IAI America XSEL-S User Manual
Page 97
Chapter 2 Operations
89
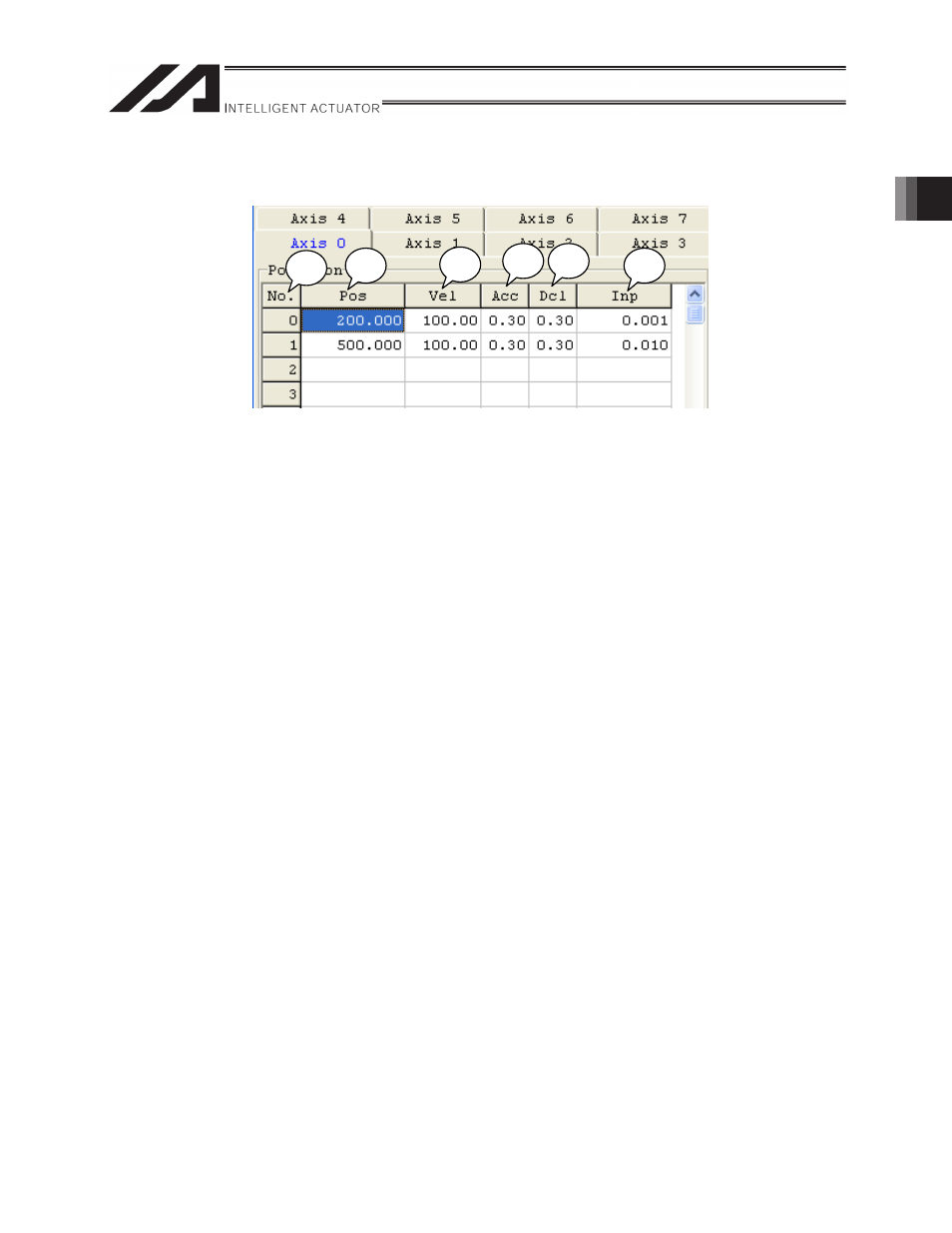
Figure 2.6.5 Extension Motion Control Board Axis Position Data Section
[1] No.
Values in this column indicate position data numbers. Different from position data for main CPU
control axes, the number starts from 0.
[2] Pos (target position) [mm]
Values in this column indicate target positions to which you want to move the actuator.
Absolute coordinate specification: Distance from actuator’s home
Relative coordinate specification: Relative movement amount from the current position
Whether the target position is specified as absolute or relative coordinate is determined by the SEL
command.
(Example: Absolute coordinate specification in case of the XMVP command and relative coordinate
specification in case of the XMPI command)
[3] Vel (speed) [mm/s]
Values in this column indicate the speed at which to make the actuator PTP move. The speed at CP
movement (interpolation movement) is set using the VEL collumn input data. If the speed is not set,
the actuator moves at the speed set by the VEL and VLMX commands.
[4] ACC (acceleration) [G]
Values in this column indicate acceleration at which to make the actuator PTP move. The
acceleration at CP movement (interpolation movement) is set using the ACC column input data. If the
acceleration is not set, the actuator moves at the acceleration set by the ACC command.
[5] Dcl (deceleration) [G]
Values in this column indicate deceleration at which to make the actuator PTP move. The
deceleration at CP movement (interpolation movement) is set using the DCL column input data. If the
deceleration is not set, the actuator moves at the deceleration set by the DCL command.
[6] Inp (positioning band) [mm]
It is possible to set how far in advance the command position from a extension motion control board
with respect to the target position is acknowledged as position complete. This allows rough
positioning without changing positioning band parameters of the RC controller.
It is used to shorten the tact time by performing another processing such as IO processing during the
axis movement.
Refer to “2.6.3 Positioning Completion” for the detailed explanation.
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
