Rockwell Automation 5370-CVIM2 Module User Manual
Page 376
Chapter 7
Inspection Tools
7–138
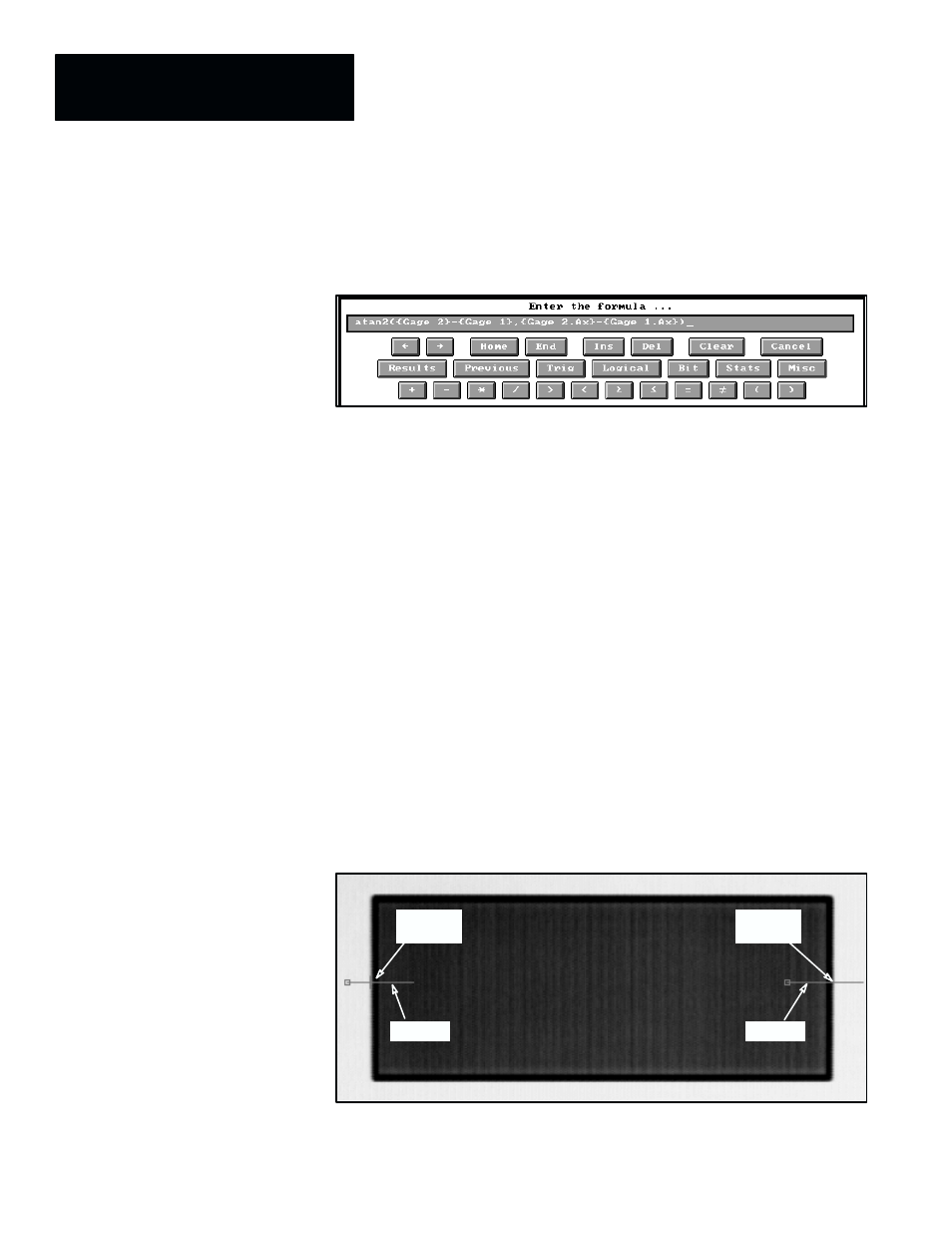
The X and Y values are derived in a formula that is set up on the formula
entry keyboard as shown in Figure 7.104.
Figure 7.104 Example: Using the ATN2 Function in a Math Tool Formula
In this formula, inspection results from Gage 1 and Gage 2 are used. Since
these gages are both configured for the
Y Position
operation, the primary
results are the Y–axis coordinate values. Thus,
{Gage 2}–{Gage 1}
is
evaluated as 86 – 227, which is –141. The secondary results are the X–axis
coordinate values. Thus,
{Gage 2.Ax}–{Gage 1.Ax}
is evaluated as 398 –
141, which is +257. (In effect, this formula operates as though it were set up
using the constants –141 and +257, as in
atan2(–141,257)
, which calculates
the angle as –28.751
°.)
With the formula set up as shown in Figure 7.104, when you pick the
Nominal
field in the math tool edit panel, the system performs one “test”
operation of the formula and returns an angle of
–
28.603
°.
Example: DST Function
The “
dst
” (distance) function returns the distance, in pixels, from one point
to another in the image, using the X– and Y–axis coordinates of each point to
perform a calculation based on the Pythagorean theorem. Figure 7.105
provides an example that demonstrates its use in a formula.
Figure 7.105 Example: Two Gages Configured for Use in DST Function
Gage 1
Gage 2
X = 478
Y = 246
X = 33
Y = 246
