Rockwell Automation 5370-CVIM2 Module User Manual
Page 380
Chapter 7
Inspection Tools
7–142
The first element in the formula is “
avg(
” from the
Stats. Functions
panel;
the second element is “
{Tool 1.Area#}
” from the
Results
panel; and the
third element is a closing parenthesis from the keyboard. Thus, the complete
formula appears as follows:
avg({Tool 1.Area#})
When the
Nominal
field in the math tool
Edit
panel is picked, it displays the
average area of the 12 objects.
Example: Using Formulas to Perform Complex Inspections
Some inspection decisions require more than using only the results data from
inspection tools as the direct basis for the decision. For some application
situations, results data from multiple tools, and from a previous math tool,
may be usefully employed in a second math tool. Figure 7.111 illustrates
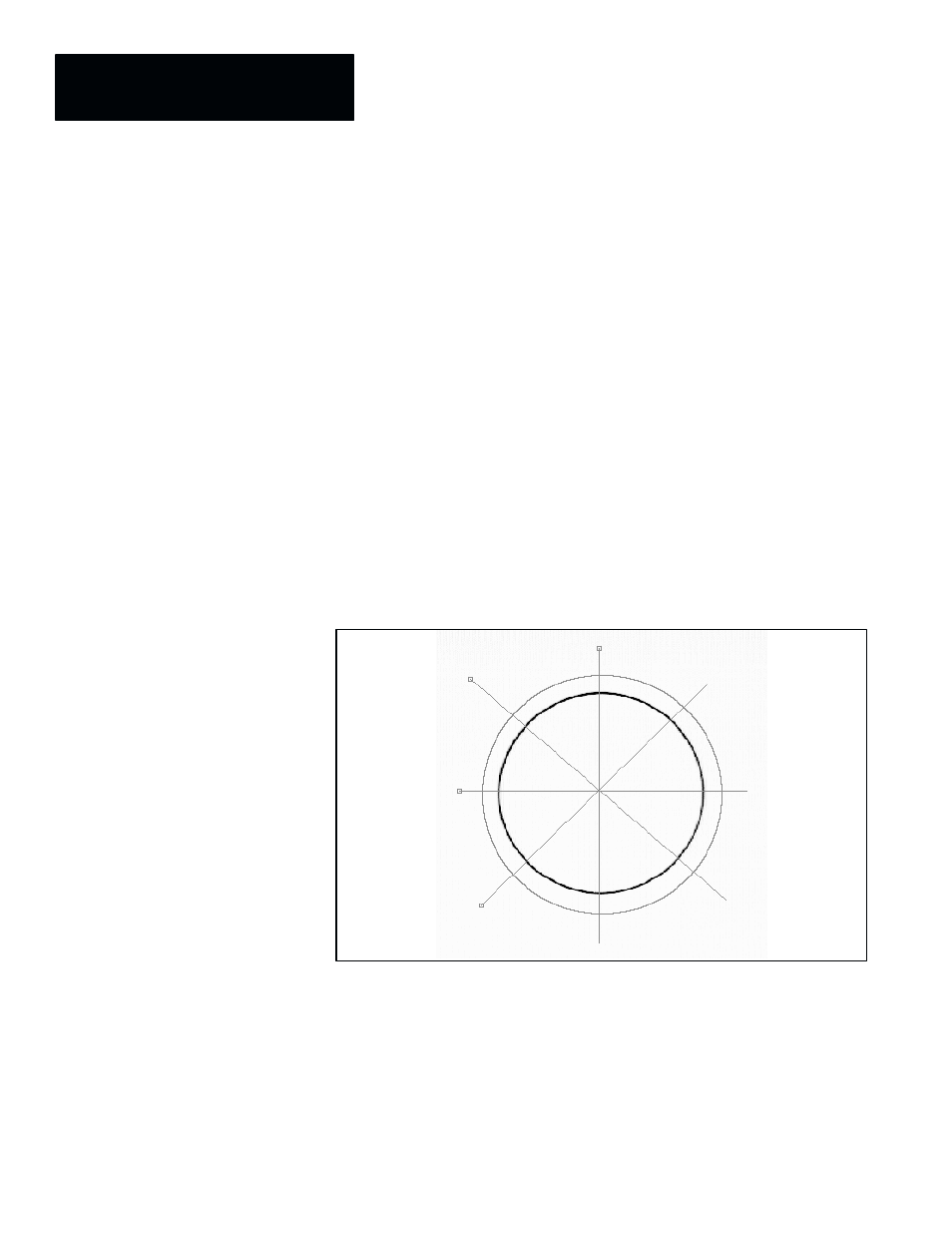
using four gages and window to measure a circular workpiece.
Figure 7.111 Example: Four Gage Tools and One Window Tool Configured to Measure
Workpiece
In this example, the four gages measure the diameter of the circular object,
and the window measures its area. The gages all have their
Fail High
and
Fail Low
range limits set to 10.5 and 9.5, respectively.
The first formula evaluates the “pass” result of each gage (which yields a
logic “1” for pass, and a logic “0” for fail), then adds the logic results. Thus,
if all four gages pass, the math tool result is 4.000, the sum of the four logic
“1” results. This formula is set up on the formula entry keyboard as shown in
Figure 7.112 (page 7–143).
