Returning media identifiers to hosts, Working with library control paths, Creating partitions – HP StoreEver ESL G3 Tape Libraries User Manual
Page 36: Sampling of media type identifiers, Return media identifier behavior example
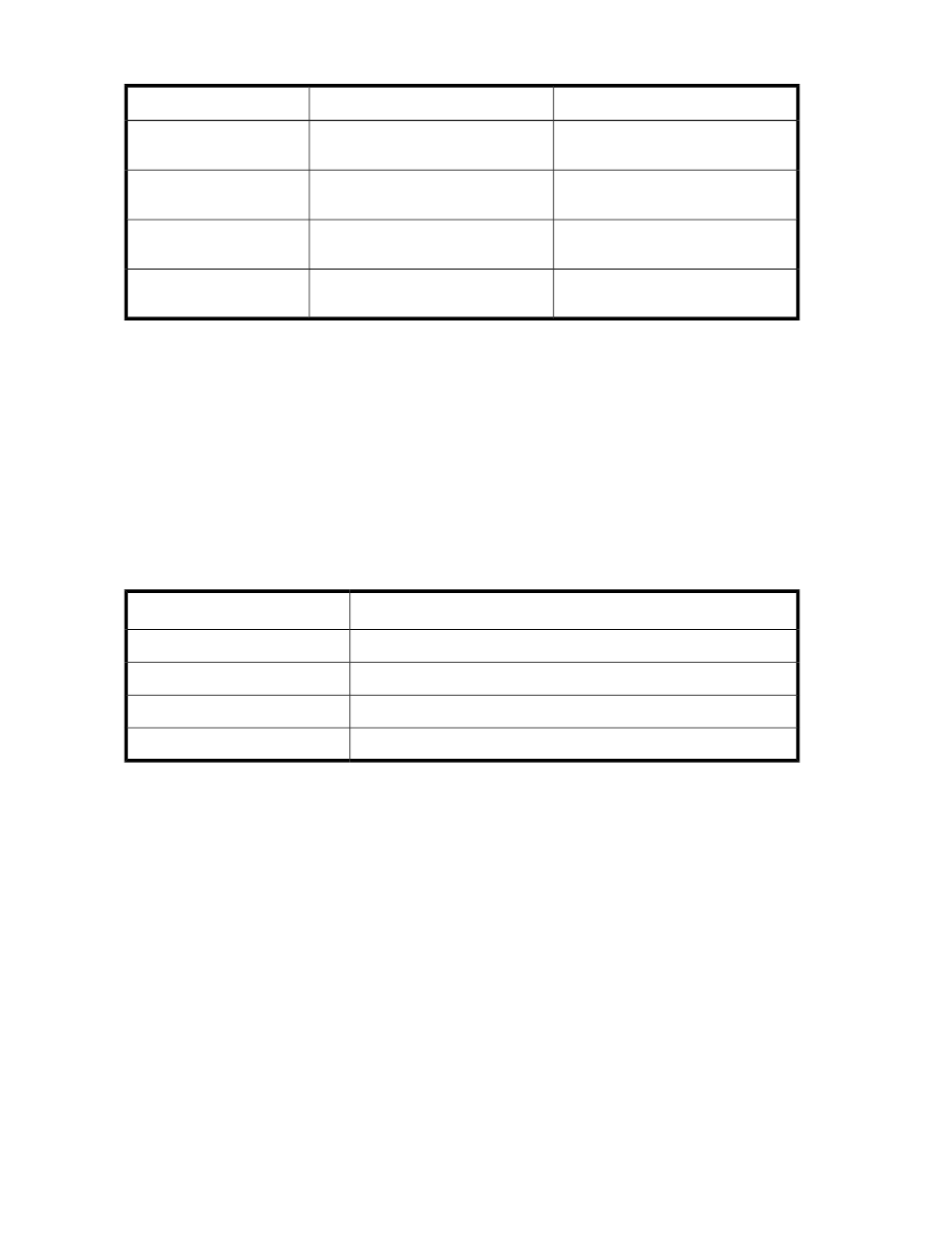
Table 3 Sampling of Media Type Identifiers
Identifier
Media Type
Media Domain
“L4” as the last two characters in the
barcode
LTO-4
LTO
“LU” as the last two characters in the
barcode
LTO-4 WORM
LTO
“L5” as the last two characters in the
barcode
LTO-5
LTO
“LV” as the last two characters in the
barcode
LTO-5 WORM
LTO
With a valid media type identifier present and the Media Type Checking setting enabled, which is
the case by default, a host is prevented from executing invalid media moves across differing media
types. For example, a host can be prevented from moving LTO-5 media to an LTO-4 drive. If an invalid
move is attempted, the library returns an error to the host.
Returning media identifiers to hosts
With the Return Media Identifier setting, you can control if and where a media type identifier appears
in the volume serial number that is returned to the host.
shows an example of how the return media identifier behaves, depending on the setting you
choose: Disabled, Prefix, Suffix, and Pass Through. The bold, underlined portion is the media identifier.
Table 4 Return Media Identifier Behavior Example
Volume Serial Number Returned to Host
1
Setting
AB1234
Disabled
L5AB1234
Prefix
AB1234L5
Suffix
AB1234L5
Pass Through
1
Based on actual LTO-4 barcode: AB1234L5
For more information about configuring the Media Type Checking and Return Media Identifier settings,
see
.
Working with Library Control Paths
You must define a control path for each library partition. The control path is used to connect a partition
to a host application. The ESL G3 does not automatically assign a control path when you create a
partition. When selecting a library control path for a partition, you are selecting which tape drive
will present (or proxy) the virtual robot LUN to the SAN and hosts.
Creating Partitions
You can create library partitions in the following ways:
• Creating Partitions with the Setup Wizard
Modifying the Library Configuration
36
