Sgct anode-to-cathode resistance – Rockwell Automation 7000L PowerFlex Medium Voltage AC Drive (C-Frame) - ForGe Control User Manual
Page 198
198
Rockwell Automation Publication 7000L-UM301D-EN-P - June 2014
Chapter 4
Commissioning
If a device or snubber component is found to be damaged, it must be replaced
using the detailed procedures in Component Definition and Maintenance.
SGCT Anode-to-Cathode Resistance
Performing an Anode-to-Cathode resistance test not only tests the integrity of
the SGCT but also the integrity of the sharing resistor. An abnormal device
resistance measurement will indicate either a shorted device or damaged sharing
resistor.
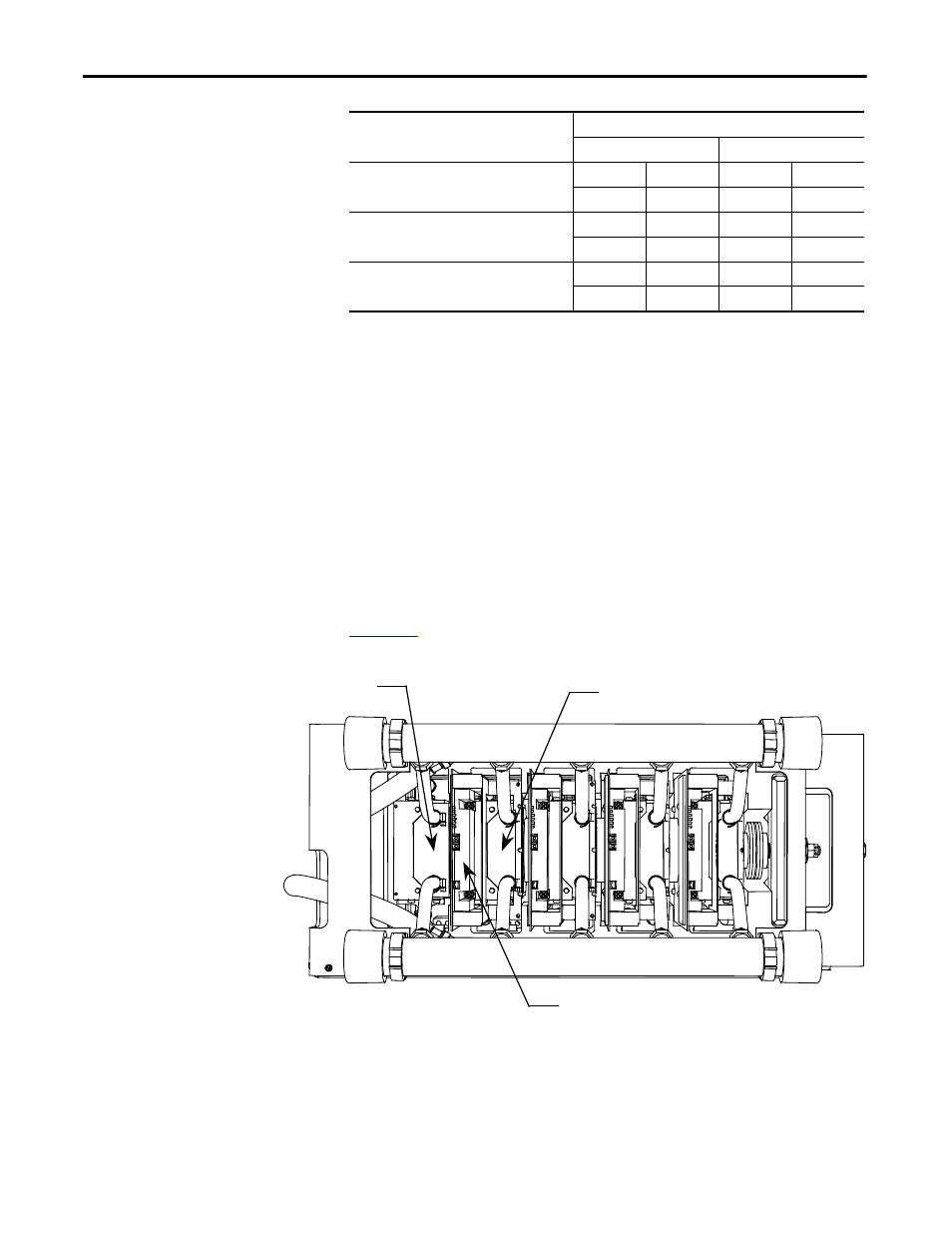
Using an ohmmeter, measure the anode-to-cathode resistance each SGCT,
looking for similar resistance values across each device. Easy access from the
anode-to-cathode is available by going from chill block to chill block as shown in
:
Figure 182 - Anode-to-Cathode Resistance Test Points
An SGCT when not gated on is an open circuit. A healthy device resistance value
should be close to the value-sharing resistor, however due to parallel resistances in
the firing card, the resistance value will be slightly lower.
SGCT Resistance Measurement
Measured Resistance
Inverter
Rectifier (AFE only)
SGCT Anode-Cathode Resistance
(Heatsink to Heatsink)
k-Ω
(Lowest)
(Highest)
(Lowest)
(Highest)
Snubber Resistance
(Test Point – Heatsink above)
Ω
(Lowest)
(Highest)
(Lowest)
(Highest)
Snubber Capacitance
(Test Point – Heatsink on Right)
μF
(Lowest)
(Highest)
(Lowest)
(Highest)
SGCT
Cathode Chill Block
Anode Chill Block
