5 how to read the model – IAI America MSEP User Manual
Page 29
Chapter 1 Specifications Check
21
1.1.5
How to read the model
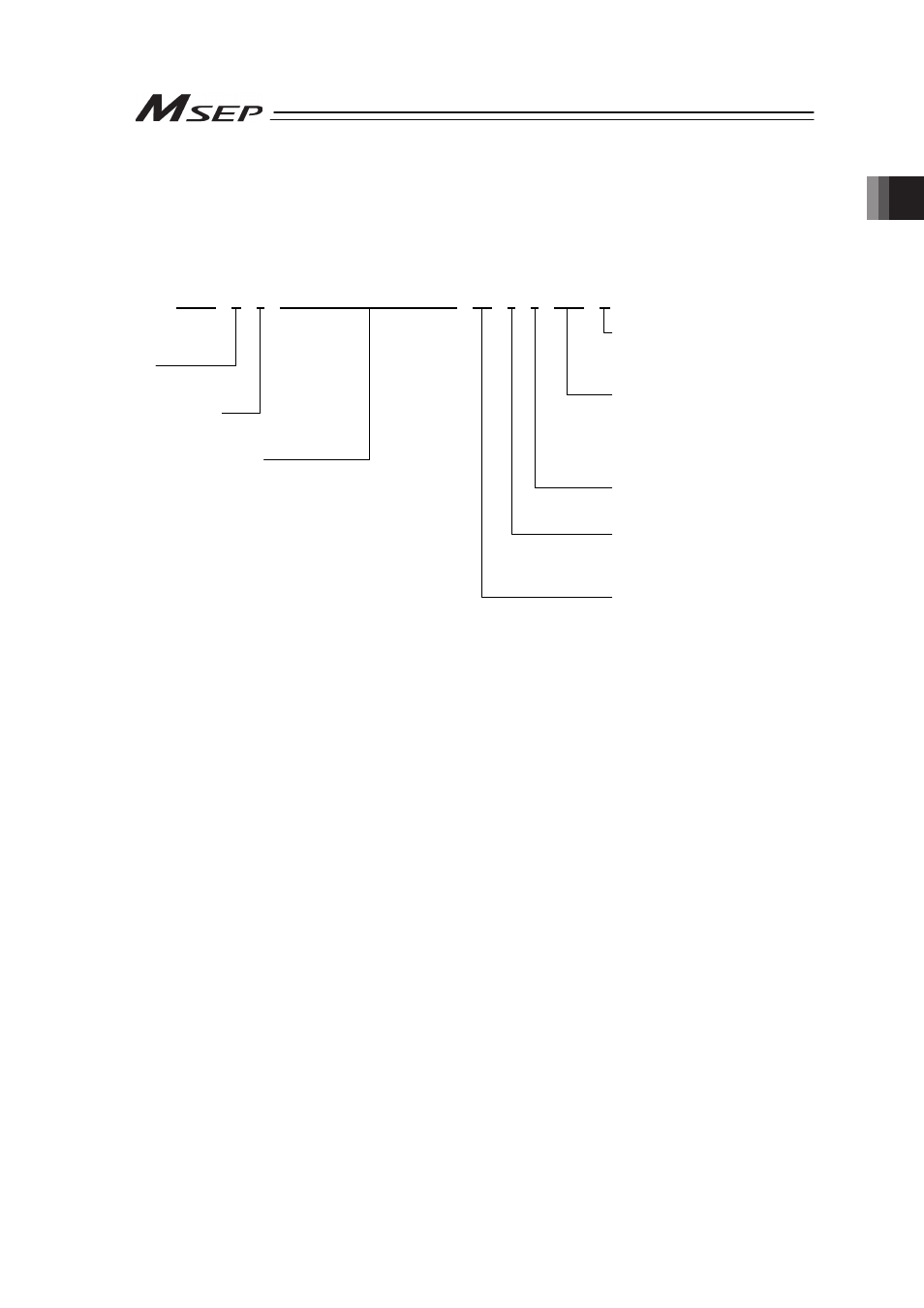
(Example) Consists of 5 axes: Axes No.0, 2, 3 : Pulse motor type
Axes No.4, 5
: Servo motor type
Axis No.1
: Not connected
Axis No.3
: Inactive Axis
MSEP – C – 5 – 20PI–N–42PI–PI–10I–20ILA – DV – 2 – 0 – ABB – **
C : Standard Type
1 to 8 : Number of driver axes
[Motor Type]
20P : Applicable for 20Ƒ pulse motor
28SP: Applicable for 20Ƒ pulse motor
28P : Applicable for 28Ƒ pulse motor
28SP : Applicable for 28Ƒ pulse motor
35P : Applicable for 35Ƒ pulse motor
42P : Applicable for 42Ƒ pulse motor
56P : Applicable for 56Ƒ pulse motor
2
: Applicable for 2W servo motor
5
: Applicable for 5W servo motor
5S : Applicable for 5W servo motor
10 : Applicable for 10W servo motor
20 : Applicable for 20W servo motor
20S : Applicable for 20W servo motor
30 : Applicable for 30W servo motor
A
: Ineffective axis (equipped with pulse motor driver)
P
: Ineffective axis (equipped with servo motor driver)
N
: Not connected (not equipped with motor driver)
[Encoder Type]
I : Incremental
[Option (if servo motor is selected)]
HA : High Acceleration/Deceleration Type
LA : Low Power Consumption Type
* There is no identification in some
cases
ABB : Simple Absolute Type
(with absolute battery)
ABBN : Simple Absolute Type
(with no absolute battery)
No description : Incremental Type
0: 24V DC
0 : No cable
2 : 2m (Standard)
3 : 3m
5 : 5m
NP : NPN PIO Type (Sink type)
PN : PNP PIO Type (Source type)
DV : DeviceNet Type
CC : CC-Link Type
PR : PROFIBUS-DP Type
CN : CompoNet Type
ML : MECHATROLINK Type
EC : EtherCAT Type
EP : EtherNet/IP Type
C
