Figure 6–3 – Altera Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express User Manual
Page 80
6–6
Chapter 6: IP Core Architecture
Protocol Layers
Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express
December 2013
Altera Corporation
User Guide
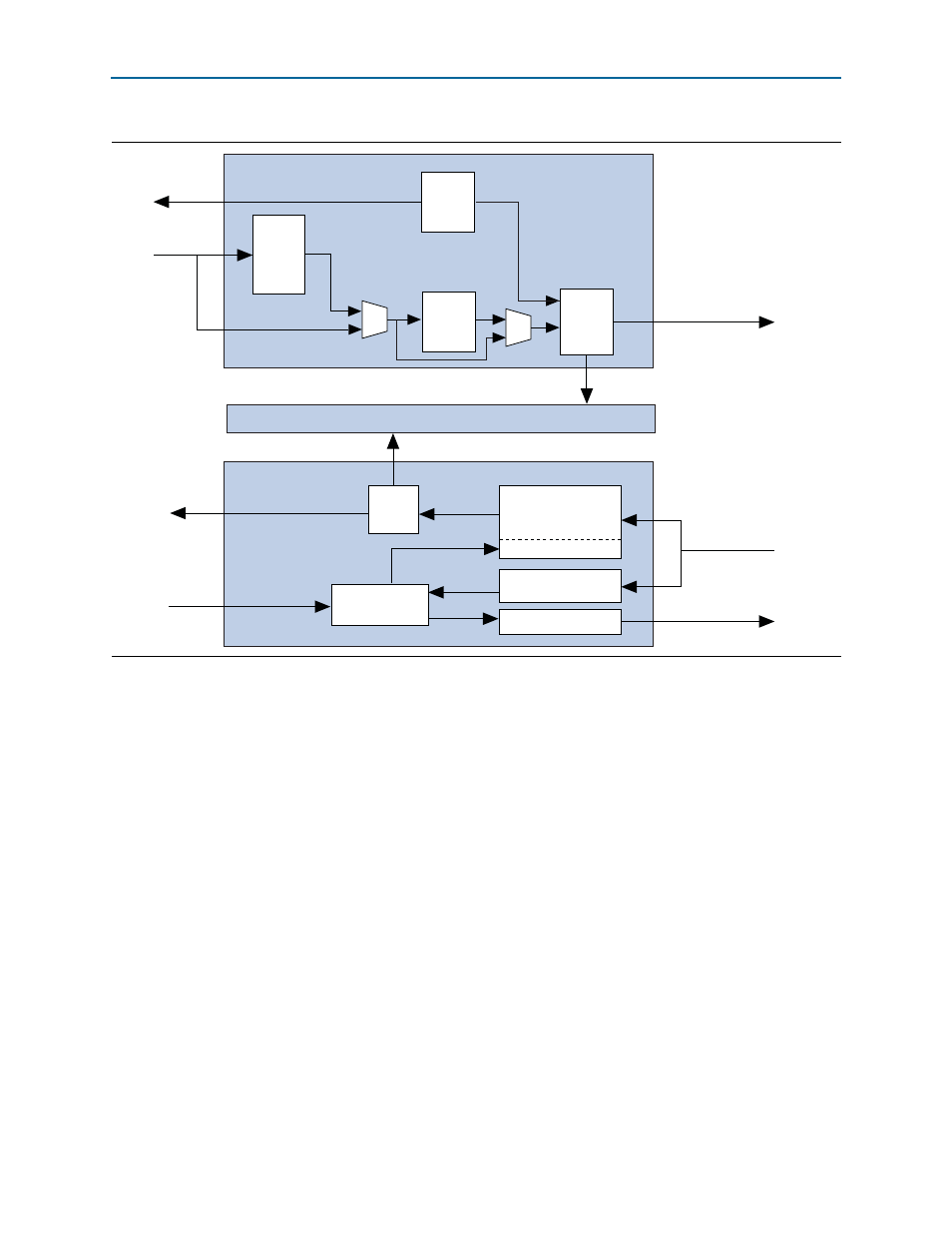
Tracing a transaction through the RX datapath includes the following steps:
1. The Transaction Layer receives a TLP from the Data Link Layer.
2. The Configuration Space determines whether the TLP is well formed and directs
the packet based on traffic class (TC).
3. TLPs are stored in a specific part of the RX buffer depending on the type of
transaction (posted, non-posted, and completion).
4. The TLP FIFO block stores the address of the buffered TLP.
5. The receive reordering block reorders the queue of TLPs as needed, fetches the
address of the highest priority TLP from the TLP FIFO block, and initiates the
transfer of the TLP to the Application Layer.
6. When ECRC generation and forwarding are enabled, the Transaction Layer
forwards the ECRC dword to the Application Layer.
Tracing a transaction through the TX datapath involves the following steps:
1. The Transaction Layer informs the Application Layer that sufficient flow control
credits exist for a particular type of transaction using the TX credit signals. The
Application Layer may choose to ignore this information.
Figure 6–3. Architecture of the Transaction Layer: Dedicated Receive Buffer
Transaction Layer TX Datapath
Transaction Layer RX Datapath
Avalon-ST
RX Control
Configuration Space
TLPs to
Data Link Layer
RX Transaction
Layer Packet
Avalon-ST RX Data
Avalon-ST
TX Data
to Application Layer
Configuration Requests
Reordering
RX Buffer
Posted & Completion
Non-Posted
Flow Control Update
Transaction Layer
Packet FIFO
Width
Adapter
( <256
bits)
Packet
Alignment
TX
Control
RX
Control
TX Flow
Control
