What data can i use in mapinfo professional – Pitney Bowes MapInfo Professional User Manual
Page 43
A query is just another word for a question. You query data to collect a particular type of information
from your database. For example, if you wanted to know how many customers live within a certain
number of miles of your store, (and you had that kind of information in your database), you could query
the database to find out that information. The result of the query is query data. You can think of query
data as a subset of your data as in the example - a list of all the customers within 5 miles and none of
the customers who live further away. MapInfo Professional has tools to help you query your data and
display it on a map. For more about querying your data, see
What Data Can I Use in MapInfo Professional?
MapInfo Professional allows you to use data that was created in other file formats. When you bring data
into MapInfo Professional for the first time, you need to specify its format. For example, if your data is
in delimited ASCII format, choose Delimited ASCII from the File Format drop-down list.
Data file choices include:
• Microsoft Access
• Microsoft Excel
• dBASE DBF
• ESRI shapefiles
• Raster Images
• Grid Images
• ASCII Delimited Text
• Lotus 1-2-3
• Remote Databases (Oracle, SQL Server, PostGIS)
• Workspace
• Comma Delimited CSV files
For database versions that MapInfo Professional supports, see the MapInfo Professional Install Guide.
When you choose a particular file format, the File Name box will only list files that have the appropriate
extension. For example, if you choose dBASE DBF from the File Format drop-down list, MapInfo
Professional will only list files that are in dBASE format.
When you choose a file other than a MapInfo-formatted file type, MapInfo Professional creates a table
structure for that data based on the type of file that it is.
During the .TAB file creation process, the original file is in no way altered. The file retains its
original properties.
Note:
When you open that table in future work sessions, MapInfo Professional will treat these files as if they
were in MapInfo Professional's native format. The next time you want to open the table, you should
choose the .TAB format for the table. If you accidentally attempt to open the file again with its original
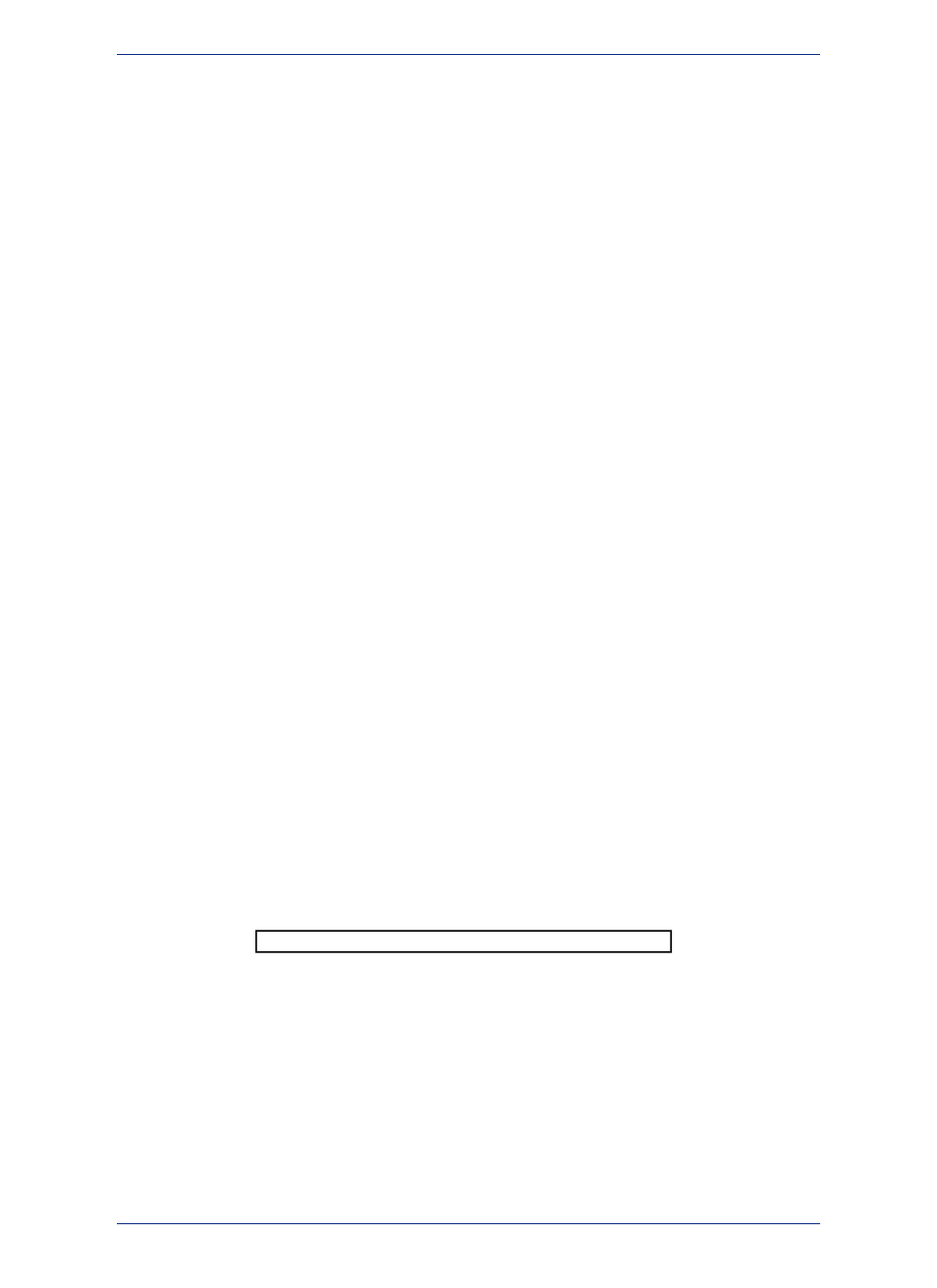
file format, MapInfo Professional prompts you with the message:
Table definition already exists. Overwrite it?
This message displays because MapInfo Professional has already created a table for that file. To use
the file you have already created, click Cancel and open the associated .TAB file.
Also keep in mind that MapInfo Professional supports long filenames and UNC paths. The UNC paths
allow you to access your data without having to remember your drive mappings from one session to
another.
To display your table in the Map window, your data must contain X and Y coordinates. If it does not
already, you can add them using MapInfo Professional. Assigning these coordinates is called geocoding.
More about geocoding follows later in this chapter and in
The Help System contains these related topics:
43
MapInfo Professional User Guide
Chapter 3: The Basics of MapInfo Professional
