Dilution ratio – Teledyne 6200E - Sulfides Analyzer User Manual
Page 77
Model 6200E Instruction Manual
Operating Instructions
M6200E Rev: A1
77
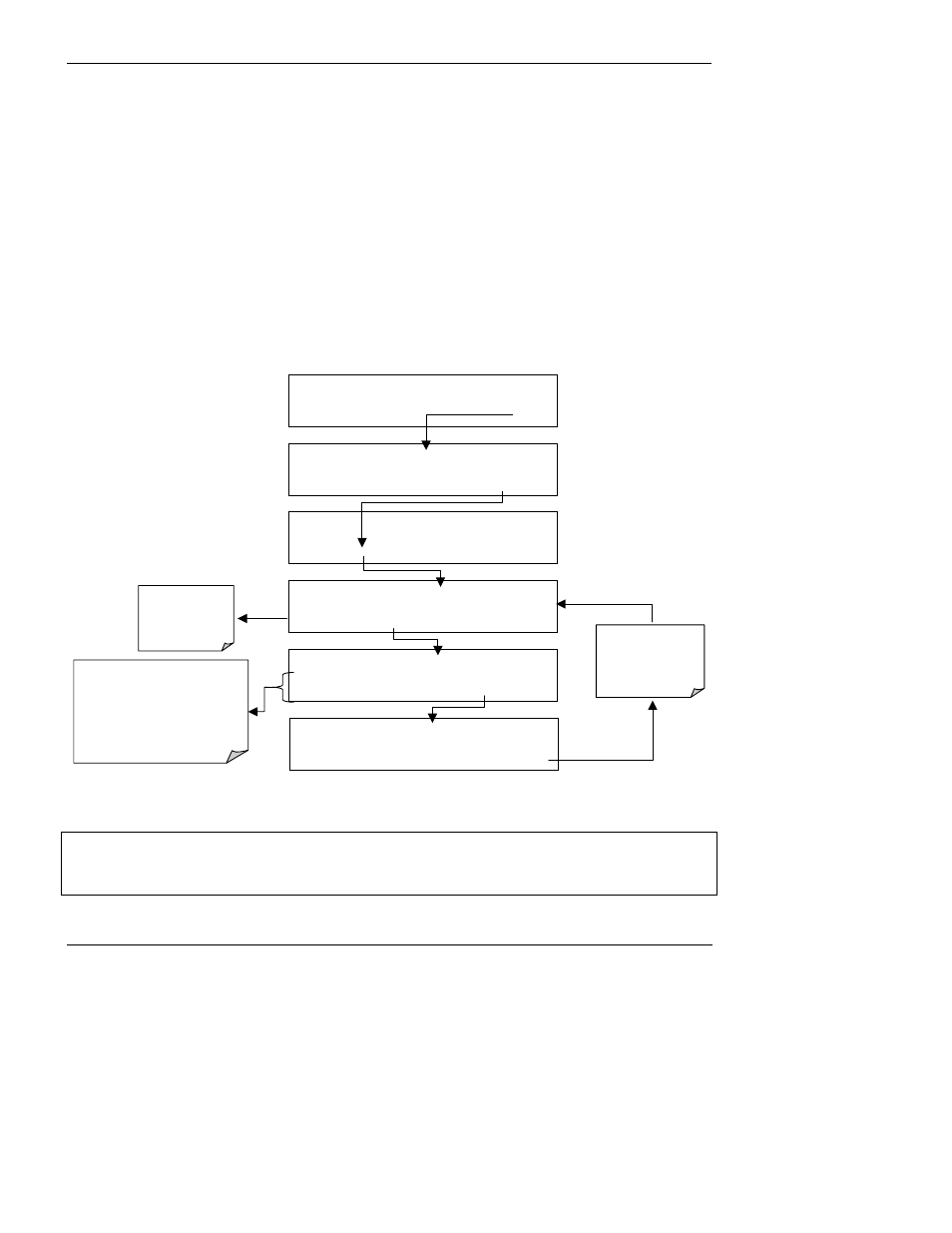
6.7.8. Dilution Ratio
The dilution ratio is a software option that allows the user to compensate for any dilution of the
sample gas before it enters the sample inlet. Using the dilution ratio option is a 4-step process:
1. Select reporting range units: Follow the procedure in Section 6.7.7.
2. Select the range: Use the procedures in Section 6.7.3 – 6.7.6. Make sure that the SPAN value
entered is the maximum expected concentration of the undiluted calibration gas and that the
span gas is either supplied through the same dilution inlet system as the sample gas or has an
appropriately lower actual concentration. For example, with a dilution set to 100, a 1 ppm gas
can be used to calibrate a 100 ppm sample gas if the span gas is not routed through the
dilution system. On the other hand, if a 100 ppm span gas is used, it needs to pass through the
same dilution steps as the sample gas.
3. Set the dilution factor as a gain (e.g., a value of 20 means 20 parts dilutent and 1 part of
sample gas):
SAMPLE RANGE = 500.0 PPB
H2S
=XXX.X
< TST TST > CAL
SETUP
SETUP C.3
PRIMARY SETUP MENU
CFG DAS
RNGE
PASS CLK MORE
EXIT
SETUP C.3
RANGE CONTROL MENU
MODE
SET UNIT
DIL
EXIT
DIL only appears
if the dilution ratio
option has been
installed
SETUP C.3
DIL FACTOR: 1.0 GAIN
0 0 0 1 .0
ENTR
EXIT
Toggle these keys to set the dilution
factor.
This is the number by which the
analyzer will multiply the H
2
S
concentrations of the gas passing
through the reaction cell.
SETUP C.3
DIL FACTOR: 20.0 GAIN
0 0 2 0 .0
ENTR
EXIT
EXIT ignores the
new setting.
ENTR accepts the
new setting.
SAMPLE
ENTER SETUP PASS : 818
8 1 8
ENTR
EXIT
The analyzer multiplies the measured gas concentrations with this dilution factor and displays the
result.
NOTE
Once the above settings have been entered, the instrument needs to be recalibrated
using one of the methods discussed in Chapter 7.
