6 power control (torque limitation), Application examples, Motec – Lenze 8200 motec frequency inverter 0.25kW-7.5kW User Manual
Page 200
Application examples
Power control
13−15
l
EDB82MV752 EN 5.2
13.6
Power control (torque limitation)
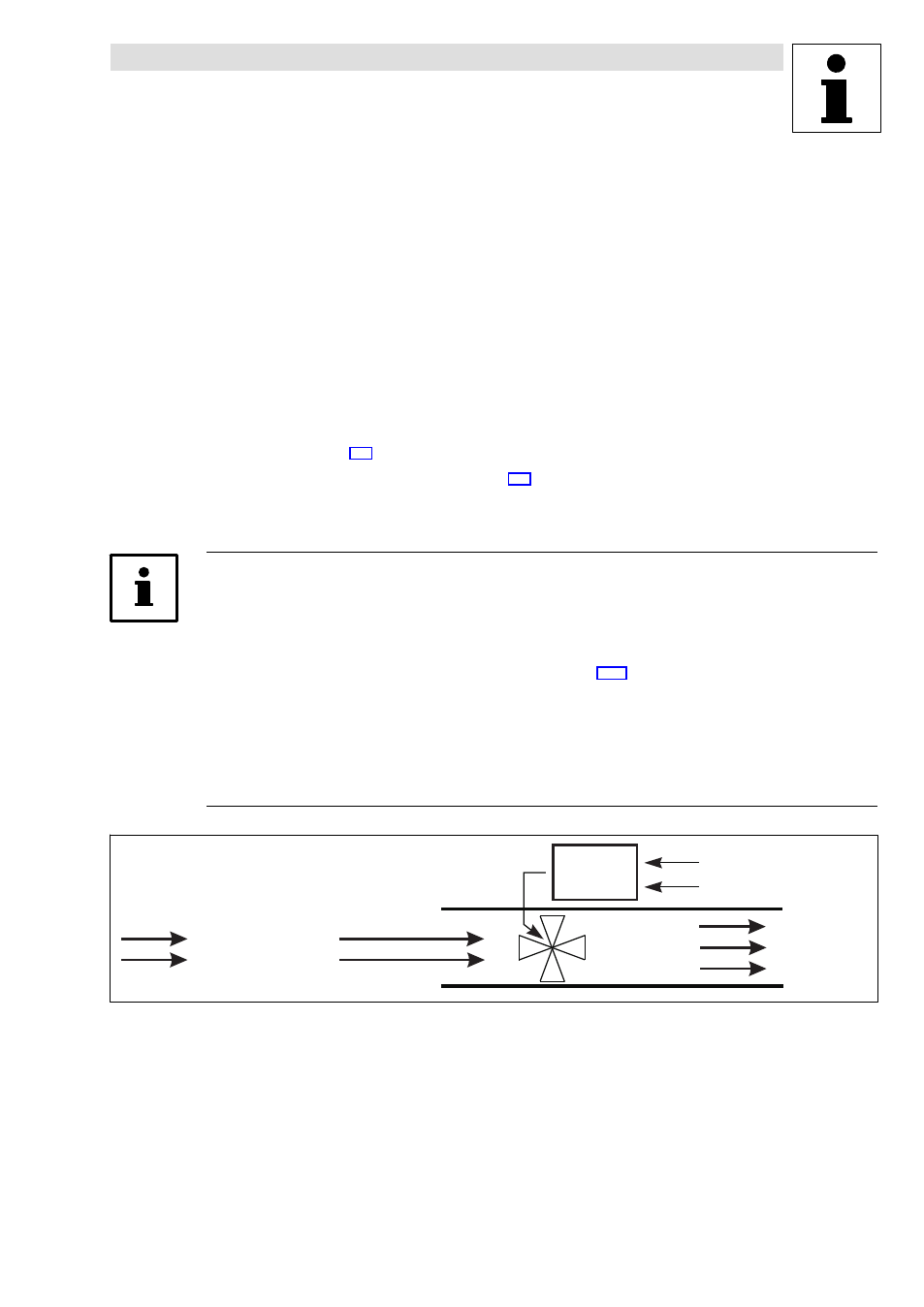
The power control (torque limitation) generates a constant mass flow when moving masses which
change their specific weight, usually air exposed to different temperatures.
Torque limit and speed setpoint are selected for the controller. The torque limit will not be exceeded
because the speed is automatically adapted if the specific weight changes. The speed setpoint must
be set in a way that it does not limit the speed adaptation.
"Sensorless torque control" mode (C0014 = 5):
With sensorless torque control, a constant torque is preselected. A defined speed limit is not
exceeded (speed limitation).
Application−specific configuration
·
Basic settings.
(
^ 6−2)
·
Operating mode selection: C0014
¹
5!
(
·
Torque limit value configuration: Assign C0412/6.
·
Speed setpoint configuration: Assign C0412/1.
Tip!
·
Set max. output frequency C0011 to the max. permissible speed. Thus, the speed does not
have a limiting effect, and the drive is constantly running at the defined torque limit.
·
The torque limit value can be displayed under C0047.
·
Possible ways to select the speed and torque limit:
(
^ 7−32 ff)
·
With controllers with standard I/O, the speed setpoint must be selected via PC, keypad, fixed
frequency (JOG) or via the "motor potentiometer" function, since only one analog input is
available.
·
Acceleration time and moment of inertia require a torque reserve.
·
The power control should not be used for group drives.
motec
air/discharge
heavy
cold
warm
M
f
light
Fan
mass
flow
m = const.
Fig. 13−7
Principle power control example: fan
8200:
8200 motec or 8200 vector
