Incremental compilation, Avalon-mm interface – Altera IP Compiler for PCI Express User Manual
Page 66
4–8
Chapter 4: IP Core Architecture
Application Interfaces
IP Compiler for PCI Express User Guide
August 2014
Altera Corporation
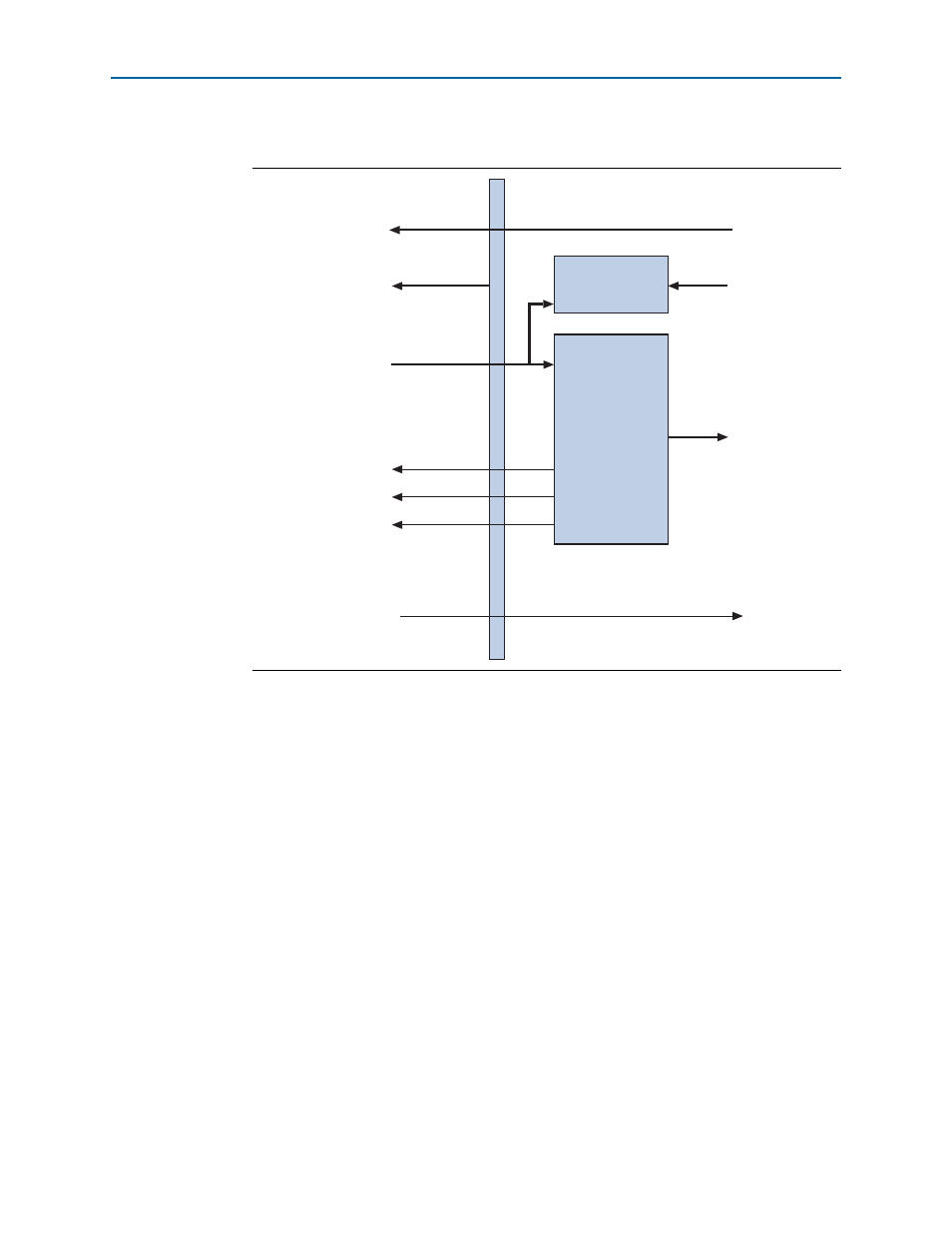
illustrates the Avalon-ST TX and MSI datapaths.
Incremental Compilation
The IP core with Avalon-ST interface includes a fully registered interface between the
user application and the PCI Express transaction layer. For the soft IP implementation,
you can use incremental compilation to lock down the placement and routing of the
IP Compiler for PCI Express with the Avalon-ST interface to preserve placement and
timing while changes are made to your application.
1
Incremental recompilation is not necessary for the PCI Express hard IP
implementation. This implementation is fixed. All signals in the hard IP
implementation are fully registered.
Avalon-MM Interface
IP Compiler for PCI Express variations generated in the Qsys design flow are PCI
Express Avalon-MM bridges: PCI Express endpoints with an Avalon-MM interface to
the application layer. The hard IP implementation of the PHYMAC and data link
layers communicates with a soft IP implementation of the transaction layer optimized
for the Avalon-MM protocol.
Figure 4–5. Avalon-ST TX and MSI Datapaths
FIFO
Buffer
tx_st_data0
app_msi_req
Non-Posted Credits
To Transaction
Layer
To Application
Layer
tx_cred0 for Completion
and Posted Requests
(from Transaction Layter)
tx_cred0 for
Non-Posted Requests
tx_fifo_empty0
tx_fifo_wrptr0
tx_fifo_rdptr0
Registers
