Pitney Bowes MapInfo Professional User Manual
Page 254
Us_custg.order_amt > 10000
Select * from Us_custg,States,City_125
where Us_custg.state = States.state and Us_custg.order_amt > 10000 and
States.state = City_125.state
Some of the data used in this example is from the MapInfo Professional Tutorial, which is only
available from the Pitney Bowes Software Inc. web
Note:
Error Handling
If an invalid Where condition that uses an OR as a logical operator is detected, MapInfo Professional
will indicate an error has occurred. Usually this error will display whenever MapInfo Professional cannot
find a join between two tables. For example, if you have specified the following incorrect condition:
Select * from A,B where A.field1 = B.field1
or A.field1 = B.field2
This error message displays:
No join specified between A and B. Invalid join condition in Where clause
Joining Tables Geographically (Using Geographic Operators)
When two tables have graphic objects, MapInfo Professional can join the tables based on the spatial
relationship between those objects. Thus, even if your tables do not share a common column, you may
be able to join the tables.
Geographic operators allow you to select objects on the basis of their spatial relationship to some other
object. MapInfo Professional has a special column name you use with geographical operators: "obj" or
"object". This column name refers to the graphic objects that are attached to your table.
The geographic operators go between the objects being specified. Select the geographic operators from
the Operators drop-down list.
The following table lists the geographic operators:
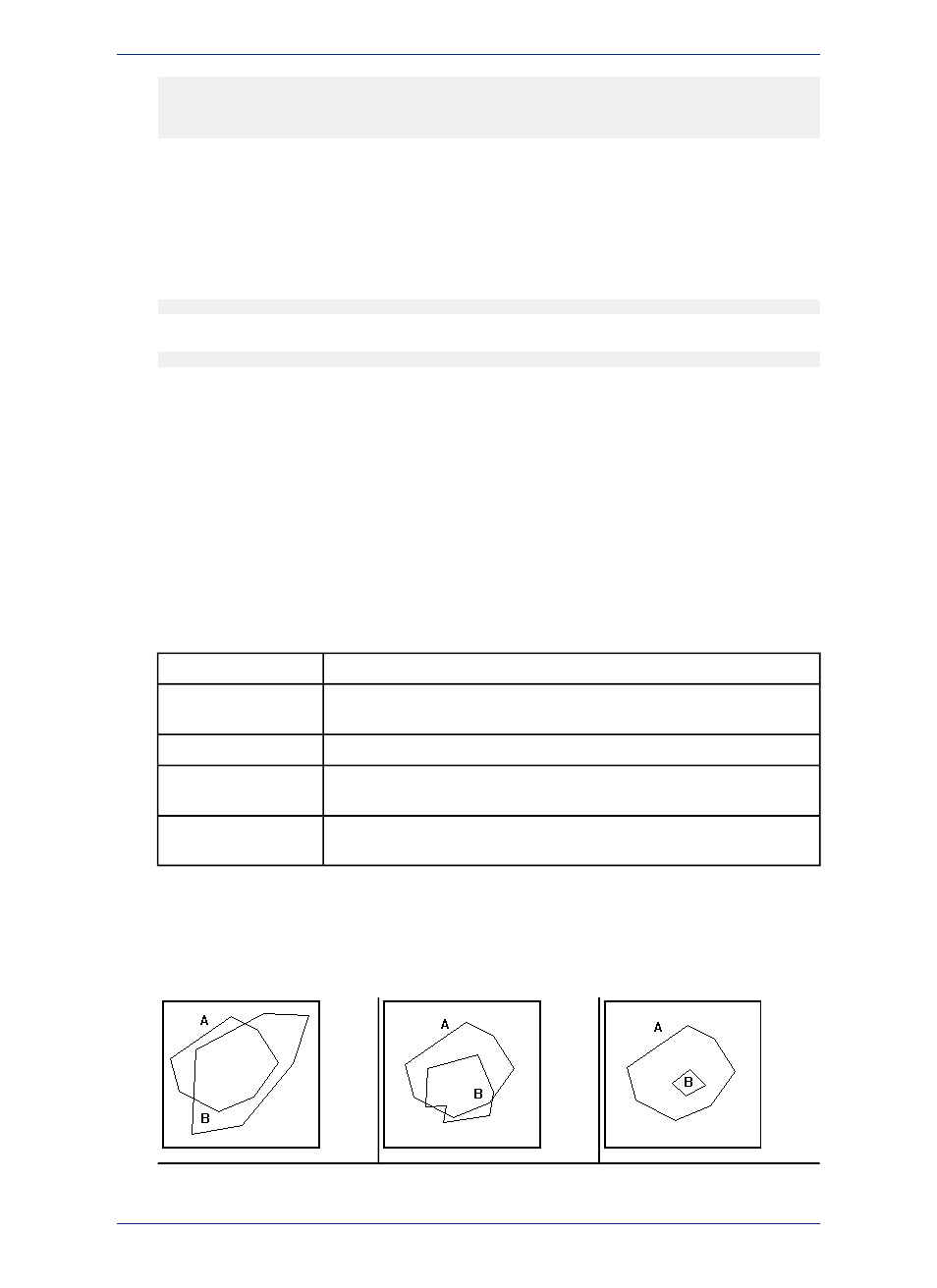
Object A Contains Object B if B's centroid is anywhere within A's boundary.
Contains
Object A Contains Entire Object B if B's boundary is entirely within A's
boundary.
Contains Entire
Object A is Within Object B if its centroid is inside B's boundary.
Within
Object A is Entirely Within Object B if A's boundary is entirely within B's
boundary.
Entirely Within
Object A Intersects Object B if they have at least one point in common or if
one of them is entirely within the other.
Intersects
The difference between Contains and Within on the one hand, and Contains Entire and Entirely
Within on the other, hinges on how the geographic comparison is made. For Contains and Within, the
comparison is based on object centroids. For Contains Entirely and Entirely Within, the comparisons
are based on the whole object.
The following graphic illustrates this point:
MapInfo Professional 12.5
254
Querying Your Data in MapInfo Professional
