4 3-axis linear interpolation control, Melsec-q, Operation chart – MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC Mitsubishi Programmable Logic Controller QD75D User Manual
Page 333
9 - 33
MELSEC-Q
9 MAJOR POSITIONING CONTROL
9.2.4 3-axis linear interpolation control
In "3-axis linear interpolation control" (" Da.2 Control system" = ABS linear 3, INC
linear 3), three motors are used to carry out position control in a linear path while
carrying out interpolation for the axis directions set in each axis.
(Refer to Section 9.1.6 "Interpolation control" for details on interpolation control.)
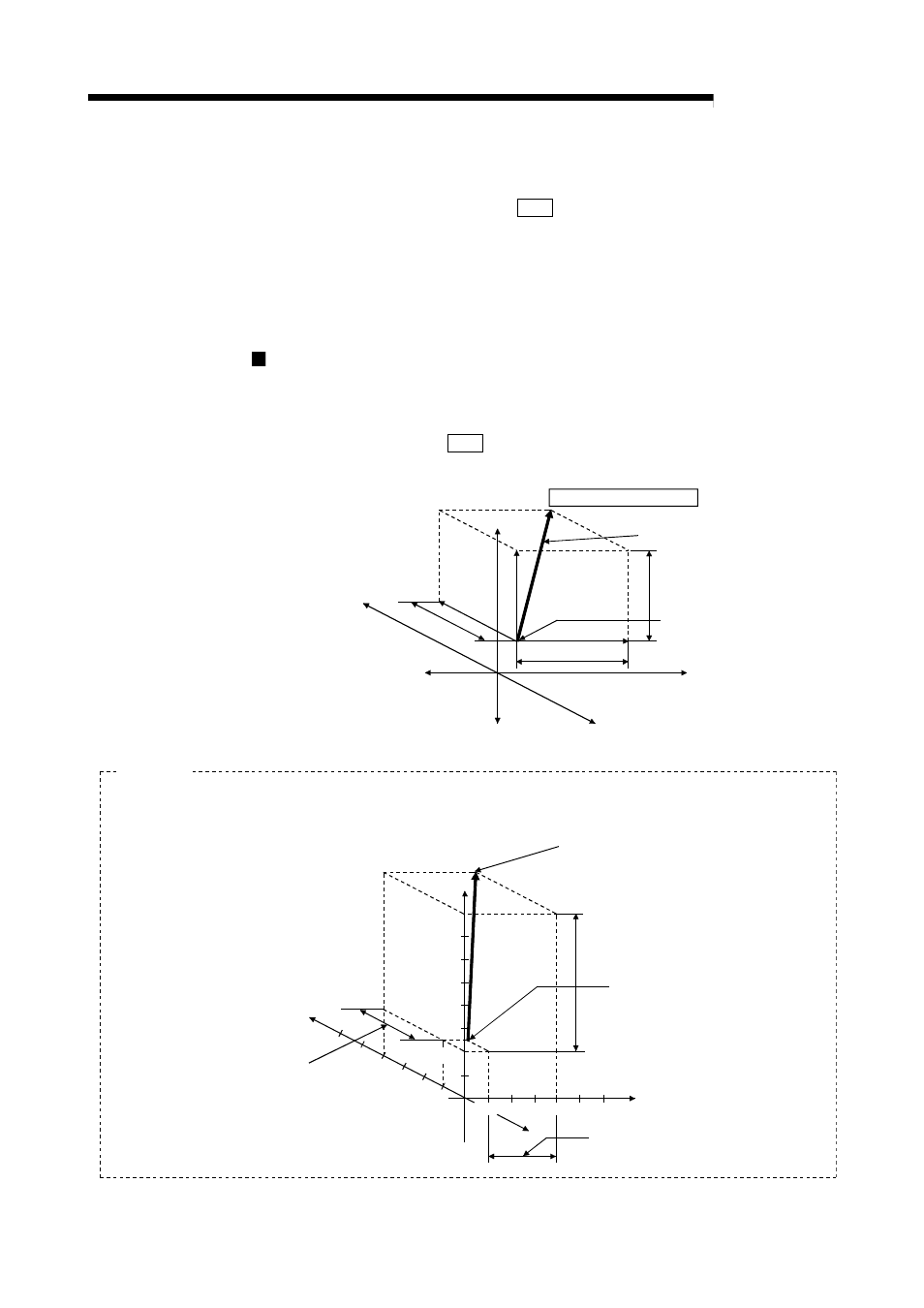
[1] 3-axis linear interpolation control (ABS linear 3)
Operation chart
In the absolute system 3-axis linear control, using an address established by a
machine OPR in the 3-axis coordinate space, a linear interpolation positioning is
carried out from the current stop position (start point address) to the address (end
point address) set in the " Da.6 Positioning address/movement amount".
End point address (X
2
,Y
2,
Z
2
)
(Positioning address)
Movement by linear interpolation
of the X axis, Y axis and Z axis
Y axis movement amount
Start point address (X
1
,Y
1
,Z
1
)
(Current stop position)
Forward direction (X axis)
Forward direction (Z axis)
Reverse direction
Forward direction
(Y axis)
X axis movement amount
Z ax
is m
ove
men
t am
ou
nt
Reverse direction Reverse direction
End point address
(positioning address)
Axis 2 movement amount (8000-2000=6000)
Start point address
(current stop position)
Axis 1
Axis 3
Axis 2
8000
Axis 3 movement amount
(4000-1000=3000)
4000
2000
1000
1000
0
4000
Axis 1 movement amount
(4000-1000=3000)
Example
When the start point address (current stop positon) is (1000, 2000, 1000) and the end point address
(positioning address) is (4000, 8000, 4000), positioning is carried out as follows.
