2 standard addition - overview, Stdadd – Metrohm tiamo 2.3 Patch 1 User Manual
Page 949
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
5 Method
tiamo 2.3 Patch 1
■■■■■■■■
933
■
STDADD dos
Standard addition with addition of the standard addition solution from
a dosing device.
■
STDADD auto
Standard addition with automatic addition of the standard addition
solution from a dosing device in such a way that a constant potential
difference results.
5.6.4.2
Standard addition - Overview
Menu item: Method
▶ Insert ▶ New command... ▶ Measure
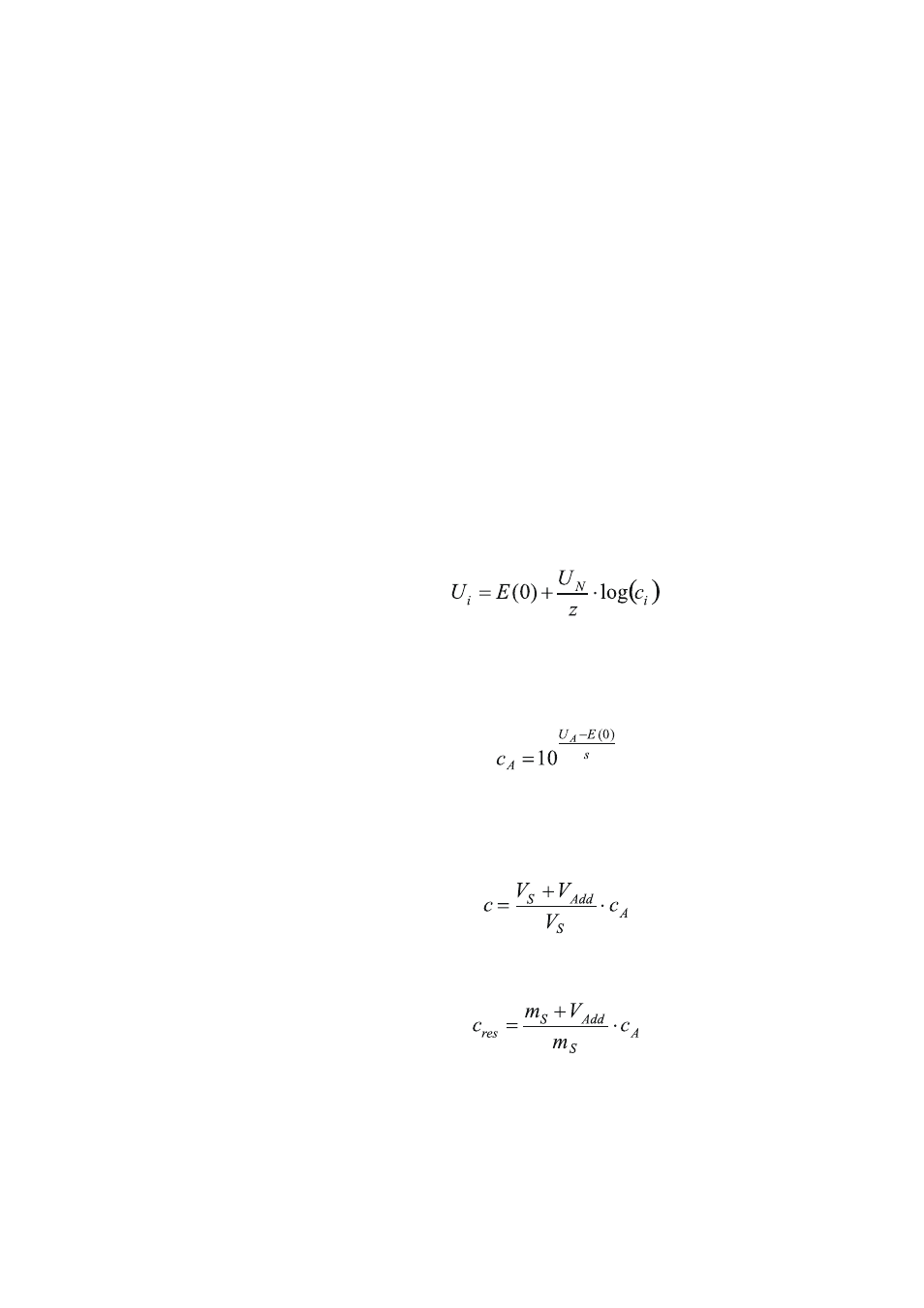
Principle
With the standard addition procedure an known amount of the substance
to determine is once or more than once added to the sample, whereby
the addition can be carried out manually or automatically. In contrast to
the normal ion measurement with ion-selective electrodes (see Chapter
5.6.5.6.1, page 1107), with the standard addition procedure it cannot be
differentiated between ions searched and interfering ions, because both
are present in the sample at the beginning. Only the sum can be deter-
mined. Therefore a linear correlation of U and log(c
i
) is generally assumed
for standard addition measurements.
This way, the regression line (linear regression) is determined iteratively
according to the method of least squares. This procedure provides the axis
intercept E(0), the slope s and the concentration of the measuring ion in
the diluted measuring solution c
A
.
The dilution is taken into account via the method parameters sample vol-
ume V
S
(= Sample size in mL) and addition volume V
Add
, so that the end
result c
S
(concentration of the ion searched in the sample solution) deter-
mined by tiamo can be calculated and directly displayed:
If instead of the sample volume the sample amount m
S
(= Sample size in
g) is entered, the result c
res
is calculated by tiamo.
In order to obtain the required end result c
S
(concentration of the ion
searched in the sample solution) out of this, this must be calculated with
