Manually making a remote table mappable – Pitney Bowes MapInfo Professional User Manual
Page 485
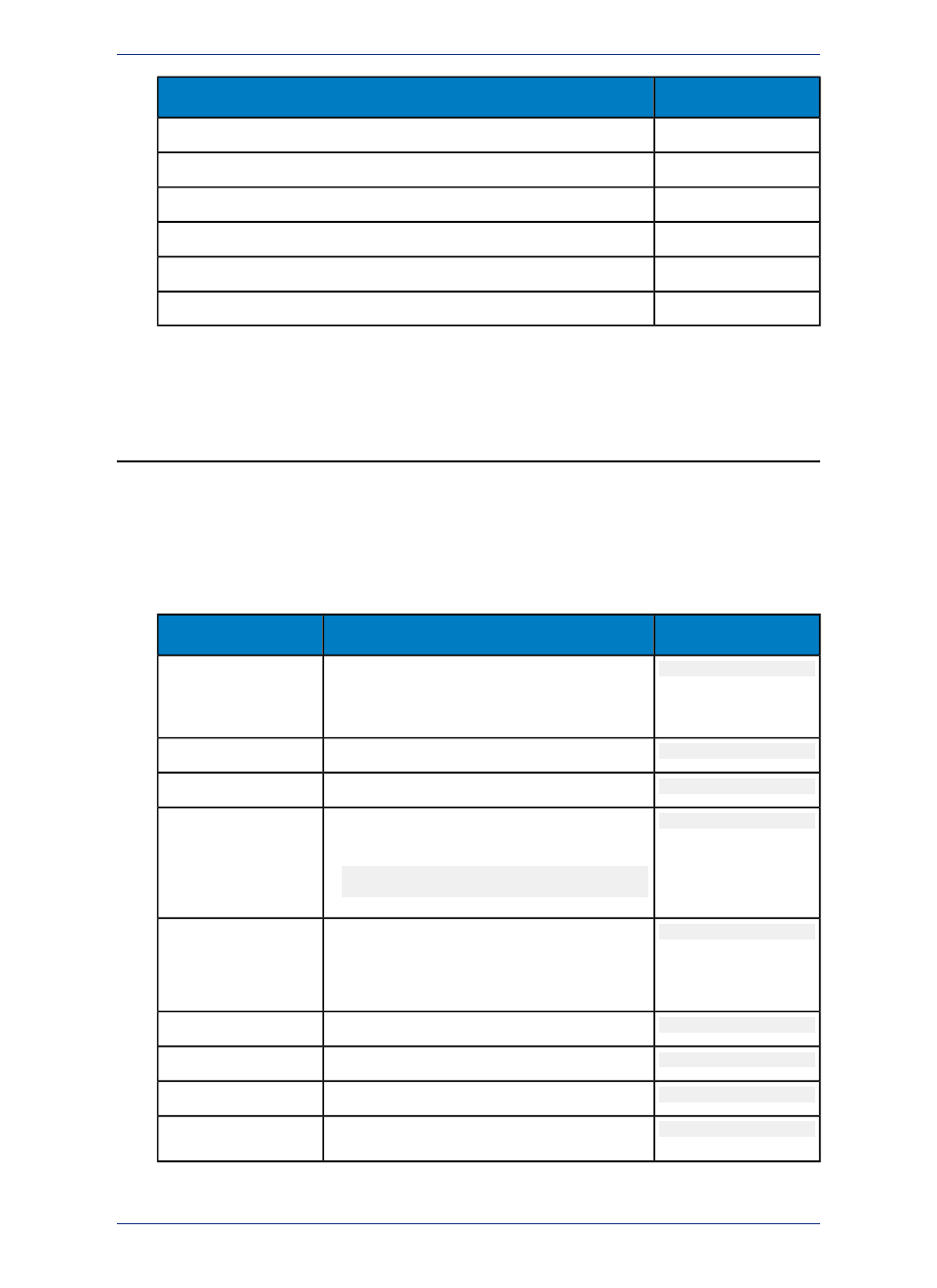
Type Number
Spatial Index Type
16
Oracle Spatial Annotation Text
17
SQL Server Spatial (for geometry)
18
SQL Server Spatial (for geography)
19
PostGIS for PostgreSQL
20
SQL Server Spatial with M and Z values (for geometry)
21
SQL Server Spatial with M and Z values (for geography)
You use the XY Coordinates option when there is no index
Manually Making a Remote Table Mappable
For each spatial table in the remote database that you want to access in MapInfo Professional, you must
add a row to the MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG table. This is carried out in MapInfo Professional when you
select Table > Maintenance > Make DBMS Table Mappable.
If you do not use MapInfo Professional to manage the Map Catalog, you must manually add rows to the
MAPINFO_MAPCATALOG table for each spatial table in the database that you want to geocode. Each
entry must contain the following information about the table.
Example
Values to Assign
Column Name
4.0
4.0 for X,Y spatial index tables
SPATIALTYPE
(Support for additional spatial servers is under
development)
Drainage
Name of the table.
TABLENAME
Georgetown
Owner name.
OWNERNAME
NO_COLUMN
Name of the column, if any containing spatial
features. The name is:
SPATIALCOLUMN
• NO_COLUMN (for mappable tables using
X,Y)
-360
X coordinate of the lower left corner of the layer's
bounding rectangle, in units indicated by the
DB_X_LL
COORDINATESYSTEM as defined by MapInfo
Professional.
-90
Lower left bounding Y value.
DB_Y_LL
360
Upper right bounding X value.
DB_X_UR
90
Upper right bounding Y value.
DB_Y_UR
-360
X coordinate of the lower left corner of the view's
bounding rectangle, in units indicated by the
VIEW_X_LL
485
MapInfo Professional User Guide
Appendix C: Manually Creating a MapInfo_MapCatalog
