Table 6.1 scripts instructions, Scripts instructions – Avago Technologies LSI8751D User Manual
Page 198
6-2
Instruction Set of the I/O Processor
boundary since all SCRIPTS are 8 or 12 bytes long. Instructions are
fetched until an interrupt instruction is encountered, or until an
unexpected event (such as a hardware error) causes an interrupt to the
external processor.
Once an interrupt is generated, the LSI53C875 halts all operations until
the interrupt is serviced. Then, the start address of the next SCRIPTS
instruction may be written to the
register
to restart the automatic fetching and execution of instructions.
The SCSI SCRIPTS mode of execution allows the LSI53C875 to make
decisions based on the status of the SCSI bus, which offloads the
microprocessor from servicing the numerous interrupts inherent in I/O
operations.
Given the rich set of SCSI oriented features included in the instruction
set, and the ability to re-enter the SCSI algorithm at any point, this high
level interface is all that is required for both normal and exception
conditions. Switching to low level mode for error recovery should never
be required.
The following types of SCRIPTS instructions are implemented in the
LSI53C875 as shown in
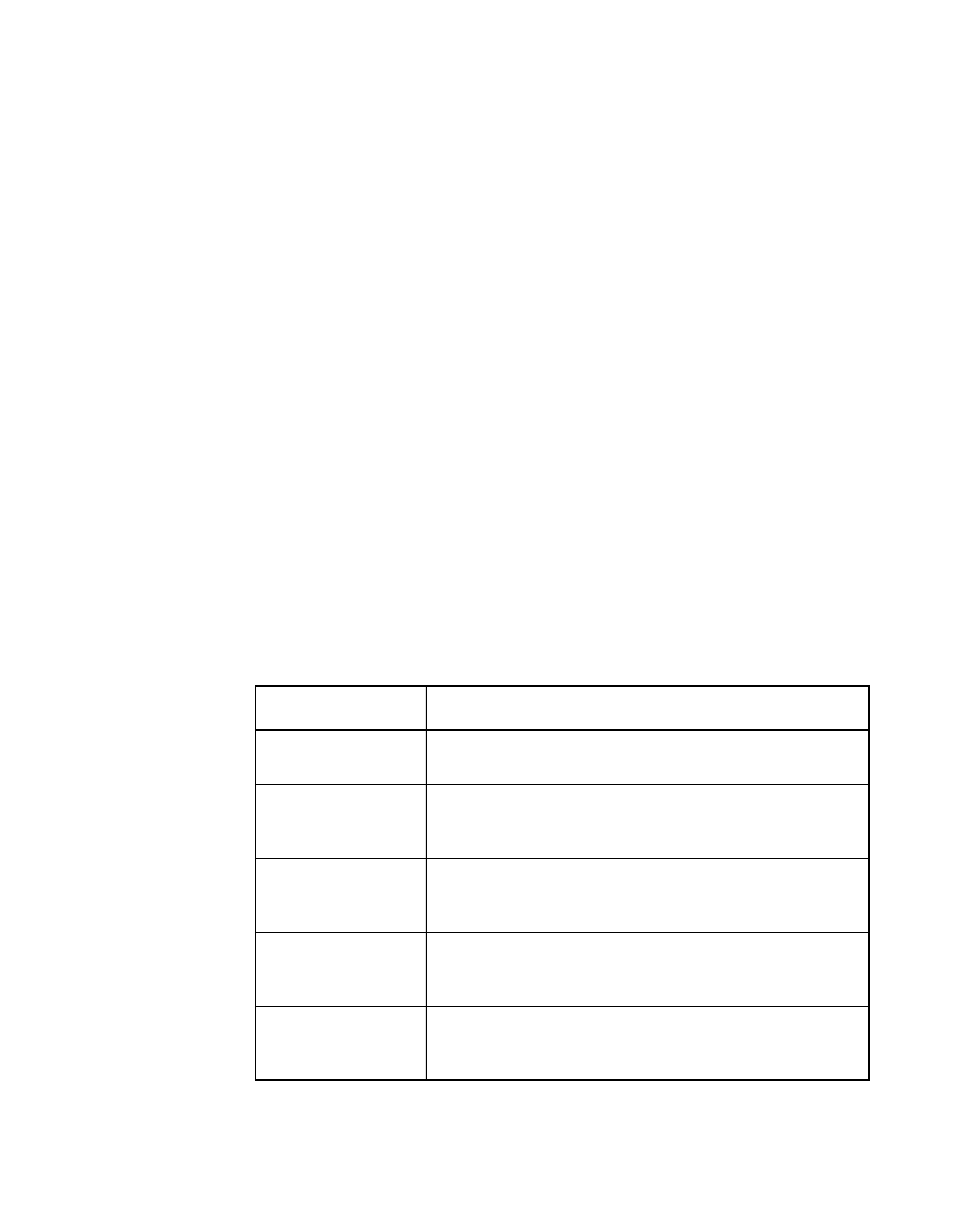
Table 6.1
SCRIPTS Instructions
Instruction
Description
Block Move
Block Move instruction moves data between the SCSI
bus and memory.
I/O or Read/Write
I/O or Read/Write instructions cause the LSI53C875 to
trigger common SCSI hardware sequences, or to move
registers.
Transfer Control
Transfer Control instruction allows SCRIPTS instructions
to make decisions based on real time SCSI bus
conditions.
Memory Move
Memory Move instruction causes the LSI53C875 to
execute block moves between different parts of main
memory.
Load and Store
Load and Store instructions provide a more efficient way
to move data to/from memory from/to an internal register
in the chip without using the Memory Move instruction.
