How electro-static charges cause damage – Teledyne 6200E - Sulfides Analyzer User Manual
Page 266
A Primer on Electro-Static Discharge
Model 6200E Instruction Manual
266
M6200E Rev: A1
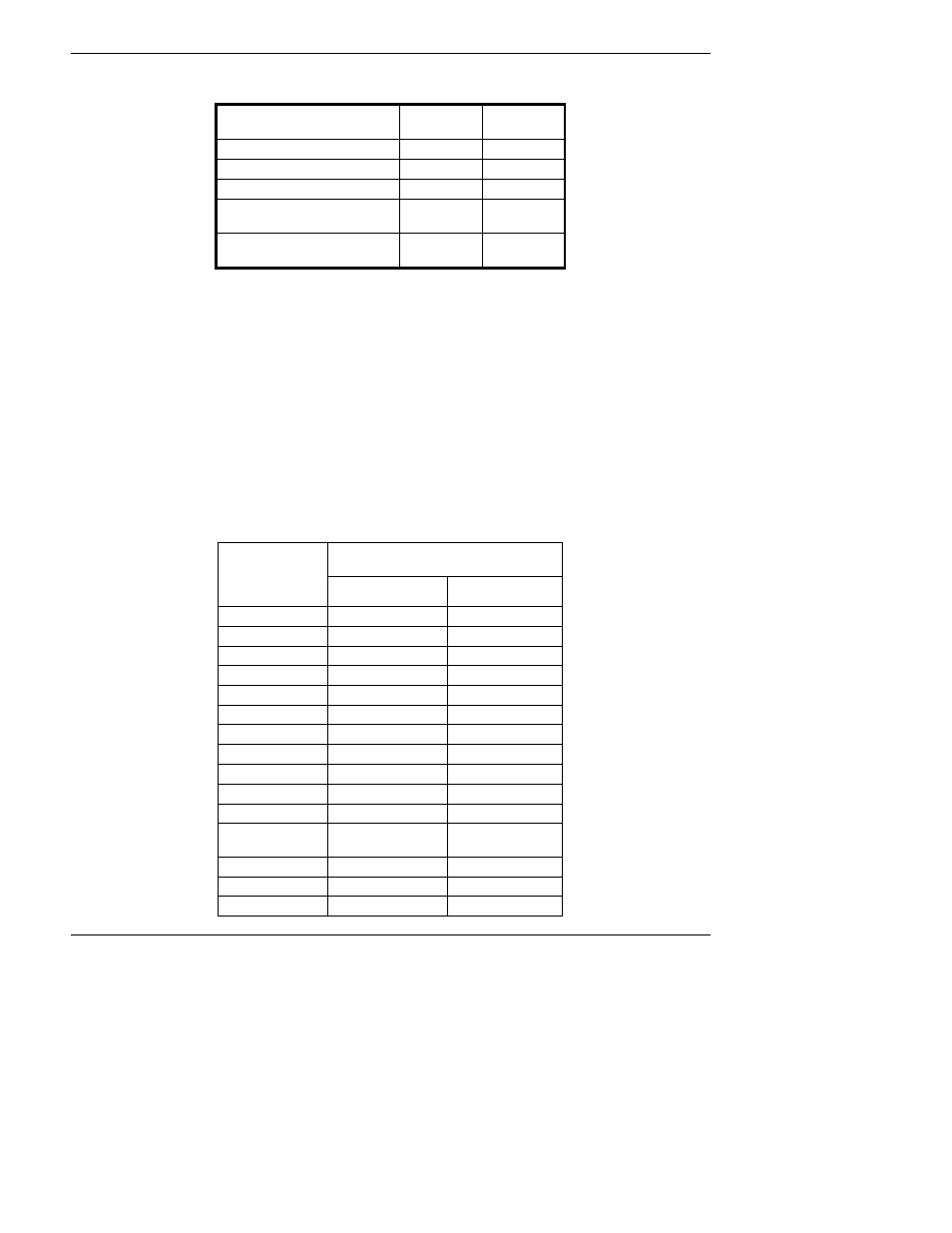
Table 12-1: Static Generation Voltages for Typical Activities
MEANS OF GENERATION
65-90%
RH
10-25%
RH
Walking across nylon carpet
1,500V
35,000V
Walking across vinyl tile
250V
12,000V
Worker at bench
100V
6,000V
Poly bag picked up from
bench
1,200V 20,000V
Moving around in a chair
padded with urethane foam
1,500V 18,000V
12.2. How Electro-Static Charges Cause Damage
Damage to components occurs when these static charges come in contact with an electronic
device. Current flows as the charge moves along the conductive circuitry of the device and the
typically very high voltage levels of the charge overheat the delicate traces of the integrated
circuits, melting them or even vaporizing parts of them. When examined by microscope the
damage caused by electro-static discharge looks a lot like tiny bomb craters littered across the
landscape of the component’s circuitry.
A quick comparison of the values in Table 12-1 with the those shown in the Table 12-2, listing
device susceptibility levels, shows why Semiconductor Reliability News estimates that
approximately 60% of device failures are the result of damage due to electro-static discharge.
Table 12-2: Sensitivity of Electronic Devices to Damage by ESD
DAMAGE SUSCEPTIBILITY
VOLTAGE RANGE
DEVICE
DAMAGE BEGINS
OCCURRING AT
CATASTROPHIC
DAMAGE AT
MOSFET 10
100
VMOS 30
1800
NMOS 60
100
GaAsFET 60
2000
EPROM 100
100
JFET 140
7000
SAW 150
500
Op-AMP 190
2500
CMOS 200
3000
Schottky Diodes 300
2500
Film Resistors
300
3000
This Film
Resistors
300 7000
ECL 500 500
SCR 500 1000
Schottky TTL
500
2500
