Direct vector control, Control hardware, Direct vector control control hardware – Rockwell Automation 7000L PowerFlex Medium Voltage AC Drive (C-Frame) - ForGe Control User Manual
Page 30
30
Rockwell Automation Publication 7000L-UM301D-EN-P - June 2014
Chapter 1
Overview of Drive
Direct Vector Control
The method of control in the PowerFlex 7000 “C” Frame medium voltage AC
drive is called sensorless direct vector control, meaning that the stator current is
divided into torque producing and flux producing components, allowing the
motor torque to be changed quickly without affecting motor flux. This method
of control is used without encoder feedback for applications requiring
continuous operation above 6 Hz and less than 100% starting torque.
Full vector control can also be achieved with encoder feedback for applications
requiring continuous operation down to 0.2 Hz with up to 150% starting torque.
Vector control offers superior performance over volts/hertz type drives. The
speed bandwidth range is 5...25 rad/s, while the torque bandwidth range is
15...50 rad/s.
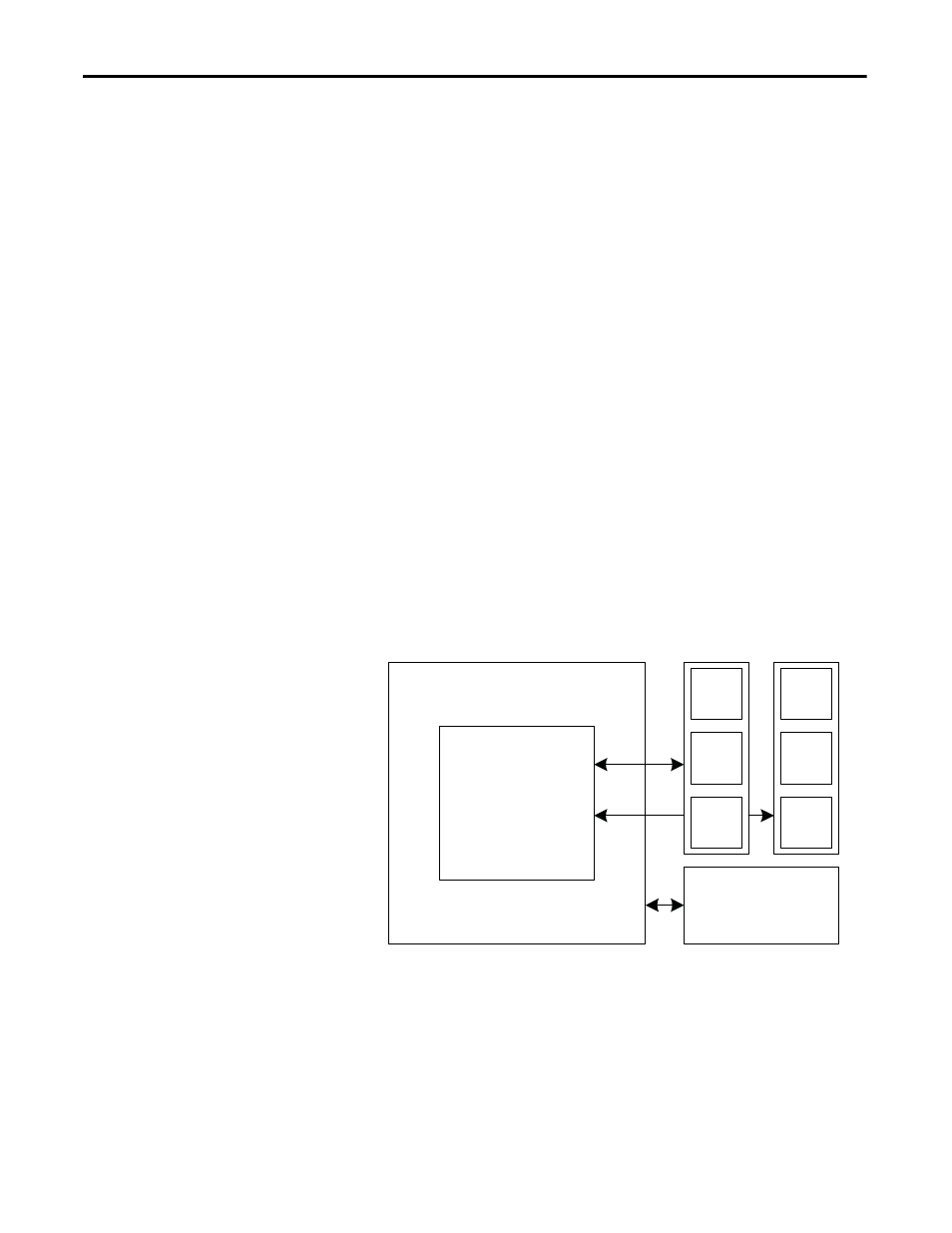
Control Hardware
The control hardware includes a processor board (DPM) with an interface to six
fiber optic boards (depending on the voltage and number of switching devices)
via OIBB, an analog conditioning board (ACB) and an external IO board (XIO).
The control hardware is used for rectifier and inverter, induction or synchronous
drive control and the two rectifier types (18 Pulse or Active Front End).
The DPM features two floating point DSPs (Digital Signal Processor) and a
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) for advanced functions such as gating
and diagnostics, fault handling and drive synchronization control.
Figure 11 - Control Hardware Layout for PowerFlex 7000 “C” Frame
ACB
DPM
XIO
OIB
OIB
OIB
OIB
OIB
OIB
OIBB
OIBB
ACB
– Analog Conditioning Board
DPM
– Drive Processor Module
OIBB
– Optical Interface Base Board
XIO
– External Input/Output
OIB
– Optical Interface Board
