Calculated signals examples, Calculation examples – MTS Series 793 User Manual
Page 362
Calculated Signals Examples
Calculation Examples
This section contains some common uses for calculations.
Calculating Engineering Stress from Force and Area
It is common for materials researchers to calculate "Engineering Stress" from "Force" and initial specimen
cross-sectional area. This calculation simply divides force by a calculation parameter called "Area." Area is
typically a calculation parameter and is constant during the test.
It is possible to constantly recalculate area, either from constants or instantaneously measured values such
as those provided by a diametrical extensometer. Stress calculated from an instantaneously calculated value
of area is called "True Stress."
// calculate "Stress" by dividing "Force" by a calculation parameter "Area"
// or by a calculated signal "Area"
"Stress" = "Force" / "Area";
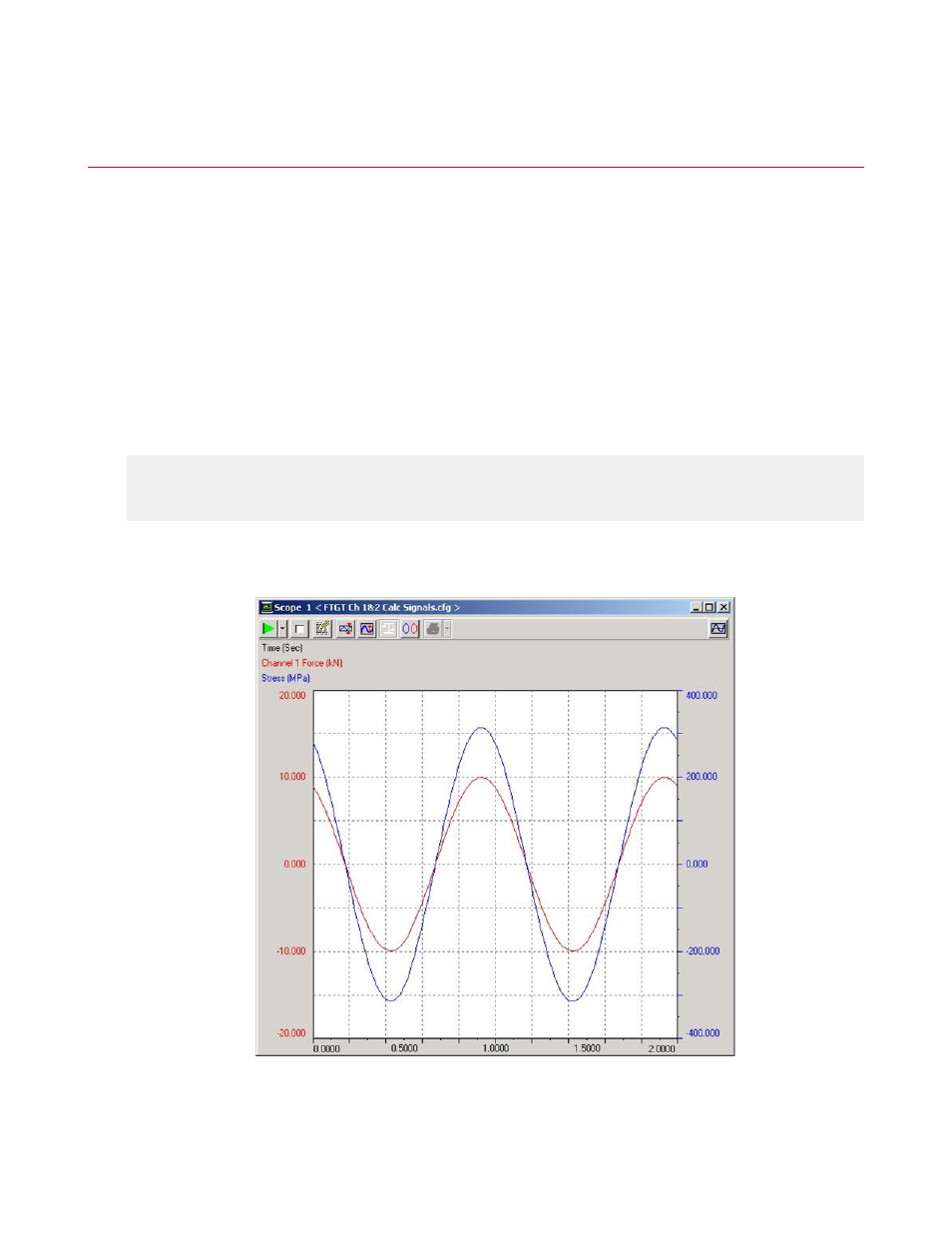
The following plot shows Force and Engineering Stress for a cyclic command with amplitude of 10kN and
mean of 0kN and a constant cross-sectional area of 6.35 mm (0.25 in.) round specimen.
Force and Engineering Stress
362 MTS Series 793 Control Software
Calculated Signals
