Math tool formula examples – Rockwell Automation 5370-CVIM2 Module User Manual
Page 375
5
Chapter
Chapter 7
Inspection Tools
7–137
This section contains several examples that demonstrate some of the methods
of using math tool formulas.
Example: ATN2 Function
Since the “
atan2
” (arc tangent “2”) function returns an angle whose value
and sign identifies the quadrant in which the angle is located, as shown in
Figure 7.96 (page 7–123), it can be used to indicate the angle of rotation of a
line in the image, where 0
° is at the 3 o’clock position, as shown by the
example in Figure 7.103.
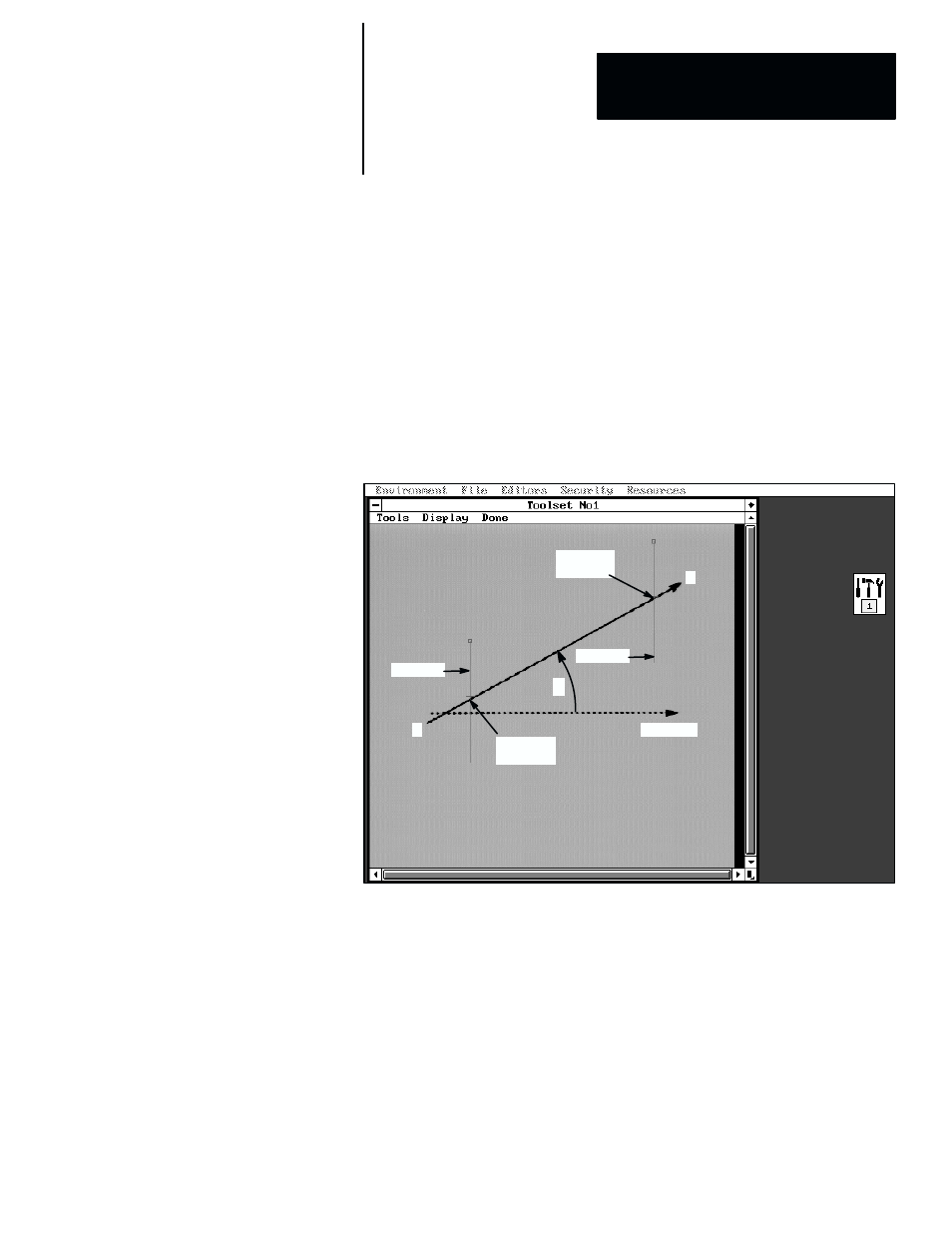
Figure 7.103 Example: Two Gages Configured for Use in ATN2 Function
A
B
0
° Axis
Gage 1
Gage 2
X = 141
Y = 227
X = 398
Y = 86
q
In the example, line A–B is rotated clockwise from the 0
° axis of the image.
Two gage tools are used to determine the X–axis and Y–axis coordinates of
two points (edges) along line A–B. The coordinates of the Gage 1 edge are X
= 141 and Y = 227, while the coordinates of the Gage 2 edge are X = 398
and Y = 86.
The
atan2(Y,X)
function uses positive or negative values along the Y–axis
and X–axis in order to calculate an angle (and its quadrant). In the example
above, these Y and X values are derived from the changes in the values of Y
and X between Gage 1 and Gage 2; thus, the change in Y is from 227 (Gage
1) to 86 (Gage 2), or –141, while the change in X is from 141 (Gage 1) to
398 (Gage 2), or +257.
Math Tool Formula
Examples
