7applications – Lenze DSD User Manual
Page 117
Lenze · Drive Solution Designer · Manual · DMS 4.2 EN · 12/2013 · TD23
117
7
Applications
7.8
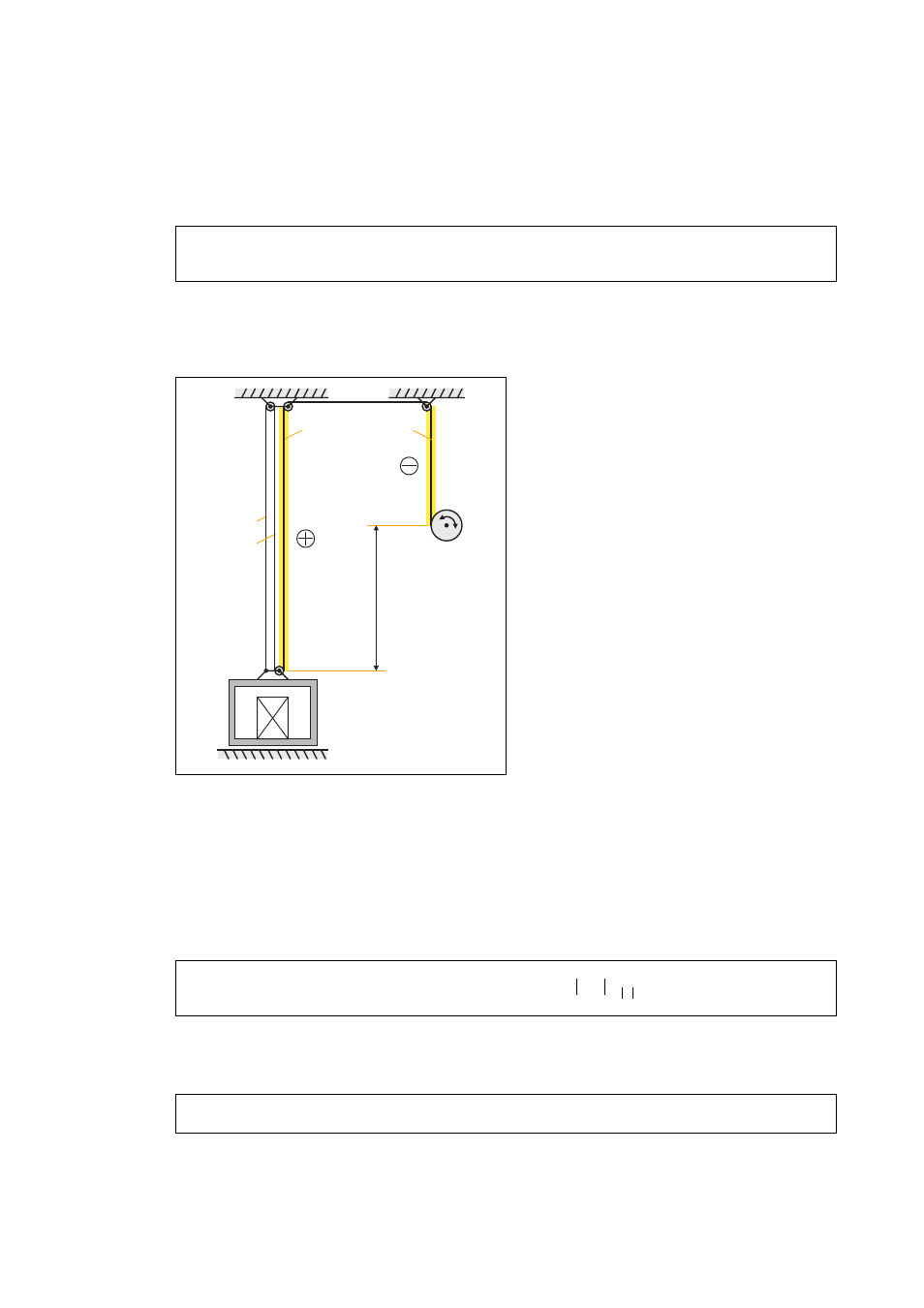
Hoist drive without counterweight
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Ascertainment of the active cable mass
The active cable mass is ascertained by means of the mass calculator (field: cylinder) and is calculat-
ed with the following equation:
[7-87] Equation 11: Active cable mass for the stationary torque
Ascertainment of the height difference
For the stationary torque the maximum height difference Δh is required.
[7-88] Determination of Δh
Torque loss
For including the losses for the hoist the friction torque is calculated from the individual efficiencies.
When carrying out a dimensioning process with a user-definable motion profile, the efficiency for a
travel with the maximum stationary torque is assumed.
• The sign is considered with the fraction n/|n|.
• The following equation calculates the torque loss in generator and motor mode:
[7-89] Equation 12: Torque loss
Torque of the application
[7-90] Equation 14: Torque of the application
m
acv Rop
,
ρ
Rop
Δh 10 π
d
Rop
200
-----------
2
⋅
⋅
⋅ ⋅
=
• The height Δh typically is the height differ-
ence from the winding drum to the cable
end of the payload at the lowest position
of the payload.
• The yellow highlighted cable sections
(+) are decisive for the steady-state
torque.
• The other cable sections (+) cancel
each other out.
Dh
?
?
M
th
1
η
Gdn
η
Pll
η
Cor
⋅
⋅
-----------------------------------------
1
–
max M
sds
(
) nn------
⋅
⋅
=
M
App
M
sds
J
sum
α M
th
+
⋅
+
=
