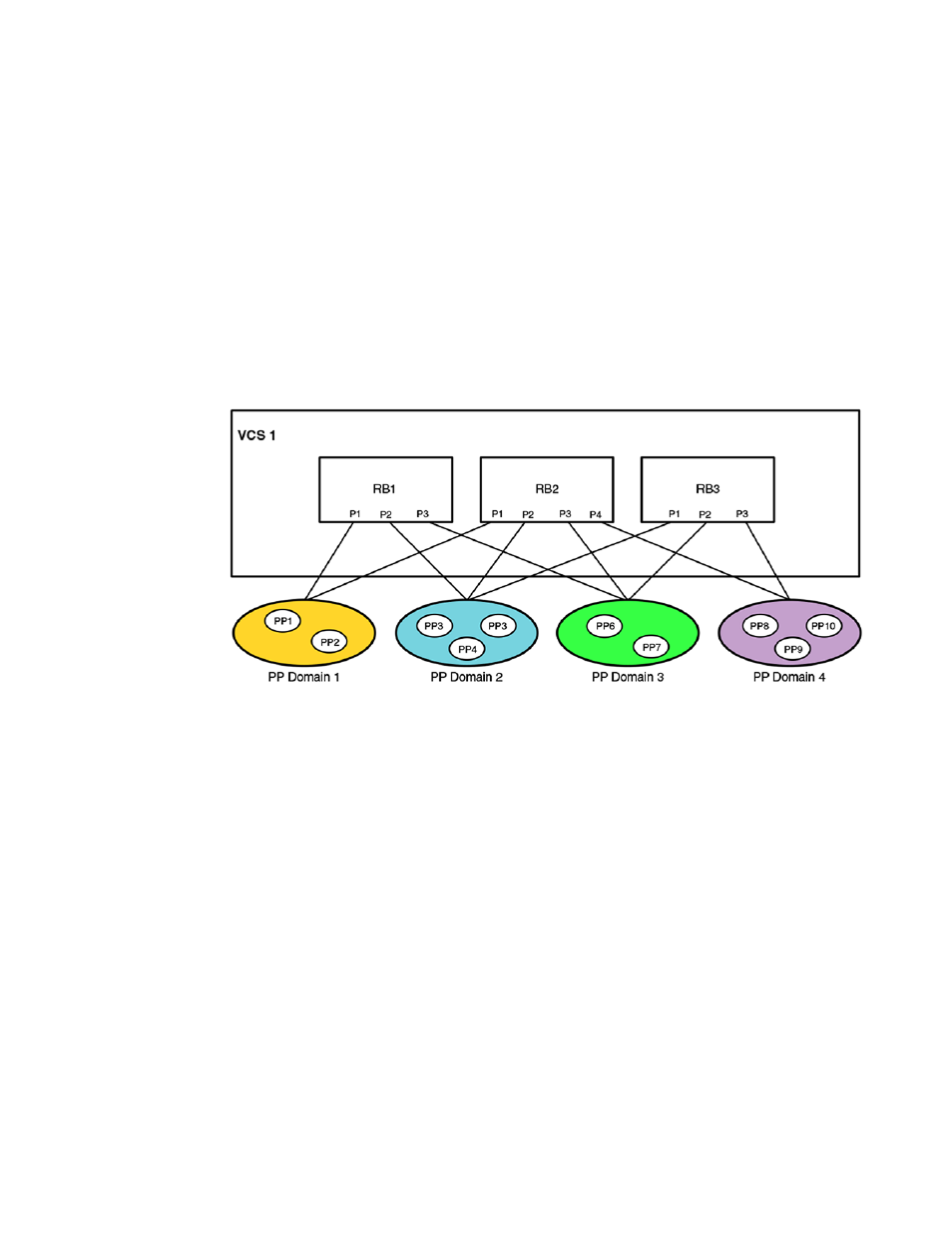
The following illustrates an example VCS Fabric that serves four port-profile domains across three
RBridges.
FIGURE 47 Port-profile domains
Port-profile configuration rules
The VLAN classifications in a port-profile domain follow these rules:
1. Each profiled-port is associated with a PP domain. Different profiled-ports (on the same RBridge)
may belong to different domains.
2. The same port-profile may be associated with multiple domains.
a.
This allows a service VF that is defined in one domain to extend into another domain.
b.
The VM MAC address must be unique within a domain.
3. The service VF classification rules within a domain are as follows:
a.
MAC-based classification is allowed only on an access port.
b.
C-TAG classification is allowed only on a trunk port
c.
Service VF classification cannot overlap across port-profiles in the same PP domain.
d.
Classification can overlap across PP domains.
4. The following example configurations are allowed for classification across all port-profiles in the
same domain:
a.
switchport trunk allow vlan add 5000 ctag 10
b.
switchport trunk allow vlan add 6000 ctag 20
c.
switchport trunk allow vlan add 7000 ctag 30
5. The following example configurations are allowed for MAC-based classification on an access port:
AMPP provisioning with service VFs
384
Network OS Administrator’s Guide
53-1003225-04
