Chapter 17 programming for the µpd78p214, 1 operating mode, 2 procedure for writing into prom – NEC PD78214 User Manual
Page 428
399
17
CHAPTER 17 PROGRAMMING FOR THE
µPD78P214
The
µPD78P214 employs an electrically writable PROM of 16384 × 8 bits for program memory. Use the NMI and
RESET pins to set the
µPD78P214 to PROM programming mode when programming the PROM.
The
µPD78P214 provides programming characteristics compatible with the µPD27C256A
Note
.
Note 100
µs program pulses are not supported.
17.1 OPERATING MODE
When +6 V is applied to the V
DD
pin and +12.5 V to the V
PP
pin, the
µPD78P214 enters PROM programming mode.
This mode can be changed to each of the operating modes shown in Table 17-1 according to the settings of the
CE and OE pins.
Setting the
µPD78P214 to read mode enables it to read the contents of PROM.
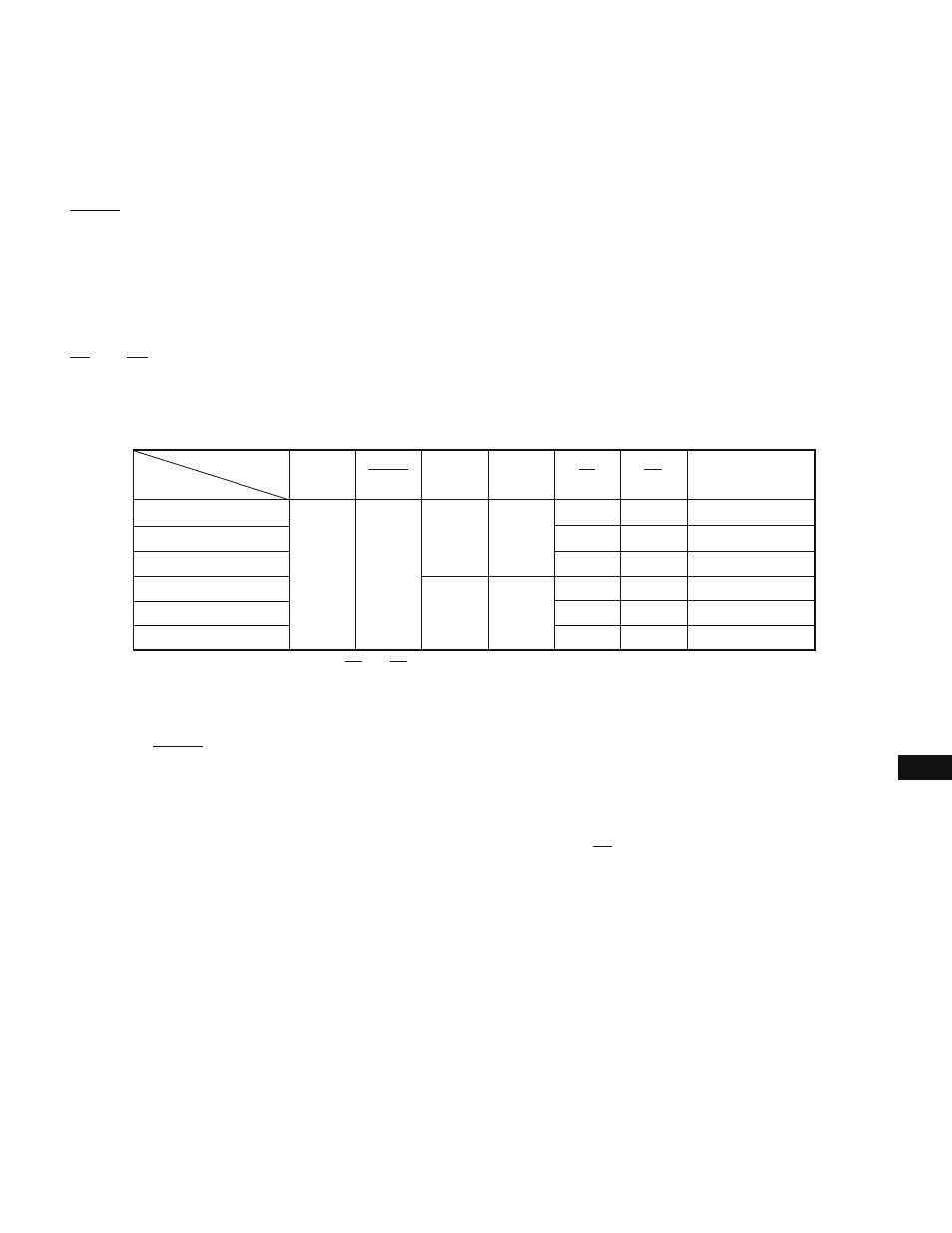
Table 17-1 Operating Modes for PROM Programming
Data input
Data output
High-impedance
Data output
High-impedance
High-impedance
Pin
Mode
Program write
Program verify
Program inhibit
Read
Output disable
Standby
L
H
H
L
L
H
H
L
H
L
H
L/H
+12.5 V
L
+5 V
+5 V
+12.5 V
+6 V
NMI
RESET
V
PP
V
DD
CE
OE
D0-D7
★
Caution When V
PP
is +12.5 V and V
DD
is +6 V, CE and OE must not be set to low at the same time.
17.2 PROCEDURE FOR WRITING INTO PROM
Data can be written into PROM at high speed by following the procedure below:
(1) Fix the RESET pin to the low level. Apply +12.5 V to pin NMI. Handle unused pins as described in Section 1.3.2.
(2) Apply +6 V to the V
DD
pin and +12.5 V to the V
PP
pin.
(3) Input an initial address.
(4) Input the write data.
(5) Input a program pulse (active low), having a period of 1 ms, to the CE pin.
(6) Check that data has been written into the PROM (verify mode). When the data has been written correctly, go
to step (8). Otherwise, repeat steps (4) to (6). If data has still not been written successfully after repeating this
part of the procedure 25 times, go to step (7).
(7) Assume the device to be defective and abandon the write operation.
(8) Input the write data, then input a program pulse which has a period of (number of times steps (4) to (6) have
been repeated)
× 3 ms (additional write).
(9) Increment the address.
(10) Repeat steps (4) to (9) until the address exceeds the previous address.
Fig. 17-1 is the timing chart for steps (2) to (8) above.
