5 design, 11 drive dimensioning – Lenze DSD User Manual
Page 330
11
Drive Dimensioning
11.3
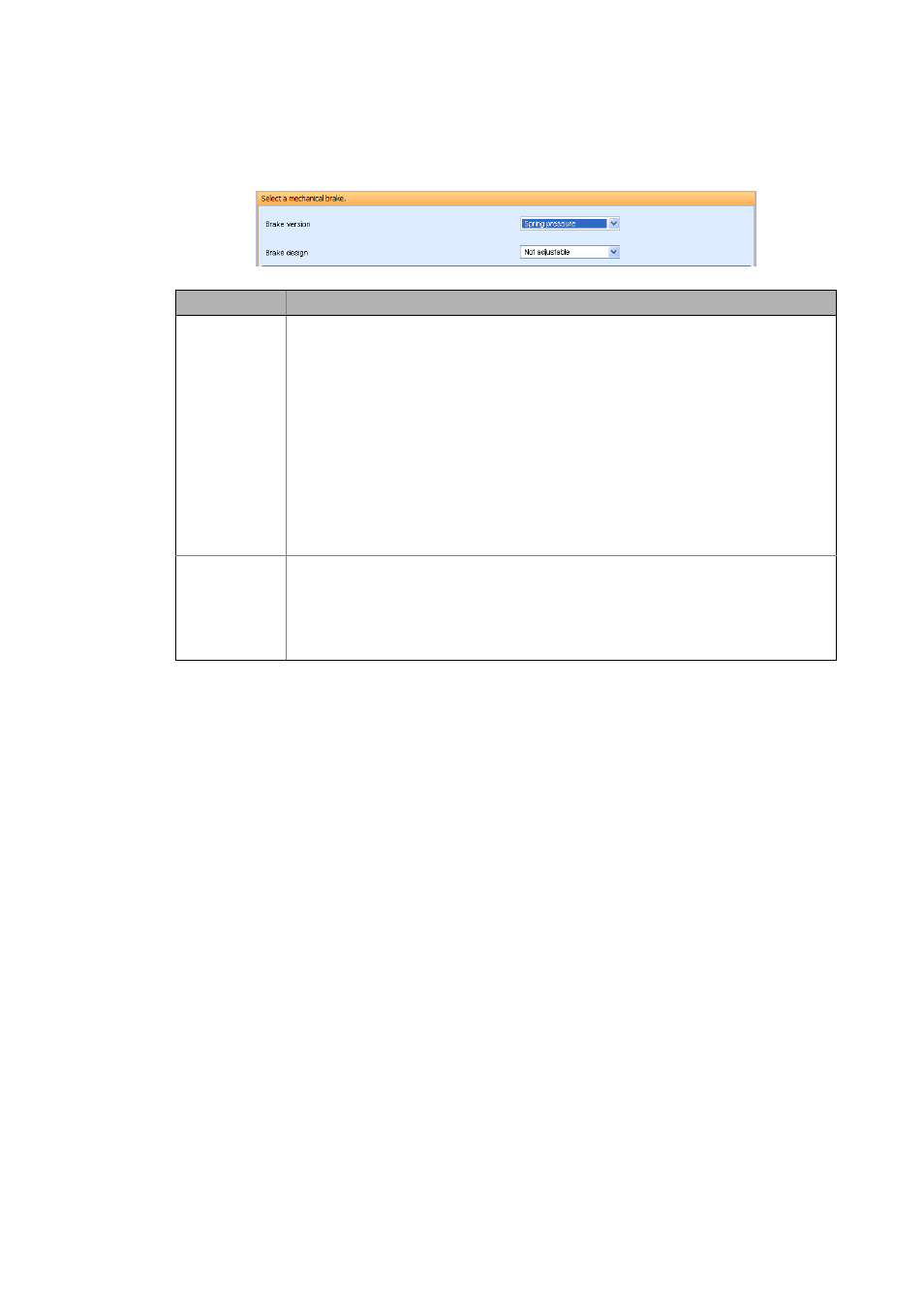
Mechanical brake selection
330
Lenze · Drive Solution Designer · Manual · DMS 4.2 EN · 12/2013 · TD23
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
11.3.5
Design
Parameter
Description
Brake version
Spring pressure
• Single-disk brakes with two friction surfaces. By several compression springs the braking
torque in the deenergised state is generated by means of friction locking. The brake is re-
leased electromagnetically.
Spring pressure, Cold Brake
• Spring-applied brake as Cold-Brake variant. By decreasing the holding current the power in-
put of the open brake is reduced. Since the brake is less heated, this type of control is referred
to as Cold Brake. Also at low speeds, the geared motor can be operated only with an integral
fan. A blower is not required.
Spring pressure, overexcited
• The brake coil is overexcited by activation with twice the rated voltage.
• Advantages: The disengagement time is reduced, the brake releases much faster and the
wear of the friction lining decreases.
• Particularly suitable for hoist applications, hence only available in combination with a
brake with an increased braking torque.
Brake design
Adjustable
• Design E, braking torque can be adjusted (by means of setting ring gauge).
Not adjustable
• Design N, braking torque cannot be adjusted (without setting ring gauge).
Long-life
• Stronger brake mechanics for applications with very high operating frequencies.
